Capitalization in real estate investment refers to the process of estimating a property's value based on its net operating income (NOI) and the capitalization rate (cap rate). Investors calculate the cap rate by dividing the NOI by the property's current market value or purchase price. This metric helps determine the potential return on investment and compare profitability across different properties. Data such as rental income, operating expenses, and market trends are essential for accurate capitalization analysis. For example, a property with an annual NOI of $100,000 and a cap rate of 8% would be valued at $1,250,000 ($100,000 / 0.08). Understanding capitalization enables investors to make informed decisions, optimize portfolio performance, and identify undervalued opportunities in the real estate market.
Table of Comparison
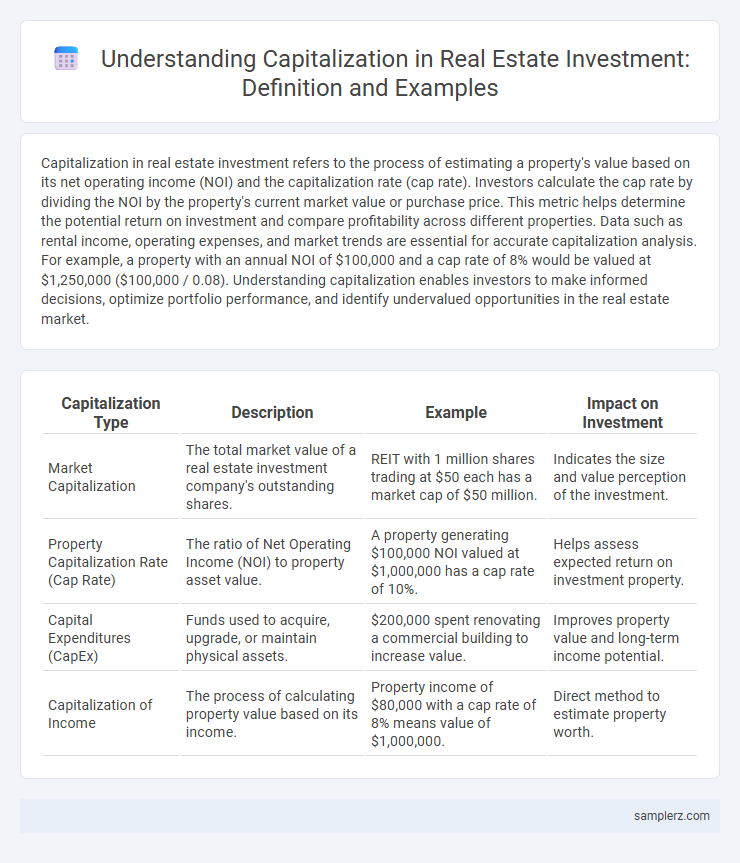
| Capitalization Type | Description | Example | Impact on Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | The total market value of a real estate investment company's outstanding shares. | REIT with 1 million shares trading at $50 each has a market cap of $50 million. | Indicates the size and value perception of the investment. |
| Property Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate) | The ratio of Net Operating Income (NOI) to property asset value. | A property generating $100,000 NOI valued at $1,000,000 has a cap rate of 10%. | Helps assess expected return on investment property. |
| Capital Expenditures (CapEx) | Funds used to acquire, upgrade, or maintain physical assets. | $200,000 spent renovating a commercial building to increase value. | Improves property value and long-term income potential. |
| Capitalization of Income | The process of calculating property value based on its income. | Property income of $80,000 with a cap rate of 8% means value of $1,000,000. | Direct method to estimate property worth. |
Understanding Capitalization in Real Estate Investments
Capitalization in real estate investment refers to the process of converting income generated from a property into an estimated value through the capitalization rate (cap rate), which is calculated by dividing net operating income (NOI) by the property's current market value. Understanding capitalization helps investors assess the potential return on investment and make informed decisions when comparing different properties or markets. For example, a property with an NOI of $100,000 and a market value of $1,000,000 has a cap rate of 10%, indicating its profitability relative to its price.
What Is Capitalization Rate?
Capitalization rate, or cap rate, measures the expected rate of return on a real estate investment property, calculated by dividing the net operating income (NOI) by the property's current market value. For example, a property generating $100,000 in annual NOI with a market value of $1,000,000 has a cap rate of 10%. This metric helps investors assess potential profitability and compare investment opportunities across various real estate markets.
The Role of Cap Rate in Property Valuation
Cap rate, or capitalization rate, plays a crucial role in real estate investment by indicating the potential return on a property based on its net operating income (NOI) relative to its market value. Investors use the cap rate to assess risk and compare the profitability of various investment opportunities, with higher cap rates typically reflecting greater risk and potentially higher returns. Understanding cap rate trends in specific markets helps investors make informed decisions on property valuation and capitalization.
Example: Calculating Capitalization Rate for Rental Properties
Calculating the capitalization rate (cap rate) for rental properties involves dividing the property's net operating income (NOI) by its current market value or purchase price, expressed as a percentage. For example, a rental property generating $50,000 in annual NOI with a market value of $500,000 has a cap rate of 10%, indicating the expected return on investment. Investors use this metric to compare properties' profitability and assess risk in real estate investment decisions.
Capitalization Scenario: Commercial Real Estate Investments
In commercial real estate investments, capitalization refers to the process of determining the property's value based on its net operating income (NOI) divided by the capitalization rate (cap rate). For example, a retail building generating $150,000 in annual NOI with a cap rate of 6% would have a valuation of $2.5 million ($150,000 / 0.06). This capitalization scenario helps investors assess the expected return and market value, influencing financing and acquisition decisions.
Single-Family vs. Multi-Family Property Capitalization
Single-family property capitalization typically involves lower upfront costs but may yield higher per-unit returns due to exclusive ownership and simpler management. Multi-family property capitalization requires larger initial investments supported by multiple rental incomes, offering diversified revenue streams and economies of scale. Investors often weigh the trade-off between single-family liquidity and multi-family cash flow stability when optimizing portfolio capitalization.
Factors Affecting Capitalization Rate in Real Estate
Capitalization rate in real estate investment is influenced by factors such as location, property condition, and market trends, determining the potential return on investment. Higher cap rates often reflect increased risk, while lower rates indicate stable, high-demand areas with consistent income. Economic conditions, interest rates, and property management quality also play crucial roles in shaping capitalization rates.
How Investors Use Cap Rate for Decision Making
Investors utilize the capitalization rate (cap rate) as a key metric to evaluate the profitability of real estate investments by dividing the property's net operating income by its current market value. A higher cap rate often indicates a potentially higher return but may also reflect increased risk, guiding investors to balance their investment choices. This ratio enables comparison across properties, facilitating informed decisions based on expected income performance relative to the purchase price.
Risks and Limitations of Capitalization in Investments
Capitalization in real estate investment involves assessing net operating income relative to property value to estimate returns, but it carries risks like market volatility and inaccurate income projections that can mislead valuation. Overreliance on capitalization rates may overlook important factors such as property condition, location, and economic trends, limiting investment reliability. Investors must consider these limitations to avoid underperformance and financial losses in fluctuating market conditions.
Maximizing Returns: Best Practices for Capitalization Analysis
Effective capitalization in real estate investment involves analyzing net operating income (NOI) and applying accurate capitalization rates (cap rates) to determine property value and forecast returns. Prioritizing thorough market research and regularly updating cap rate assumptions based on comparable sales data maximizes investment accuracy and profitability. Leveraging capitalization analysis techniques such as discounted cash flow (DCF) models enhances decision-making for long-term wealth creation and risk mitigation.
example of capitalization in investment Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com