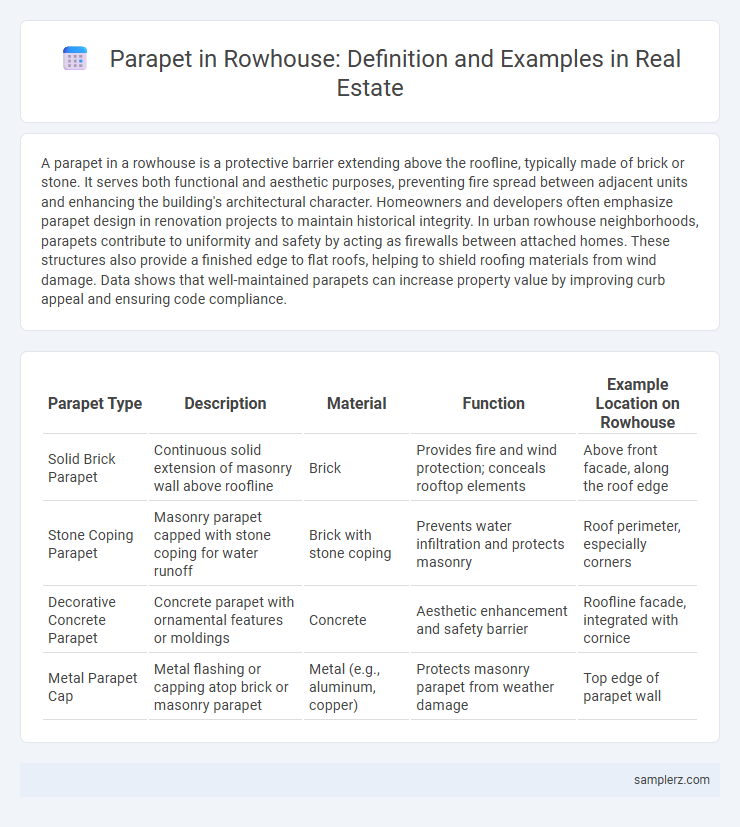
A parapet in a rowhouse is a protective barrier extending above the roofline, typically made of brick or stone. It serves both functional and aesthetic purposes, preventing fire spread between adjacent units and enhancing the building's architectural character. Homeowners and developers often emphasize parapet design in renovation projects to maintain historical integrity. In urban rowhouse neighborhoods, parapets contribute to uniformity and safety by acting as firewalls between attached homes. These structures also provide a finished edge to flat roofs, helping to shield roofing materials from wind damage. Data shows that well-maintained parapets can increase property value by improving curb appeal and ensuring code compliance.
Table of Comparison
| Parapet Type | Description | Material | Function | Example Location on Rowhouse |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Brick Parapet | Continuous solid extension of masonry wall above roofline | Brick | Provides fire and wind protection; conceals rooftop elements | Above front facade, along the roof edge |
| Stone Coping Parapet | Masonry parapet capped with stone coping for water runoff | Brick with stone coping | Prevents water infiltration and protects masonry | Roof perimeter, especially corners |
| Decorative Concrete Parapet | Concrete parapet with ornamental features or moldings | Concrete | Aesthetic enhancement and safety barrier | Roofline facade, integrated with cornice |
| Metal Parapet Cap | Metal flashing or capping atop brick or masonry parapet | Metal (e.g., aluminum, copper) | Protects masonry parapet from weather damage | Top edge of parapet wall |
Defining Parapets in Rowhouse Architecture
Parapets in rowhouse architecture are low protective walls extending above the roofline, often serving as both a safety feature and a decorative element. These structures help shield rooftops from wind and prevent water runoff, while also enhancing the aesthetic appeal of urban rowhouses. Commonly constructed from brick or stone, parapets contribute to the historic and architectural character of tightly packed residential streetscapes.
Historical Significance of Parapets on Rowhouses
Parapets on rowhouses historically served both functional and decorative purposes, protecting rooftops from fire spread between adjoining homes while enhancing the architectural style of urban neighborhoods. These low protective walls often feature intricate brickwork or stone detailing that reflects the design trends of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Preserving parapets on historic rowhouses maintains the integrity of the streetscape and provides valuable insight into past construction practices and aesthetic preferences.
Common Materials Used for Rowhouse Parapets
Common materials used for rowhouse parapets include brick, concrete, and stone, chosen for their durability and weather resistance. Metal flashing, often copper or aluminum, is frequently incorporated to enhance waterproofing and prevent structural damage. These materials ensure the parapet effectively protects the roof edge while maintaining the rowhouse's architectural style.
Distinctive Design Styles of Rowhouse Parapets
Rowhouse parapets showcase distinctive design styles that enhance both aesthetic appeal and structural function, including Flemish bond brickwork, ornate corbeling, and stepped or curved profiles. These parapets often feature decorative elements such as stone coping, terra cotta accents, and intricate cornices, reflecting architectural trends from Victorian to Art Deco eras. The variation in parapet design not only defines the rowhouse's historic character but also contributes to its urban streetscape identity.
Functional Purposes of Parapets in Urban Housing
Parapets in rowhouses serve critical functional purposes including enhancing safety by providing a protective barrier that prevents falls from rooftops and terraces. They also act as firebreaks, reducing the risk of fire spreading between closely positioned urban housing units. Furthermore, parapets contribute to water management by directing rainwater away from building facades, preventing potential water damage and structural deterioration.
Notable Rowhouse Parapet Examples in Major Cities
Notable rowhouse parapet examples in major cities include Philadelphia's iconic Greek Revival rowhouses, where brick parapets often feature decorative corbelling and stone coping, adding both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. In Boston's South End, wrought iron and cast stone parapets contrast with red brick facades, showcasing historic craftsmanship and urban architectural heritage. New York City's Brownstone rowhouses display parapets with intricate molding and dentil courses, serving as distinctive silhouette accents along classic urban streetscapes.
Parapet Restoration Techniques for Older Rowhouses
Parapet restoration techniques for older rowhouses often involve meticulous masonry repairs to address deteriorating brickwork and prevent water infiltration. Repointing the mortar joints with compatible materials and applying waterproof sealants enhance structural integrity and protect against freeze-thaw damage. Incorporating flashing and installing coping stones improve drainage, reducing long-term maintenance and preserving the building's historic facade.
Modern Interpretations of Parapets in Contemporary Rowhouses
Modern interpretations of parapets in contemporary rowhouses often feature minimalist designs that blend functionality with aesthetic appeal, utilizing materials like steel, glass, and concrete to create clean lines and enhanced rooftop safety. These parapets serve not only as protective barriers but also as architectural statements that contribute to the overall urban streetscape, emphasizing height and geometric form. Innovations in lighting and integrated planters further transform parapets into multifunctional elements that enhance outdoor living spaces and promote sustainability.
Building Codes and Safety Standards for Rowhouse Parapets
Rowhouse parapets must comply with local building codes that specify minimum height requirements, typically ranging from 30 to 42 inches, to ensure fire resistance and structural stability. Safety standards mandate the use of non-combustible materials and proper flashing to prevent water infiltration and deterioration. Compliance with these regulations reduces risks of fire spread and structural failure, safeguarding both the property and occupants.
Enhancing Rowhouse Curb Appeal with Decorative Parapets
Decorative parapets on rowhouses elevate architectural interest by adding unique shapes and intricate masonry details to otherwise flat rooflines. These parapets not only enhance curb appeal but also provide practical benefits such as concealing rooftop equipment and offering additional safety. Incorporating ornamental elements like corbels, balustrades, or brick patterns helps distinguish each unit while maintaining a cohesive streetscape.
example of parapet in rowhouse Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com