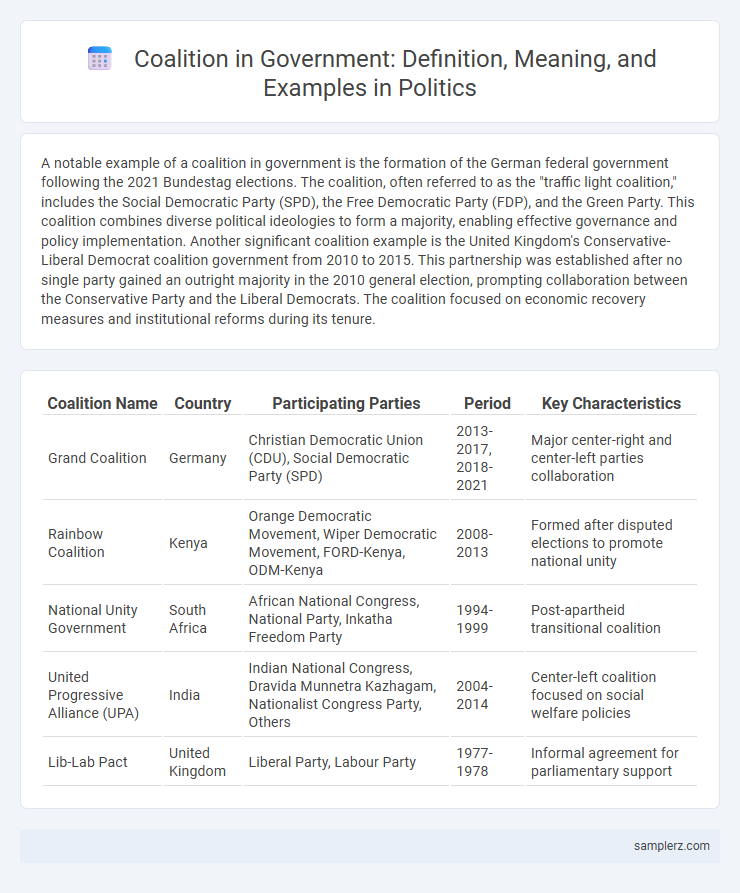
A notable example of a coalition in government is the formation of the German federal government following the 2021 Bundestag elections. The coalition, often referred to as the "traffic light coalition," includes the Social Democratic Party (SPD), the Free Democratic Party (FDP), and the Green Party. This coalition combines diverse political ideologies to form a majority, enabling effective governance and policy implementation. Another significant coalition example is the United Kingdom's Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition government from 2010 to 2015. This partnership was established after no single party gained an outright majority in the 2010 general election, prompting collaboration between the Conservative Party and the Liberal Democrats. The coalition focused on economic recovery measures and institutional reforms during its tenure.
Table of Comparison
| Coalition Name | Country | Participating Parties | Period | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grand Coalition | Germany | Christian Democratic Union (CDU), Social Democratic Party (SPD) | 2013-2017, 2018-2021 | Major center-right and center-left parties collaboration |
| Rainbow Coalition | Kenya | Orange Democratic Movement, Wiper Democratic Movement, FORD-Kenya, ODM-Kenya | 2008-2013 | Formed after disputed elections to promote national unity |
| National Unity Government | South Africa | African National Congress, National Party, Inkatha Freedom Party | 1994-1999 | Post-apartheid transitional coalition |
| United Progressive Alliance (UPA) | India | Indian National Congress, Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam, Nationalist Congress Party, Others | 2004-2014 | Center-left coalition focused on social welfare policies |
| Lib-Lab Pact | United Kingdom | Liberal Party, Labour Party | 1977-1978 | Informal agreement for parliamentary support |
Definition and Importance of Government Coalitions
Government coalitions refer to alliances formed between multiple political parties to establish a majority and govern effectively. These coalitions are crucial for ensuring political stability, enabling diverse representation, and facilitating the passage of legislation in parliamentary systems. Their importance lies in balancing power, promoting compromise, and preventing single-party dominance in fragmented political landscapes.
Historical Examples of Coalition Governments
The Weimar Republic in Germany provides a notable example of coalition governments, where multiple parties such as the Social Democrats, Centre Party, and German Democratic Party formed alliances to maintain parliamentary stability during the 1920s. In post-war Italy, the Christian Democrats frequently led coalition governments involving the Italian Socialist Party and Italian Communist Party to balance ideological differences. The United Kingdom's wartime coalition under Winston Churchill combined Conservatives, Labour, and Liberals to ensure unity against external threats during World War II.
Notable Coalition Governments in Europe
The CDU-CSU and SPD coalition in Germany, known as the "Grand Coalition," exemplifies a significant partnership between major political forces to ensure stability and governance. In Italy, the coalition government includes parties such as the Democratic Party and the Five Star Movement, showcasing a diverse alliance to navigate complex political landscapes. The United Kingdom's coalition government between the Conservative Party and Liberal Democrats in 2010-2015 marks a notable example of power-sharing arrangements in recent European political history.
Coalition Governments in Parliamentary Systems
Coalition governments in parliamentary systems often arise when no single party secures an absolute majority, prompting multiple parties to collaborate for a functioning government. Examples include Germany's CDU/CSU and SPD coalition, which balances conservative and social-democratic policies, and India's diverse alliances such as the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) led by the BJP. These coalitions facilitate policy compromise and political stability but require continuous negotiation to maintain legislative support.
Power-Sharing in Coalition Cabinets
Power-sharing in coalition cabinets involves multiple political parties collaborating to form a majority government, as seen in Germany's federal government where the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and Social Democratic Party (SPD) share executive roles and ministerial positions. This arrangement ensures representation of diverse political agendas and promotes stability by balancing power among coalition partners. Effective power-sharing often includes negotiated distribution of key ministries, joint policy platforms, and mechanisms for conflict resolution within the cabinet.
Coalition Building: Strategies and Challenges
Coalition building in government involves strategic negotiation among diverse political parties to form a majority alliance, often requiring compromise on policy priorities and power-sharing arrangements. Key challenges include managing conflicting interests, maintaining party cohesion, and ensuring effective communication to sustain long-term cooperation. Successful coalitions leverage mutual benefits and coordinated legislative agendas to stabilize governance and advance shared objectives.
Case Study: The United Kingdom’s Coalition Government
The United Kingdom's Coalition Government from 2010 to 2015, formed between the Conservative Party and the Liberal Democrats, serves as a prominent example of coalition governance. This partnership was established to achieve a parliamentary majority following the 2010 general election, enabling shared policy-making and power distribution. The coalition influenced significant fiscal austerity measures and education reforms while demonstrating challenges in maintaining party unity and voter support.
Coalition Success Stories in Asia
The coalition government formed in India in 2004, known as the United Progressive Alliance (UPA), successfully implemented significant economic reforms that boosted GDP growth and poverty reduction. In Japan, the Liberal Democratic Party's coalition with the Komeito Party since 1999 has ensured political stability and sustained infrastructure development. Malaysia's Barisan Nasional coalition, despite challenges, maintained decades-long governance promoting ethnic harmony and economic modernization.
Coalition Failures and Their Impact
Coalition failures often stem from ideological clashes and conflicting policy priorities between participating parties, leading to governmental instability and policy paralysis. The collapse of the German grand coalition in 2021 highlighted how divergent views on climate policy and immigration can dissolve alliances, triggering early elections and eroding public trust. Such breakdowns disrupt legislative agendas, hinder effective governance, and can shift political power toward opposition parties.
The Future of Coalition Governments in Modern Politics
Coalition governments, such as Germany's CDU-SPD alliance, demonstrate the increasing need for collaboration among diverse political parties to achieve stable governance in fragmented electorates. These coalitions facilitate policy compromises that reflect a broader spectrum of voter interests, enhancing democratic legitimacy and government effectiveness. With rising political polarization, future coalition governments must adapt through innovative negotiation strategies and power-sharing arrangements to maintain stability and public trust.
example of coalition in government Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com