A laneway house is a small, secondary dwelling built on an existing residential lot, typically located at the rear and accessed via a narrow lane or alley. These structures are common in urban infill development, where maximizing land use and increasing housing density are priorities. Cities like Vancouver and Toronto have incorporated laneway houses into their zoning policies to address housing shortages and optimize underutilized spaces. Infill development involving laneway houses improves neighborhood diversity by adding affordable housing options without altering the established streetscape significantly. Data from municipal records show that laneway houses can add 300 to 700 square feet of livable area, making them attractive for multi-generational families or rental income. These houses often feature modern designs that integrate seamlessly with the primary residence, increasing property values while supporting sustainable urban growth.
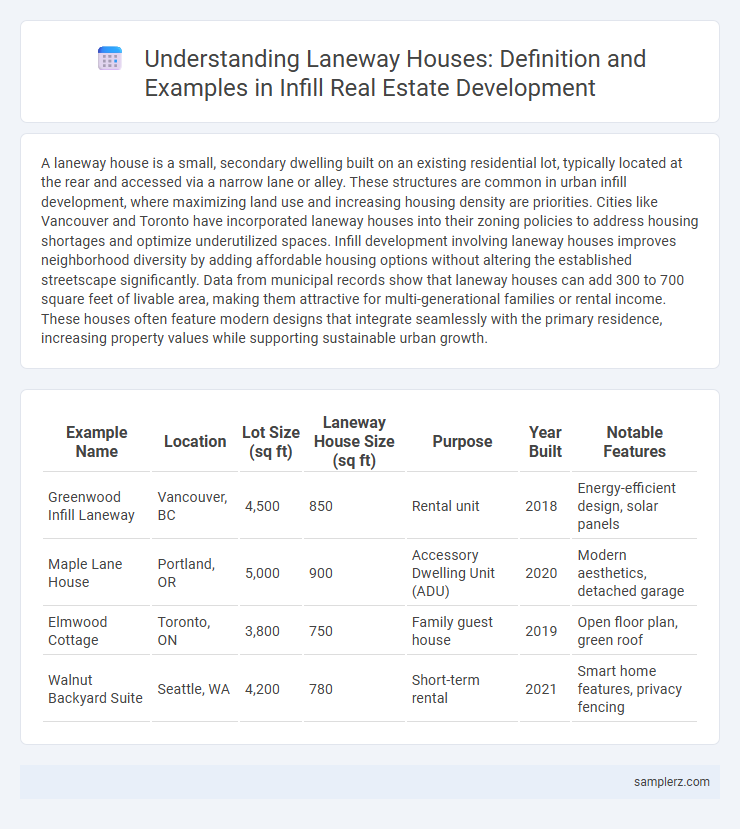
Table of Comparison
| Example Name | Location | Lot Size (sq ft) | Laneway House Size (sq ft) | Purpose | Year Built | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greenwood Infill Laneway | Vancouver, BC | 4,500 | 850 | Rental unit | 2018 | Energy-efficient design, solar panels |
| Maple Lane House | Portland, OR | 5,000 | 900 | Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) | 2020 | Modern aesthetics, detached garage |
| Elmwood Cottage | Toronto, ON | 3,800 | 750 | Family guest house | 2019 | Open floor plan, green roof |
| Walnut Backyard Suite | Seattle, WA | 4,200 | 780 | Short-term rental | 2021 | Smart home features, privacy fencing |
Defining Laneway Houses in Infill Development
Laneway houses are compact, detached dwellings constructed on the same lot as a primary residence, often located at the rear of the property and accessed via a narrow lane or alley. These structures maximize urban infill development by increasing housing density without expanding the urban footprint, offering affordable, sustainable living options in established neighborhoods. Their design emphasizes efficient land use, privacy, and integration with existing infrastructure, making them a strategic solution to urban housing challenges.
Key Features of a Laneway House
Laneway houses in infill development showcase compact, detached secondary dwellings typically situated on underutilized urban lots, maximizing space efficiency and increasing housing density without altering neighborhood character. Key features include a separate entrance, sustainable design elements such as energy-efficient windows and solar panels, and flexible interior layouts that accommodate multi-generational living or rental income opportunities. These structures often integrate seamless access to existing utilities while maintaining privacy and enhancing urban green space through thoughtful landscaping.
Benefits of Laneway Houses for Urban Densification
Laneway houses exemplify effective infill development by maximizing underutilized urban spaces, typically in residential neighborhoods with existing infrastructure. These secondary units increase housing density without altering neighborhood character, providing affordable options for diverse households and contributing to reduced urban sprawl. Incorporating laneway houses supports sustainable land use, enhances property values, and promotes walkability by maintaining close proximity to public transit and amenities.
Successful Laneway House Infill Projects
Successful laneway house infill projects, such as Vancouver's popular Kitsilano neighborhood development, showcase efficient use of underutilized urban spaces by adding secondary dwellings behind primary homes. These projects increase housing density without altering neighborhood character, providing affordable rental options and contributing to sustainable urban growth. Key examples demonstrate how laneway houses effectively respond to rising housing demands while preserving community aesthetics and infrastructure.
Design Considerations for Laneway Homes
Laneway homes in infill development require careful attention to privacy, natural light, and efficient use of limited space to maximize comfort and functionality. Design considerations include appropriate setbacks, integration with existing streetscapes, and sustainable materials to ensure environmental performance. Prioritizing soundproofing and access to utilities enhances livability while preserving neighborhood character.
Zoning and Regulatory Aspects
Laneway houses in infill development are subject to specific zoning regulations that vary by municipality, often including restrictions on floor area, height, setback, and parking requirements. Regulatory frameworks typically mandate compliance with local land use bylaws and building codes to ensure compatibility with the surrounding neighborhood character and infrastructure capacity. Understanding zoning overlays, permitted land uses, and development permits is crucial for successful laneway house projects and maximizing infill potential.
Cost Analysis of Building a Laneway House
The cost analysis of building a laneway house in infill development typically ranges between $150,000 to $300,000, depending on size, design complexity, and local building regulations. Key expenses include foundation work, utility connections, and labor, with average construction costs per square foot between $250 and $400 in urban areas like Vancouver and Toronto. Effective budgeting for laneway houses also considers permit fees, architectural design, and potential landscaping improvements to maximize property value.
Challenges in Laneway Infill Developments
Laneway infill developments, such as laneway houses in urban neighborhoods like Vancouver and Toronto, face significant challenges including zoning restrictions, limited lot size, and infrastructure constraints. Developers often encounter difficulties obtaining permits due to concerns about privacy, parking shortages, and increased density impacting neighborhood character. Addressing noise, utility connections, and adherence to building codes requires careful planning to integrate laneway homes successfully into existing residential areas.
Case Studies: Innovative Laneway House Examples
Laneway houses in infill development showcase innovative urban solutions, exemplified by Vancouver's Dockside Green project, which integrates sustainable laneway homes to maximize limited space. Seattle's Capitol Hill neighborhood features laneway houses with modern designs that increase density while preserving community character. Toronto's laneway house initiatives demonstrate how flexible zoning policies enable homeowners to add affordable, energy-efficient living spaces in established urban areas.
Future Trends in Laneway Housing
Laneway houses in infill development are evolving to meet rising urban density demands while preserving neighborhood character. Innovations include eco-friendly designs featuring solar panels, green roofs, and energy-efficient systems that reduce environmental impact and utility costs. Future trends emphasize smart home integration, modular construction for faster builds, and flexible living spaces to accommodate multi-generational families and remote work needs.
example of laneway house in infill development Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com