Phantom inventory in a retail storeroom occurs when the inventory management system shows stock levels that do not match the physical count of products. For instance, a clothing retailer's storeroom may reflect 100 units of a popular shirt style, but only 80 units are physically present due to theft, misplacement, or data entry errors. This discrepancy affects order fulfillment and leads to inaccurate sales forecasting and inventory replenishment decisions. The root causes of phantom inventory include unrecorded damages, misplaced items within the storeroom, or system errors during product receipts and returns. Retailers use cycle counts and barcode scanning technologies to reconcile data discrepancies between electronic records and actual stock. Accurate inventory data is essential for optimizing supply chain operations, minimizing stockouts, and reducing excess inventory costs in retail environments.
Table of Comparison
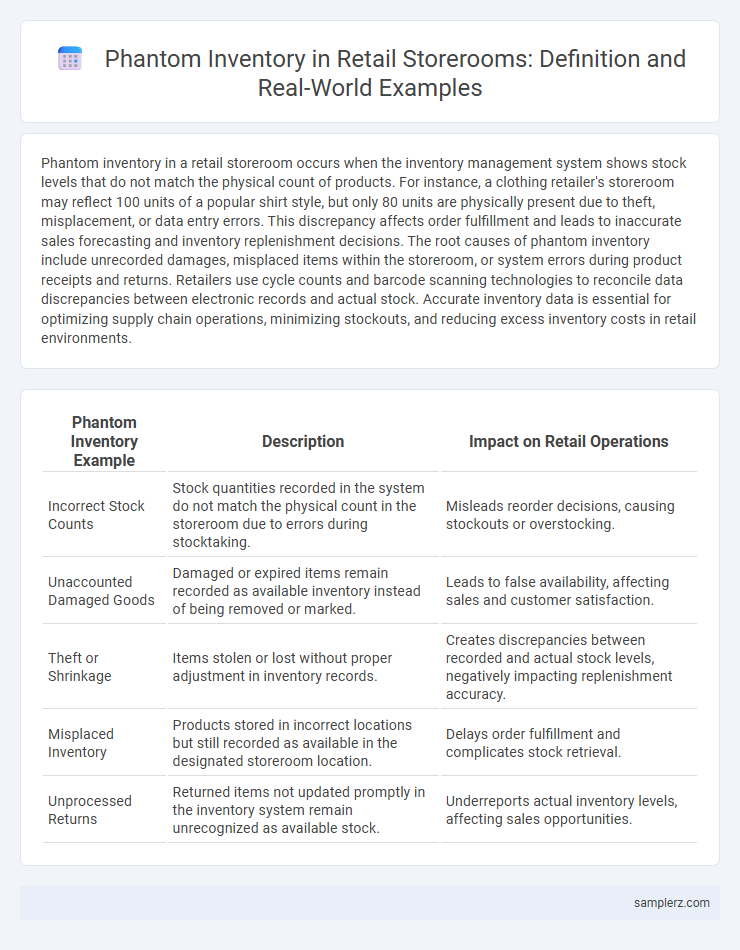
| Phantom Inventory Example | Description | Impact on Retail Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Stock Counts | Stock quantities recorded in the system do not match the physical count in the storeroom due to errors during stocktaking. | Misleads reorder decisions, causing stockouts or overstocking. |
| Unaccounted Damaged Goods | Damaged or expired items remain recorded as available inventory instead of being removed or marked. | Leads to false availability, affecting sales and customer satisfaction. |
| Theft or Shrinkage | Items stolen or lost without proper adjustment in inventory records. | Creates discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels, negatively impacting replenishment accuracy. |
| Misplaced Inventory | Products stored in incorrect locations but still recorded as available in the designated storeroom location. | Delays order fulfillment and complicates stock retrieval. |
| Unprocessed Returns | Returned items not updated promptly in the inventory system remain unrecognized as available stock. | Underreports actual inventory levels, affecting sales opportunities. |
Common Causes of Phantom Inventory in Retail Storerooms
Phantom inventory in retail storerooms often results from inaccurate stock counts due to misplaced items or scanning errors during receiving and stocking processes. Employee theft and unrecorded sales also contribute significantly to discrepancies, causing inventory records to reflect items that are no longer physically present. Inventory mismanagement, such as improper shelf labeling or data entry mistakes in inventory management systems, further exacerbates phantom stock issues.
Shrinkage and Its Role in Phantom Inventory
Phantom inventory in retail storerooms arises when shrinkage, caused by theft, misplacement, or administrative errors, leads to discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels. Shrinkage directly inflates the recorded inventory, masking true stock shortages and complicating demand forecasting and replenishment processes. Accurate shrinkage tracking is essential to mitigate phantom inventory, reduce stockouts, and optimize inventory management systems.
Barcode Scanning Errors Leading to Phantom Stock
Phantom inventory in retail storerooms often arises from barcode scanning errors that misregister stock quantities, causing discrepancies between actual and recorded inventory levels. Misread or improperly scanned barcodes can result in items being marked as sold or missing when they are physically present, leading to inaccurate stock counts and potential stockouts or overstocking. Retail systems integrating real-time inventory management with AI-driven barcode verification reduce phantom stock by minimizing human scanning errors and enhancing data accuracy.
Discrepancies from Manual Inventory Counts
Phantom inventory in retail storerooms occurs when manual inventory counts reveal discrepancies, such as items recorded as in stock but physically missing or misplaced. These inconsistencies arise from undetected theft, unrecorded sales, or data entry errors during stock replenishment. Accurate inventory management software combined with regular cycle counts can help minimize phantom inventory by reconciling manual records with actual stock levels.
Impact of Misplaced Products on Stock Records
Misplaced products in the storeroom cause phantom inventory, leading to discrepancies between physical stock and recorded data. This misalignment results in inaccurate stock levels, affecting order fulfillment and inventory forecasting. Retailers face increased operational costs due to unnecessary reordering and lost sales opportunities.
Effect of Returns Not Processed Properly
Phantom inventory in retail storerooms often arises when returned items are not processed correctly, causing stock levels to appear inaccurate. This discrepancy leads to misleading inventory data, resulting in overstocking or stockouts on sales floors. Inefficient return processing directly impacts inventory management systems, reducing overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Unauthorized Stock Removal and Phantom Inventory
Phantom inventory occurs when stock records show items that are no longer physically present in the storeroom due to unauthorized stock removal by employees or theft. This discrepancy leads to inaccurate inventory counts, causing stockouts and lost sales as the system mistakenly believes the items are available. Effective inventory audits and stringent access controls help mitigate phantom inventory issues and improve overall retail stock accuracy.
POS System Glitches Creating Inventory Gaps
Phantom inventory often arises in retail storerooms when POS system glitches cause discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels, leading to inaccurate inventory counts. These software errors can result in items being shown as available onscreen despite physically being out of stock, complicating order fulfillment and restocking processes. Retailers relying on automated inventory management face challenges in identifying and rectifying such gaps promptly to avoid lost sales and overstocks.
The Role of Damaged Goods in Phantom Inventory
Damaged goods in the storeroom often contribute significantly to phantom inventory by being recorded as available stock despite being unsellable, leading to inaccurate inventory counts and order mismanagement. Retailers encounter phantom inventory when items are physically damaged but remain logged in the system, causing discrepancies between actual and recorded stock levels. Addressing damaged goods through regular audits and real-time inventory updates helps minimize phantom inventory and improve overall inventory accuracy.
Outdated Inventory Management Systems as a Contributing Factor
Outdated inventory management systems contribute significantly to phantom inventory by failing to synchronize real-time stock levels between the storeroom and sales floor, resulting in inaccurate records. Legacy software often lacks integration with modern point-of-sale and warehouse technologies, causing discrepancies that overstate available inventory. Retailers relying on these systems experience lost sales and increased carrying costs due to phantom stock that does not physically exist in the storeroom.
example of phantom inventory in storeroom Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com