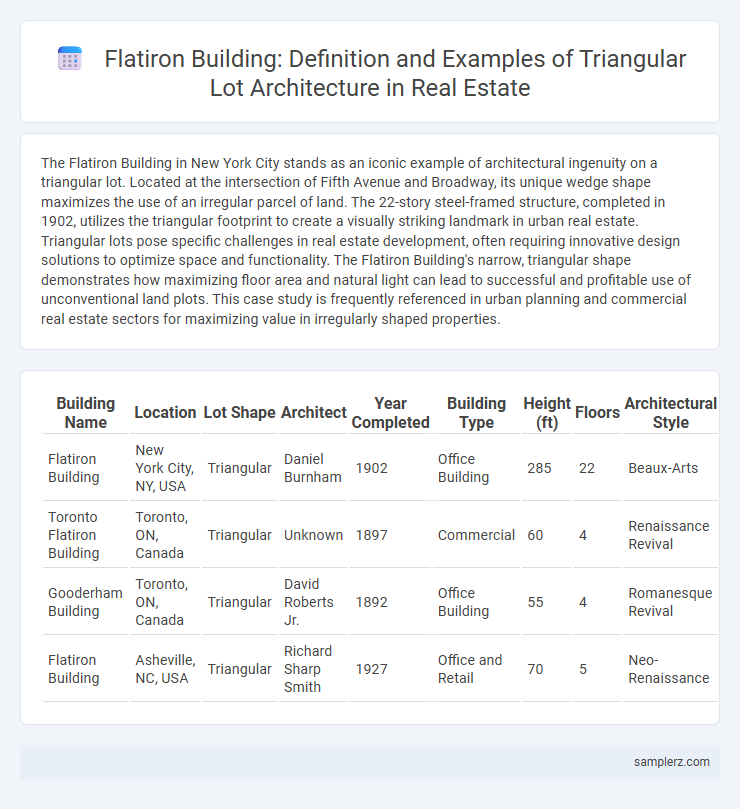
The Flatiron Building in New York City stands as an iconic example of architectural ingenuity on a triangular lot. Located at the intersection of Fifth Avenue and Broadway, its unique wedge shape maximizes the use of an irregular parcel of land. The 22-story steel-framed structure, completed in 1902, utilizes the triangular footprint to create a visually striking landmark in urban real estate. Triangular lots pose specific challenges in real estate development, often requiring innovative design solutions to optimize space and functionality. The Flatiron Building's narrow, triangular shape demonstrates how maximizing floor area and natural light can lead to successful and profitable use of unconventional land plots. This case study is frequently referenced in urban planning and commercial real estate sectors for maximizing value in irregularly shaped properties.
Table of Comparison
| Building Name | Location | Lot Shape | Architect | Year Completed | Building Type | Height (ft) | Floors | Architectural Style |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flatiron Building | New York City, NY, USA | Triangular | Daniel Burnham | 1902 | Office Building | 285 | 22 | Beaux-Arts |
| Toronto Flatiron Building | Toronto, ON, Canada | Triangular | Unknown | 1897 | Commercial | 60 | 4 | Renaissance Revival |
| Gooderham Building | Toronto, ON, Canada | Triangular | David Roberts Jr. | 1892 | Office Building | 55 | 4 | Romanesque Revival |
| Flatiron Building | Asheville, NC, USA | Triangular | Richard Sharp Smith | 1927 | Office and Retail | 70 | 5 | Neo-Renaissance |
Iconic Flatiron Buildings: Architectural Marvels on Triangular Lots
The Flatiron Building in Manhattan, situated on a distinctive triangular lot at the intersection of Fifth Avenue and Broadway, exemplifies innovative use of irregular urban parcels in real estate development. Its unique wedge-shaped design maximizes space efficiency while becoming an iconic symbol of early 20th-century architecture. This architectural marvel influences contemporary triangular lot projects, combining historical significance with modern urban planning strategies.
The Challenges of Designing Flatiron Buildings on Odd-Shaped Sites
Designing flatiron buildings on triangular lots presents significant structural and spatial challenges due to their irregular geometry, requiring innovative architectural solutions to maximize usable interior space and natural light. Engineers must address complex load distribution and foundation stability while integrating efficient circulation paths within sharp-angled layouts. These constraints often lead to bespoke design approaches that optimize functionality without compromising aesthetic appeal.
Historic Examples of Flatiron Buildings Around the World
The Flatiron Building in New York City, completed in 1902, stands as an iconic example of architecture on a triangular lot, influencing similar designs globally. Historic flatiron buildings such as the Toronto Dominion Centre in Canada and the Gooderham Building in Toronto showcase how urban planners maximize irregular plots for landmark construction. These structures highlight the creative adaptation of triangular parcels to create visually striking and functional real estate assets.
Maximizing Usable Space in Triangular Lot Developments
The Flatiron Building in New York City exemplifies innovative use of a triangular lot by maximizing usable space through its slender, wedge-shaped design that fits precisely within the intersection's acute angles. Incorporating vertical construction and customized floor plans allows developers to optimize every square foot, turning spatial constraints into unique architectural features that enhance market value. Strategically employing mixed-use layouts and efficient circulation paths further increases functionality while leveraging the distinctive geometry of triangular lots for real estate projects.
Real Estate Value of Flatiron Buildings in Urban Landscapes
Flatiron buildings, such as the iconic Flatiron Building in New York City, maximize the use of triangular lots, creating unique architectural landmarks that enhance urban real estate value. These buildings often attract premium commercial and residential tenants due to their distinctive shape and historic significance, driving higher rental rates and property appreciation. In dense urban landscapes, flatiron structures contribute to neighborhood identity and economic vitality by optimizing irregular plots for lucrative real estate development.
Flatiron Building Case Studies: Innovative Design Solutions
The Flatiron Building, located on a unique triangular lot at the intersection of Fifth Avenue and Broadway in New York City, exemplifies innovative architectural design that maximizes limited space. Its distinctive wedge shape inspired numerous case studies on optimizing unconventional urban plots to enhance structural efficiency and aesthetic appeal. Today, the Flatiron remains a landmark study in creative real estate development, blending functional design with iconic cityscape presence.
Zoning and Planning Considerations for Triangular Lots
The Flatiron Building in New York City exemplifies the unique zoning and planning challenges posed by triangular lots, where irregular parcel shapes require innovative floor area ratio (FAR) calculations and setback adjustments to maximize usable space. Zoning regulations for such lots often mandate tailored building envelopes to conform to street alignments and pedestrian flow, ensuring compliance with local ordinances while preserving urban aesthetics. Effective planning strategies include leveraging the lot's geometry to enhance natural light penetration and ventilation, optimizing property value within the constraints of triangular land parcels.
Modern Takes on the Classic Flatiron Building
Modern takes on the classic Flatiron Building redefine the iconic triangular lot by integrating sleek glass facades and sustainable materials, enhancing natural light and energy efficiency. Architects emphasize multi-functional interior layouts that maximize limited space, combining open-concept living with innovative storage solutions. These contemporary designs preserve the historic silhouette while embracing cutting-edge technology and urban living trends.
The Impact of Flatiron Buildings on Neighborhood Aesthetics
Flatiron buildings, such as the iconic Flatiron Building in New York City, utilize triangular lots to create visually striking and space-efficient structures that enhance neighborhood aesthetics. Their unique shape breaks the monotony of traditional rectangular blocks, fostering an architectural landmark that attracts tourism and boosts local identity. By integrating historic design with modern urban landscapes, flatiron buildings contribute to a distinctive streetscape that encourages pedestrian engagement and community pride.
Notable Flatiron Buildings: Inspiration for Unique Real Estate Projects
The Flatiron Building in New York City, situated on a prominent triangular lot at the intersection of Fifth Avenue and Broadway, exemplifies innovative use of unconventional urban space. This iconic structure inspires real estate developers to creatively maximize triangular plots by blending striking architectural design with functional interior layouts. Notable flatiron buildings worldwide showcase how unique geometrical constraints can lead to distinctive and valuable property developments in densely built environments.
example of flatiron building in triangular lot Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com