Geodesic domes represent a pioneering approach in experimental architecture, particularly in the field of real estate innovation. These structures use a network of triangles to create a lightweight, yet extremely strong and energy-efficient dome. One prominent example is the experimental home designed by architect Buckminster Fuller, which demonstrated the potential for sustainable and cost-effective housing solutions. The geodesic dome's design maximizes interior space while minimizing material usage, making it an attractive option for eco-conscious real estate developments. Modern applications include residential communities and alternative housing projects that emphasize resilience and environmental sustainability. Real estate investors increasingly recognize the value of geodesic domes for their durability and unique aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
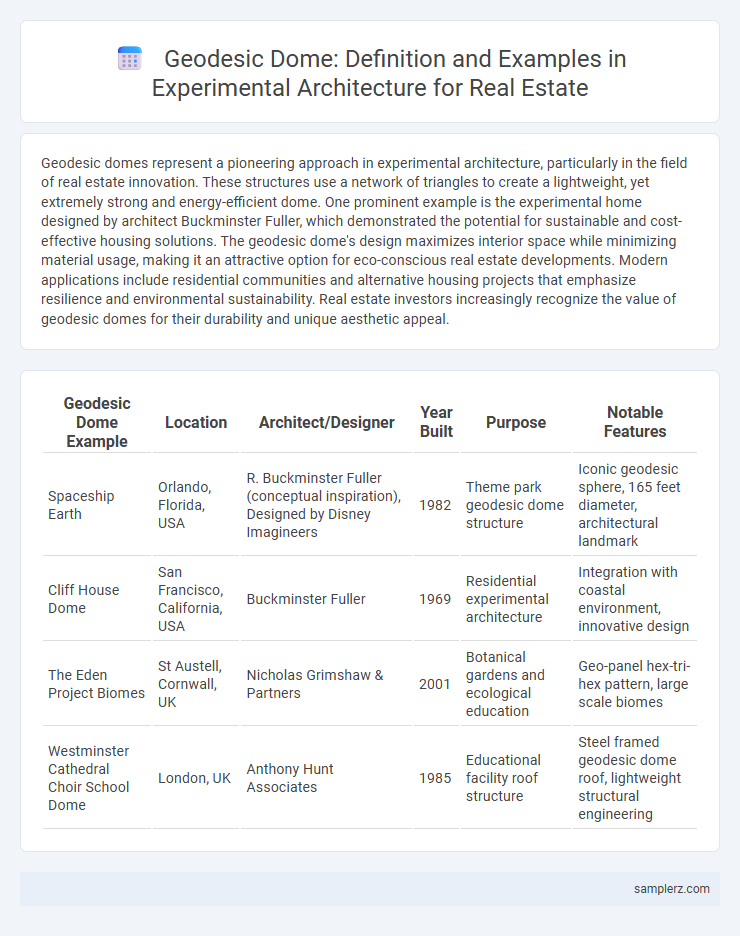
| Geodesic Dome Example | Location | Architect/Designer | Year Built | Purpose | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spaceship Earth | Orlando, Florida, USA | R. Buckminster Fuller (conceptual inspiration), Designed by Disney Imagineers | 1982 | Theme park geodesic dome structure | Iconic geodesic sphere, 165 feet diameter, architectural landmark |
| Cliff House Dome | San Francisco, California, USA | Buckminster Fuller | 1969 | Residential experimental architecture | Integration with coastal environment, innovative design |
| The Eden Project Biomes | St Austell, Cornwall, UK | Nicholas Grimshaw & Partners | 2001 | Botanical gardens and ecological education | Geo-panel hex-tri-hex pattern, large scale biomes |
| Westminster Cathedral Choir School Dome | London, UK | Anthony Hunt Associates | 1985 | Educational facility roof structure | Steel framed geodesic dome roof, lightweight structural engineering |
Iconic Geodesic Dome Examples in Experimental Architecture
The geodesic dome designed by Buckminster Fuller, such as the Montreal Biosphere, exemplifies iconic experimental architecture by maximizing structural efficiency and spatial volume with minimal materials. These domes showcase innovative use of triangular elements to distribute stress evenly, enabling lightweight yet durable constructions ideal for sustainable housing solutions. Geodesic designs continue to inspire cutting-edge real estate development focused on eco-friendly, resilient, and aesthetically unique living spaces.
Historical Milestones: Early Geodesic Dome Innovations
The early geodesic dome innovations of the mid-20th century, pioneered by architect Buckminster Fuller, marked a significant milestone in experimental architecture by introducing lightweight, strong, and efficient structural designs. One of the first notable examples was the Dymaxion House, which showcased the potential for affordable, mass-produced housing using geodesic principles. These developments laid the foundation for modern sustainable architecture and advanced prefabricated construction techniques widely used in contemporary real estate projects.
Sustainable Features of Geodesic Dome Structures
Geodesic dome structures exemplify sustainable architecture through their efficient use of materials and superior energy performance, minimizing waste and reducing heating and cooling costs. The dome's shape provides exceptional structural strength, allowing for lightweight construction while maximizing interior space and natural ventilation. Innovations such as solar panel integration and rainwater harvesting systems further enhance the environmental benefits of geodesic dome homes in real estate developments.
Famous Residential Geodesic Domes Worldwide
Famous residential geodesic domes worldwide include the iconic Dymaxion House by Buckminster Fuller, showcasing lightweight, energy-efficient design principles. The Amundsen House in Norway exemplifies sustainable architecture with its resilient dome structure adapted to harsh climates. In California, the Pacific Domes community demonstrates innovative use of geodesic designs for eco-friendly, modular living spaces optimized for natural light and ventilation.
Geodesic Domes in Modern Urban Developments
Geodesic domes in modern urban developments offer innovative solutions for sustainable housing due to their energy efficiency and structural strength. Projects like the Biosphere in Montreal and urban eco-villages integrate geodesic domes to maximize space and natural light while minimizing material usage. These domes support green building initiatives by reducing construction costs and enhancing environmental resilience in dense city environments.
Experimental Materials Used in Geodesic Dome Construction
Geodesic domes utilize innovative materials such as lightweight steel, aluminum, and advanced polymers to enhance structural integrity and energy efficiency. Experimental architectures often integrate transparent ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) cushions to maximize natural light while maintaining insulation. These materials contribute to sustainable real estate developments by reducing construction waste and improving thermal performance.
Geodesic Domes as Eco-Friendly Housing Solutions
Geodesic domes pioneered by Buckminster Fuller showcase structural efficiency and sustainability in experimental architecture. These domes use minimal materials while maximizing interior space and natural airflow, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Their aerodynamic shape withstands extreme weather, making them an eco-friendly housing solution adaptable to various climates and terrains.
Notable Public Spaces Featuring Geodesic Dome Designs
The geodesic dome of the Montreal Biosphere stands as a pioneering example of experimental architecture in real estate, showcasing sustainable and innovative design. Designed by Buckminster Fuller, this iconic public space exemplifies the structural efficiency and aesthetic appeal of geodesic domes. Its influence extends to modern eco-friendly developments and public parks, emphasizing scalability and environmental integration.
Influential Architects in Geodesic Dome Experimentation
Buckminster Fuller is a pivotal figure in experimental architecture, pioneering the geodesic dome as a sustainable and efficient housing solution. Architect Frei Otto further expanded on geodesic principles by integrating lightweight tensile structures, influencing modern eco-friendly real estate designs. Contemporary architects like Michael Reynolds apply geodesic domes in earthship projects, emphasizing self-sufficiency and environmental harmony in innovative residential developments.
Future Trends: Geodesic Domes in Real Estate Projects
Geodesic domes represent a cutting-edge architectural trend in real estate, offering energy-efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective housing solutions. Their structural strength, using minimal materials, supports innovative developments in eco-friendly residential and commercial projects. Real estate developers increasingly incorporate geodesic domes to meet future urban demands for resilience and environmental responsibility.
example of geodesic dome in experimental architecture Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com