Mews are narrow streets or lanes typically lined with small houses or converted stables, offering unique residential spaces in urban regeneration projects. In cities like London, mews have been transformed from utilitarian service roads into desirable properties that blend historical character with modern living. These developments attract buyers seeking charm and exclusivity in revitalized neighborhoods, contributing to rising property values and enhanced community appeal. The conversion of mews in urban regeneration often involves preserving original architectural features while upgrading infrastructure to meet contemporary standards. Data from real estate markets show that mews properties command premium prices compared to standard urban homes due to their rarity and aesthetic appeal. Urban planners and developers leverage these spaces to create pedestrian-friendly environments that support sustainable city living and cultural preservation.
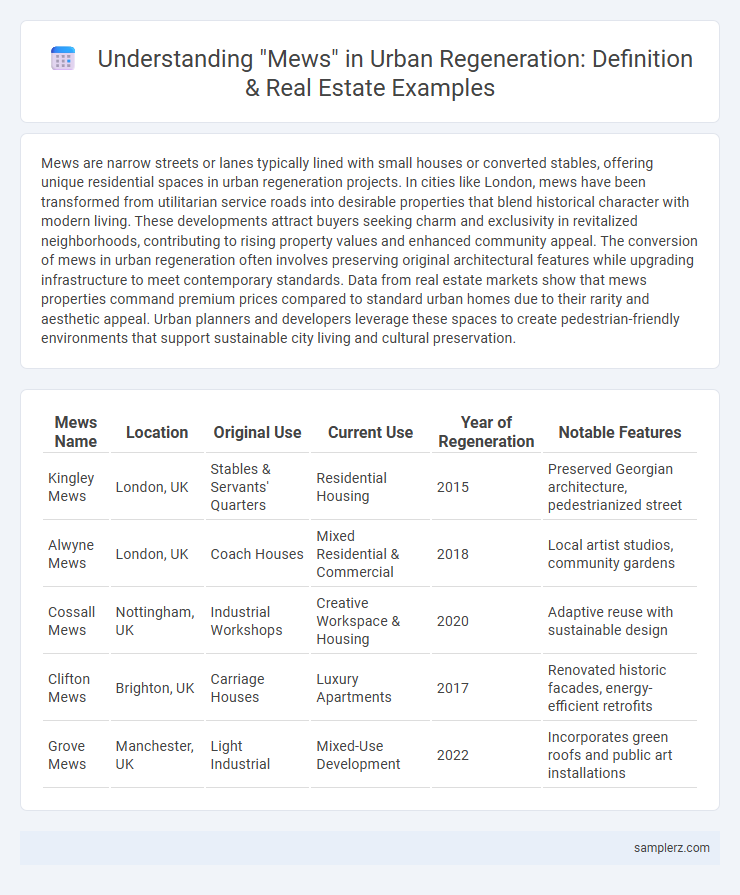
Table of Comparison
| Mews Name | Location | Original Use | Current Use | Year of Regeneration | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kingley Mews | London, UK | Stables & Servants' Quarters | Residential Housing | 2015 | Preserved Georgian architecture, pedestrianized street |
| Alwyne Mews | London, UK | Coach Houses | Mixed Residential & Commercial | 2018 | Local artist studios, community gardens |
| Cossall Mews | Nottingham, UK | Industrial Workshops | Creative Workspace & Housing | 2020 | Adaptive reuse with sustainable design |
| Clifton Mews | Brighton, UK | Carriage Houses | Luxury Apartments | 2017 | Renovated historic facades, energy-efficient retrofits |
| Grove Mews | Manchester, UK | Light Industrial | Mixed-Use Development | 2022 | Incorporates green roofs and public art installations |
Defining Mews: Historical Significance in Urban Landscapes
Mews, traditionally narrow lanes lined with former stables and carriage houses, have played a significant role in urban regeneration by transforming neglected spaces into vibrant residential and commercial areas. Their historical significance lies in showcasing adaptive reuse, preserving architectural heritage while meeting modern urban demands. Urban planners and developers leverage the unique character of mews to enhance community identity and promote sustainable revitalization in city centers.
The Role of Mews in Modern Urban Regeneration
Mews, originally service streets in historic urban areas, have become pivotal in modern urban regeneration by transforming underutilized spaces into vibrant residential and commercial hubs. Their adaptive reuse supports sustainable development, enhances community identity, and increases urban density without sprawling. Examples like London's Fitzrovia Mews illustrate how these narrow lanes foster walkability, local businesses, and mixed-use neighborhoods, driving economic revitalization within cities.
Key Features of Successful Mews Developments
Successful mews developments in urban regeneration emphasize maintaining historical architectural character while integrating modern amenities and sustainable design. They typically feature pedestrian-friendly layouts, mixed-use spaces combining residential and commercial units, and green landscaping that enhances community engagement. High-value mews projects balance privacy with connectivity, offering vibrant yet tranquil urban living environments that attract diverse demographics.
Case Studies: Notable Mews Transformations in Major Cities
Notable mews transformations in urban regeneration include the revitalization of London's Kensington Mews, where historic stables were converted into luxury residences, enhancing both heritage preservation and property values. New York City's West Village mews underwent a similar transition, blending cobblestone charm with modern amenities to attract affluent buyers and foster community vibrancy. These case studies demonstrate how adaptive reuse of mews can drive sustainable urban development and elevate neighborhood desirability.
Mews as Mixed-Use Spaces: Live, Work, and Play
Mews in urban regeneration have been transformed into vibrant mixed-use spaces, combining residential lofts, creative work studios, and trendy cafes to foster live-work-play environments. These revitalized mews maximize urban density while preserving historic architecture, attracting young professionals and entrepreneurs seeking integrated community hubs. Successful examples include London's Ladbroke Mews and New York's Meatpacking District, where adaptive reuse projects promote economic diversity and cultural vibrancy.
Sustainability and Green Design in Urban Mews Projects
Urban mews projects exemplify sustainable urban regeneration by integrating green design principles such as energy-efficient buildings, green roofs, and permeable pavements. These developments reduce carbon footprints and promote biodiversity while revitalizing underused urban spaces. Incorporating renewable energy systems and native landscaping enhances the ecological benefits and supports resilient, low-impact urban living environments.
Community Engagement and Social Value in Mews Regeneration
Mews regeneration projects in urban areas prioritize community engagement by involving local residents and stakeholders in the planning and design process, fostering a sense of ownership and social cohesion. These initiatives often transform underutilized alleyways into vibrant communal spaces, enhancing social value through improved safety, accessibility, and local economic opportunities. By integrating mixed-use developments that include affordable housing and shared amenities, mews regeneration strengthens neighborhood identity and promotes inclusive urban revitalization.
Mews and Urban Connectivity: Improving Mobility and Access
Mews developments in urban regeneration enhance connectivity by transforming underutilized narrow streets into pedestrian-friendly pathways, improving access to residential and commercial areas. These revitalized mews create seamless links between main roads and neighborhood pockets, promoting sustainable mobility options like walking and cycling. Integrating mews into city planning fosters inclusive access while reducing traffic congestion and supporting local businesses.
Challenges and Solutions in Adapting Mews for Urban Renewal
Adapting mews for urban renewal presents challenges such as preserving historic character while meeting modern building codes and accommodating increased residential density. Solutions include integrating sensitive architectural interventions, upgrading infrastructure for sustainability, and implementing flexible zoning regulations to balance heritage conservation with urban growth. Collaborative planning with local communities ensures that mews redevelopment supports both cultural identity and functional urban living.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Mews in City Planning
Mews, traditionally narrow lanes or courtyards lined with stables or garages, are increasingly integrated into urban regeneration projects as dynamic mixed-use spaces promoting sustainable city living. Future trends highlight the transformation of mews into pedestrian-friendly corridors that enhance connectivity, green infrastructure, and local community engagement in dense metropolitan areas. Incorporating smart technologies and adaptive reuse, mews contribute to resilient urban frameworks that balance historical preservation with innovative housing and commercial development.
example of mews in urban regeneration Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com