Fenestration in skyscrapers refers to the arrangement, design, and installation of windows, doors, and other openings on the building facade. An example of fenestration in a skyscraper is the use of curtain wall systems made of glass panels, which provide natural light, thermal insulation, and aesthetic appeal. These glass facades often include double-glazed or triple-glazed windows to enhance energy efficiency and control solar heat gain. In iconic skyscrapers such as the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, fenestration plays a critical role in balancing transparency and shading. The building uses advanced glazing technology combined with reflective coatings to reduce glare and improve occupant comfort. Data from building performance studies highlight how intelligent fenestration systems contribute to lowering energy consumption by optimizing daylight penetration and minimizing artificial lighting needs.
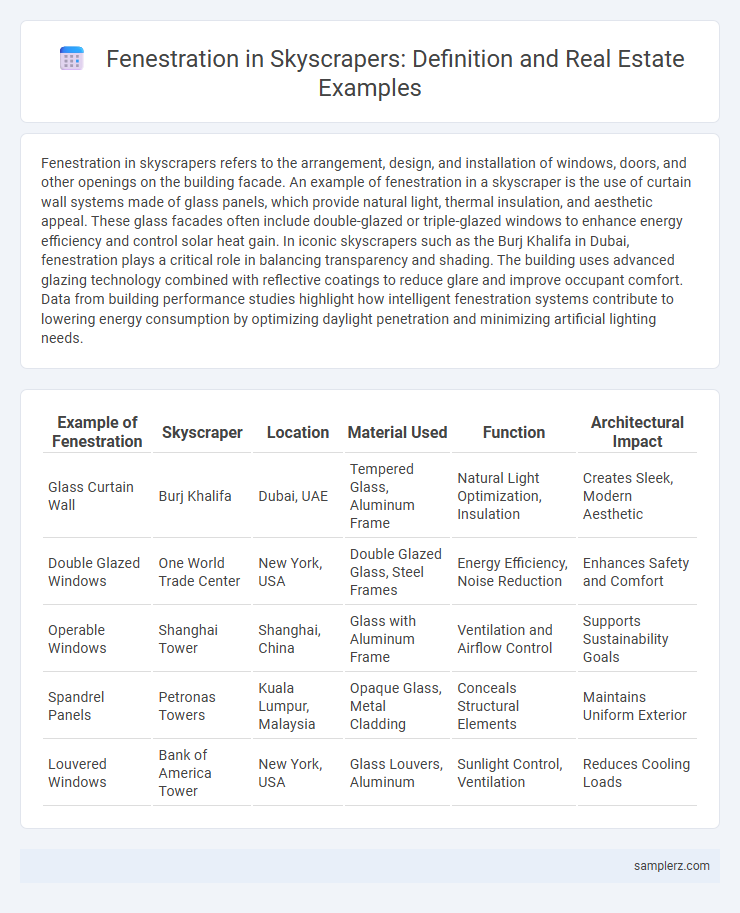
Table of Comparison
| Example of Fenestration | Skyscraper | Location | Material Used | Function | Architectural Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass Curtain Wall | Burj Khalifa | Dubai, UAE | Tempered Glass, Aluminum Frame | Natural Light Optimization, Insulation | Creates Sleek, Modern Aesthetic |
| Double Glazed Windows | One World Trade Center | New York, USA | Double Glazed Glass, Steel Frames | Energy Efficiency, Noise Reduction | Enhances Safety and Comfort |
| Operable Windows | Shanghai Tower | Shanghai, China | Glass with Aluminum Frame | Ventilation and Airflow Control | Supports Sustainability Goals |
| Spandrel Panels | Petronas Towers | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | Opaque Glass, Metal Cladding | Conceals Structural Elements | Maintains Uniform Exterior |
| Louvered Windows | Bank of America Tower | New York, USA | Glass Louvers, Aluminum | Sunlight Control, Ventilation | Reduces Cooling Loads |
Iconic Fenestration Designs in Skyscrapers
Iconic fenestration designs in skyscrapers, such as the diamond-patterned glass facade of 30 St Mary Axe in London, showcase how window arrangements enhance both aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency. The Burj Khalifa's sleek curtain wall system features reflective glass panels that optimize natural light while minimizing heat gain. These innovative fenestration techniques define a skyscraper's identity, contributing to sustainable urban architecture.
Glass Wall Systems: Modern Fenestration in High-Rise Buildings
Glass wall systems in skyscrapers serve as prime examples of modern fenestration, enhancing natural light penetration and energy efficiency in high-rise buildings. These curtain walls typically feature insulated glass units with low-emissivity coatings, reducing heat transfer while maintaining transparency. Innovations such as double-skin facades and integrated shading devices optimize thermal performance and occupant comfort in urban environments.
Curtain Wall Fenestration Examples in Skyscrapers
Curtain wall fenestration in skyscrapers often utilizes glass panels framed with aluminum or steel to create lightweight, weather-resistant building envelopes that maximize natural light and views. Notable examples include the Burj Khalifa's reflective glass curtain wall and the One World Trade Center's high-performance glass facade, which improve energy efficiency while maintaining structural integrity. These curtain wall systems integrate operable and fixed windows, allowing for ventilation and aesthetic variation in iconic high-rise designs.
Double-Skin Facades: Innovative Skyscraper Fenestration
Double-skin facades in skyscrapers enhance energy efficiency by incorporating two layers of glass separated by a ventilated cavity, reducing heat loss and solar gain. This innovative fenestration system improves thermal insulation and soundproofing while allowing natural ventilation, contributing to sustainable building design. Iconic examples include the Torre Reforma in Mexico City and the Al Bahar Towers in Abu Dhabi, which showcase advanced double-skin facade technology.
Energy-Efficient Fenestration in Urban Towers
Energy-efficient fenestration in urban towers incorporates triple-glazed windows with low-emissivity coatings and thermally broken aluminum frames to minimize heat transfer and maximize natural light. Advanced glazing technologies, such as electrochromic glass, allow dynamic control of solar heat gain, reducing reliance on HVAC systems in skyscrapers. Implementing airtight sealing and insulated spandrel panels enhances overall building envelope performance, contributing to significant energy savings in high-rise real estate developments.
Adaptive Shading and Dynamic Fenestration in Skyscrapers
Adaptive shading and dynamic fenestration in skyscrapers enhance energy efficiency by automatically adjusting window tint and shading based on sunlight intensity and angle. These technologies optimize natural lighting while minimizing heat gain, reducing reliance on HVAC systems and lowering operational costs. Prominent examples include the Salesforce Tower in San Francisco and The Edge in Amsterdam, both utilizing advanced smart glass and shading solutions for sustainable high-rise design.
Landmark Skyscrapers with Unique Window Patterns
The Burj Khalifa in Dubai features a distinctive fenestration pattern with reflective glass panels arranged in a spiraling design to reduce heat gain and maximize natural light. The Louvre Abu Dhabi's geometric window screens create a 'rain of light' effect, blending cultural aesthetics with functional shading. New York's One World Trade Center uses triangular glass panes that enhance structural integrity while providing panoramic city views.
Integration of Natural Light Through Skyscraper Fenestration
Skyscraper fenestration, such as floor-to-ceiling glass panels and expansive curtain walls, enables the seamless integration of natural light, enhancing indoor illumination and reducing reliance on artificial lighting. Examples like the Burj Khalifa utilize high-performance glazing systems that optimize light penetration while controlling heat gain, ensuring energy efficiency. This strategic use of fenestration not only improves occupant comfort but also contributes to sustainable building design in urban environments.
Architectural Trends in Skyscraper Fenestration
Modern skyscraper fenestration often features expansive glass curtain walls that enhance natural light penetration and provide panoramic city views. Innovations include double-skin facades and electrochromic glass, which improve energy efficiency by regulating heat and glare while maintaining aesthetic appeal. These architectural trends reflect a balance between functionality, sustainability, and visual impact in high-rise building design.
Sustainable Fenestration Materials for High-Rise Buildings
Sustainable fenestration materials in skyscrapers often include triple-glazed low-emissivity (low-E) glass, which enhances thermal insulation and reduces energy consumption. Electrochromic glass allows dynamic control of light and heat transmission, improving occupant comfort while minimizing reliance on HVAC systems. Incorporating recycled aluminum frames supports structural durability and sustainability, making these materials ideal for high-rise building facades.
example of fenestration in skyscraper Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com