A superdelegate is a party leader or elected official who has the right to vote at a political party's national convention and influence the nomination process without being bound by primary or caucus results. In the 2016 Democratic presidential nomination, notable superdelegates included President Barack Obama and former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who used their influence to support Clinton's bid for the presidency. These unpledged delegates played a critical role in securing Clinton's nomination over Senator Bernie Sanders, despite Sanders winning several state primaries. The Republican Party has a similar system but with fewer unpledged delegates, often referred to as automatic delegates or party leaders. In the 2016 Republican nomination process, superdelegates included members of the Republican National Committee who could cast votes independently of primary outcomes. This practice reflects the continued importance of party insiders in shaping the nomination, impacting candidate viability and party unity ahead of general elections.
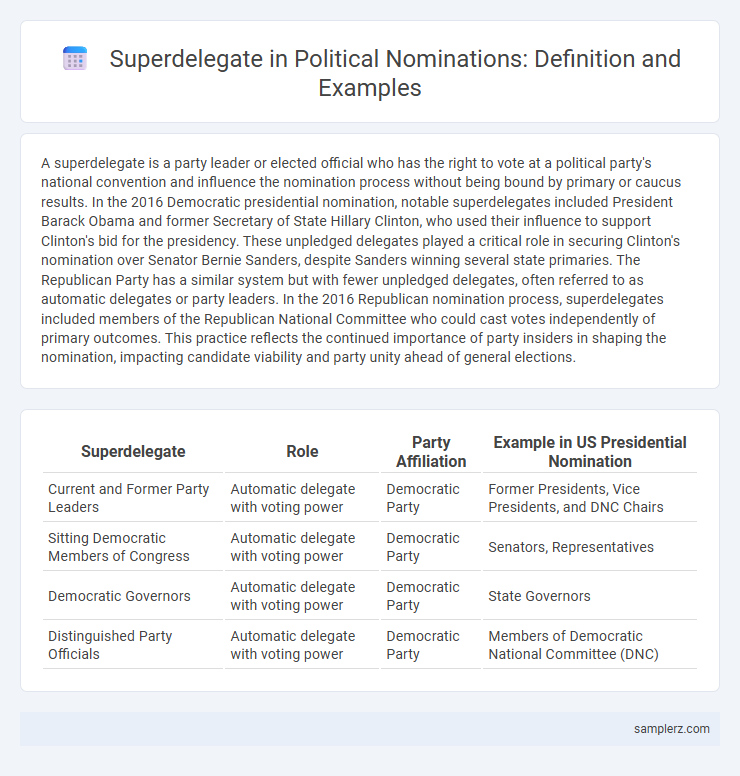
Table of Comparison
| Superdelegate | Role | Party Affiliation | Example in US Presidential Nomination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current and Former Party Leaders | Automatic delegate with voting power | Democratic Party | Former Presidents, Vice Presidents, and DNC Chairs |
| Sitting Democratic Members of Congress | Automatic delegate with voting power | Democratic Party | Senators, Representatives |
| Democratic Governors | Automatic delegate with voting power | Democratic Party | State Governors |
| Distinguished Party Officials | Automatic delegate with voting power | Democratic Party | Members of Democratic National Committee (DNC) |
Understanding Superdelegates: Key Figures in Political Nominations
Superdelegates are influential party leaders and elected officials who have the power to support any candidate at the party's national convention, regardless of primary or caucus results. Key figures often include former presidents, governors, and members of Congress, whose endorsements can sway delegate counts during contested nominations. Their role is particularly prominent in the Democratic Party, shaping the outcome of tightly contested primary races by providing experienced political insight and strategic guidance.
Historical Origins of Superdelegates in U.S. Politics
Superdelegates first emerged in the Democratic Party during the early 1980s as a response to the contentious 1968 Democratic National Convention, aiming to balance grassroots voter influence with party leadership input. These unpledged delegates include elected officials and party leaders granted automatic voting power in presidential primaries, intended to prevent populist nominees seen as unelectable. Since their introduction, superdelegates have significantly shaped the dynamics of U.S. presidential nominations by influencing outcomes beyond primary and caucus results.
Notable Superdelegate Examples in Recent Nominations
Notable superdelegate examples in recent Democratic presidential nominations include figures like Hillary Clinton and former President Barack Obama, who both secured crucial endorsements during their respective nomination campaigns. In 2016, superdelegates played a significant role by predominantly supporting Hillary Clinton over Bernie Sanders, influencing the delegate count before the primary voters finalized their decisions. These endorsements illustrate the impact superdelegates have on shaping party nominations by offering experienced political influence and early momentum.
Superdelegates’ Influence: Case Studies from Democratic Conventions
Superdelegates played a pivotal role in the 2008 Democratic National Convention, where their endorsements significantly bolstered Barack Obama's path to nomination despite close primary results against Hillary Clinton. Their influence surfaced again in 2016, as superdelegates overwhelmingly supported Hillary Clinton, demonstrating their potential to sway outcomes independently of popular votes. This mechanism highlights how superdelegates can serve as key power brokers within the Democratic Party's nomination process.
High-Profile Superdelegates: Politicians Who Shaped Nominations
High-profile superdelegates such as former President Bill Clinton and Senator Bernie Sanders played pivotal roles in shaping Democratic nominations by leveraging their delegate votes to influence candidate selection. These influential politicians often sway primary outcomes by endorsing frontrunners or rallying support behind emerging candidates. Their endorsements signal party unity and can alter delegate counts in tightly contested races, demonstrating the significant impact of superdelegates on nomination dynamics.
Superdelegates vs. Pledged Delegates: Key Differences Explained
Superdelegates in U.S. Democratic presidential primaries are unpledged party leaders and elected officials who can support any candidate, unlike pledged delegates who must vote according to primary or caucus results. Superdelegates hold significant influence as they can sway close nominations without being bound by voter preferences, whereas pledged delegates reflect the popular vote distribution. This distinction impacts the democratic process by balancing party insider input with grassroots voter engagement during candidate selection.
Superdelegate Endorsements: Impact on Presidential Candidates
Superdelegate endorsements significantly influence presidential nomination dynamics by signaling party establishment support and swaying undecided delegates. High-profile superdelegates, such as members of the Democratic National Committee and prominent elected officials, can provide early momentum and legitimacy to a candidate's campaign. Their backing often affects fundraising capabilities and media coverage, shaping voter perceptions in crucial primary states.
Controversial Superdelegate Decisions in Modern Elections
Superdelegates, influential party insiders with the power to sway presidential nominations, have sparked controversy in recent elections, notably during the 2016 Democratic primaries when their support for Hillary Clinton overshadowed Bernie Sanders' grassroots momentum. The discretionary votes of superdelegates often raise concerns about undermining the democratic process, as they can overturn the popular will expressed in pledged delegate counts. Political analysts highlight that the opaque nature of superdelegate influence fuels debates over party transparency and calls for reform in the nomination system.
Superdelegates in Action: 2008 and 2016 Democratic Primaries
Superdelegates played a critical role in the 2008 Democratic primary by initially supporting Hillary Clinton, which created tension before many shifted to Barack Obama as his delegate count increased. In the 2016 Democratic primary, superdelegates overwhelmingly backed Hillary Clinton early on, contributing to her front-runner status despite Bernie Sanders' strong popular support. The influence of superdelegates in these primaries highlighted their power to shape the nomination outcome beyond pledged delegate votes.
Reform Proposals: The Future Role of Superdelegates
Reform proposals for the future role of superdelegates emphasize reducing their influence to enhance democratic transparency in party nominations. Suggestions include limiting voting power or requiring superdelegates to align with primary or caucus outcomes. These changes aim to balance party leadership input with grassroots voter preferences, fostering greater legitimacy in candidate selection.
example of superdelegate in nomination Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com