A passive house is a highly energy-efficient building standard widely adopted in sustainable real estate construction. This type of home uses advanced insulation, airtight construction, and strategic window placement to minimize energy consumption. Data shows that passive houses can reduce heating and cooling demands by up to 90%, significantly lowering environmental impact. In sustainable construction projects, passive houses are often equipped with heat recovery ventilation systems that maintain air quality while conserving energy. Entities such as architects and developers prioritize passive house certification to meet strict energy codes and green building certifications. Real estate investors increasingly value passive houses due to their long-term operational savings and market appeal.
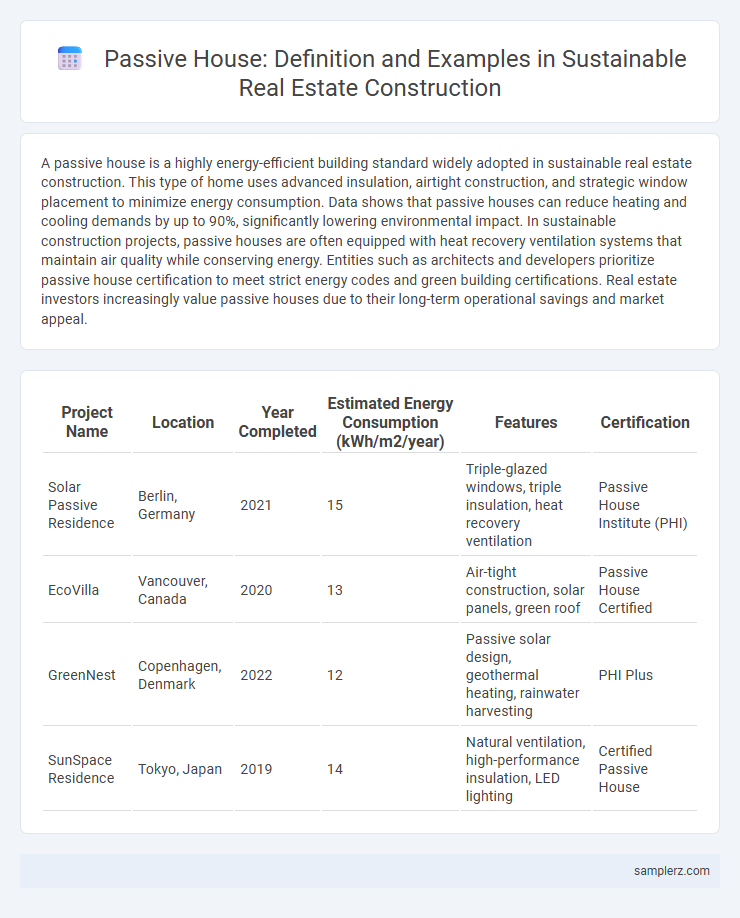
Table of Comparison
| Project Name | Location | Year Completed | Estimated Energy Consumption (kWh/m2/year) | Features | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Passive Residence | Berlin, Germany | 2021 | 15 | Triple-glazed windows, triple insulation, heat recovery ventilation | Passive House Institute (PHI) |
| EcoVilla | Vancouver, Canada | 2020 | 13 | Air-tight construction, solar panels, green roof | Passive House Certified |
| GreenNest | Copenhagen, Denmark | 2022 | 12 | Passive solar design, geothermal heating, rainwater harvesting | PHI Plus |
| SunSpace Residence | Tokyo, Japan | 2019 | 14 | Natural ventilation, high-performance insulation, LED lighting | Certified Passive House |
Key Features of Passive Houses in Sustainable Construction
Passive houses in sustainable construction feature ultra-high energy efficiency through superior insulation, airtight building envelopes, and advanced heat recovery ventilation systems. These homes maintain consistent indoor temperatures with minimal energy consumption, significantly reducing carbon footprints and utility costs. Triple-glazed windows and strategic orientation maximize natural light while minimizing heat loss, enhancing both environmental sustainability and occupant comfort.
Notable Passive House Projects Worldwide
Notable passive house projects worldwide demonstrate the effectiveness of sustainable construction through energy efficiency and minimal environmental impact. The Bahnstadt district in Heidelberg, Germany, exemplifies large-scale passive house implementation, reducing energy consumption by up to 90%. Other prominent examples include the Passive House Institute's Plus-Energy House and the multi-residential buildings in Vienna's Aspern Seestadt, showcasing cutting-edge sustainable design and innovative passive technologies.
Benefits of Passive Houses for Energy Efficiency
Passive houses exemplify sustainable construction by drastically reducing energy consumption through superior insulation, airtight building envelopes, and heat recovery ventilation systems. These homes maintain consistent indoor temperatures, minimizing the need for conventional heating and cooling, which translates to up to 90% lower energy use compared to traditional buildings. Enhanced energy efficiency in passive houses contributes to reduced carbon emissions, lower utility costs, and increased occupant comfort, making them a leading choice in eco-friendly real estate development.
Architectural Design Elements of Passive Houses
Passive houses integrate architectural design elements such as high-performance insulation, airtight building envelopes, and strategically oriented windows to maximize natural light and heat retention. Triple-glazed windows and thermal bridge-free construction significantly enhance energy efficiency, reducing the need for mechanical heating and cooling. These design strategies collectively ensure optimal indoor air quality and thermal comfort while minimizing environmental impact in sustainable construction.
Real Estate Value Impact of Passive Houses
Passive houses significantly enhance real estate value by reducing energy costs through advanced insulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilation, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers. Properties with passive house certification often command higher resale prices and quicker market transactions due to their superior energy efficiency and lower operational expenses. Incorporating sustainable construction standards like passive house principles boosts long-term asset value by minimizing environmental impact and aligning with increasing regulatory requirements on energy performance.
Construction Materials Used in Passive Houses
Passive houses utilize highly efficient construction materials such as triple-glazed windows, airtight membranes, and dense insulation made from sustainable sources like cellulose or mineral wool. Structural components often include wood and recycled steel, optimizing thermal performance while minimizing environmental impact. These materials collectively reduce energy consumption and enhance indoor air quality, setting a benchmark in sustainable construction practices.
Challenges in Implementing Passive House Standards
Implementing Passive House standards in sustainable construction faces challenges such as higher upfront costs, stringent airtightness requirements, and the need for specialized design expertise. Achieving optimal insulation and ventilation often demands precise construction techniques and quality control to prevent thermal bridges and moisture issues. Limited availability of skilled contractors and regional variations in climate impact the feasibility and efficiency of Passive House implementations.
Passive House Certification Process Explained
The Passive House Certification process involves rigorous evaluation of energy efficiency, airtightness, and thermal comfort based on stringent standards set by the Passive House Institute. Key steps include detailed design review, blower door testing to ensure minimal air leakage, and verification of energy performance through precise calculations of heating and cooling demand. Achieving certification confirms a building's superior sustainability credentials by drastically reducing energy consumption and enhancing occupant comfort.
Comparing Passive Houses to Traditional Homes
Passive houses in sustainable construction use advanced insulation, airtight building envelopes, and high-performance windows to reduce energy consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional homes. These residences maintain consistent indoor temperatures without conventional heating or cooling systems, significantly lowering utility costs and carbon emissions. Passive houses demonstrate superior energy efficiency, enhanced indoor air quality, and greater long-term durability relative to standard construction methods.
Future Trends in Passive House Real Estate Development
Passive houses in sustainable construction exemplify cutting-edge energy efficiency by incorporating advanced insulation, airtight building envelopes, and heat recovery ventilation systems that significantly reduce energy consumption. Future trends in passive house real estate development emphasize integration of smart home technologies, renewable energy sources like solar panels, and adaptive design for climate resilience. Growing investor interest and government incentives are accelerating the adoption of passive house standards in urban and suburban residential projects.
example of passive house in sustainable construction Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com