In politics, logrolling refers to the practice where legislators exchange support for each other's bills to ensure mutual legislative success. For example, a senator might agree to back a colleague's infrastructure funding bill in exchange for support on a healthcare reform proposal. This strategic trading of votes helps secure majority approval for bills that might otherwise struggle to pass. Logrolling often occurs in committees where detailed negotiations shape the final content of legislation, enhancing the bill's chances of becoming law. Data from congressional voting records show numerous instances where related yet distinct measures receive simultaneous support due to these vote-trading agreements. The practice affects legislative outcomes by fostering coalition-building and balancing diverse interests within the political landscape.
Table of Comparison
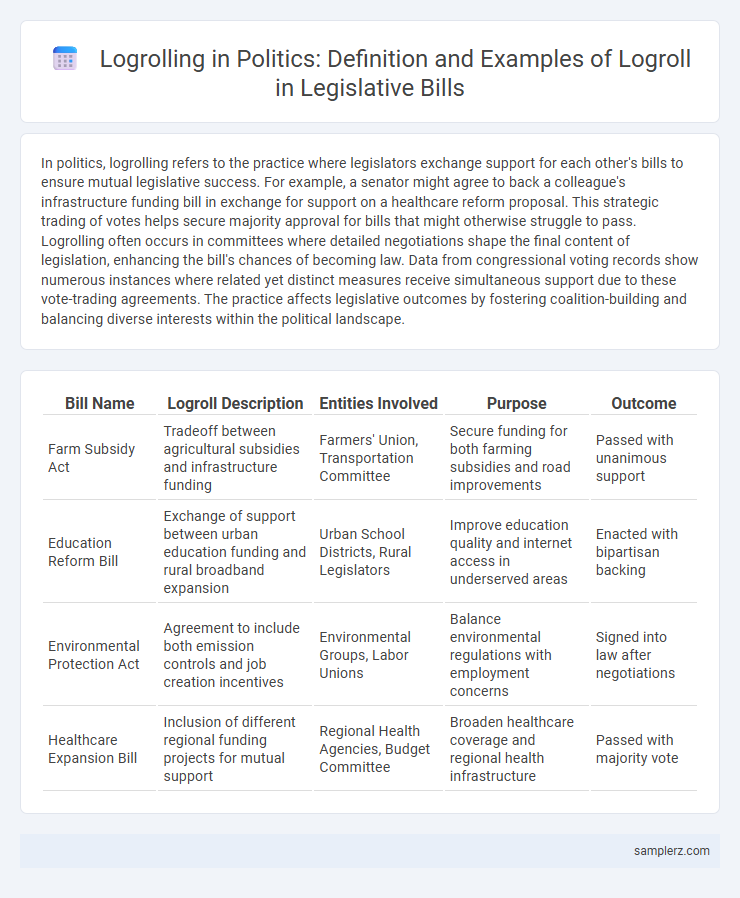
| Bill Name | Logroll Description | Entities Involved | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm Subsidy Act | Tradeoff between agricultural subsidies and infrastructure funding | Farmers' Union, Transportation Committee | Secure funding for both farming subsidies and road improvements | Passed with unanimous support |
| Education Reform Bill | Exchange of support between urban education funding and rural broadband expansion | Urban School Districts, Rural Legislators | Improve education quality and internet access in underserved areas | Enacted with bipartisan backing |
| Environmental Protection Act | Agreement to include both emission controls and job creation incentives | Environmental Groups, Labor Unions | Balance environmental regulations with employment concerns | Signed into law after negotiations |
| Healthcare Expansion Bill | Inclusion of different regional funding projects for mutual support | Regional Health Agencies, Budget Committee | Broaden healthcare coverage and regional health infrastructure | Passed with majority vote |
Understanding Logrolling: Definition and Political Context
Logrolling in politics occurs when legislators trade support for each other's proposed bills to secure mutual benefits, often resulting in the passage of measures that might not succeed independently. This practice is common in budget appropriations and local projects, where members prioritize their constituencies' interests by exchanging votes. Recognizing logrolling helps explain legislative negotiations and the complexities behind coalition-building in government decision-making.
Historical Overview of Logrolling in Legislation
Logrolling in legislation historically emerged as a strategic practice where legislators exchanged votes to ensure mutual support for their preferred bills, exemplified by the U.S. Congress during the early 19th century. The Tariff Act of 1828, also known as the "Tariff of Abominations," highlighted logrolling through reciprocal agreements between representatives from different regions protecting local industries. This practice significantly shaped legislative coalitions, influencing policy outcomes by bundling diverse interests into unified voting blocs.
Classic Examples of Logrolling in U.S. Congress
Classic examples of logrolling in the U.S. Congress include the 1980s Highway Act, where lawmakers from rural and urban districts exchanged support to secure funding for local infrastructure projects. Another notable case is the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments, which saw legislators trade votes between environmental regulation supporters and representatives protecting industrial interests. These deals illustrate how logrolling enables diverse interests to converge behind complex legislation, balancing regional priorities and federal policy goals.
Notable Logrolls in State Legislatures
In state legislatures, notable examples of logrolling include the passage of the 2019 Illinois budget, where lawmakers exchanged votes on tax hikes and infrastructure projects to secure mutual approval. Similarly, in Florida, legislators combined support for education funding with agricultural subsidies that benefited rural districts, facilitating bipartisan consensus. These strategic vote trades exemplify how logrolling enables the advancement of complex bills by aligning diverse legislative priorities.
Logrolling in Major Federal Bills: Case Studies
Logrolling in major federal bills often involves trading votes to secure passage of controversial provisions, as seen in the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, where legislators exchanged support for corporate tax cuts in return for local project funding. The Affordable Care Act also reflected logrolling, with policymakers agreeing to include specific state-level Medicaid expansions to gain votes from skeptical lawmakers. Such vote trading highlights strategic negotiation essential for enacting complex legislation amid partisan divides.
The Ethics Debate: Logrolling versus Pork Barrel
Logrolling in legislation involves legislators exchanging support for each other's bills to ensure mutual passage, often raising ethical concerns regarding transparency and accountability. Critics argue that logrolling blurs the line between strategic cooperation and unethical pork barrel spending, where projects benefit narrow interests rather than the public good. The ethics debate centers on balancing political negotiation with the potential for fostering corruption and inefficiency in the legislative process.
How Logrolling Shapes Multi-Issue Bills
Logrolling in politics involves lawmakers exchanging support for each other's proposed bills to ensure mutual passage, often combining multiple unrelated issues into a single multi-issue bill. This practice shapes legislation by bundling diverse provisions that appeal to different constituencies, increasing the overall bill's chances of approval. As a result, multi-issue bills become complex negotiations reflecting coalition-building and strategic reciprocity among legislators.
Party Strategies: Logrolling to Secure Votes
Political parties often engage in logrolling by exchanging support on different bill provisions to secure a broader coalition of votes. For instance, a bill promoting infrastructure funding may receive backing from rural representatives in exchange for their support on urban healthcare measures. This strategic vote trading helps parties overcome legislative gridlock and advance their policy agendas effectively.
Logrolling’s Role in Budget and Appropriations Bills
Logrolling plays a critical role in budget and appropriations bills by enabling legislators to secure funding for local projects in exchange for supporting others' priorities, facilitating the passage of complex multimillion-dollar budgets. This practice often results in the inclusion of earmarks and rider amendments that might not pass independently but gain approval through reciprocal agreements. Understanding logrolling helps explain how diverse interests are balanced within federal and state budget processes, impacting allocation efficiency and political negotiation outcomes.
Contemporary Examples: Recent Logrolling in Modern Politics
Recent logrolling in modern politics often involves legislators exchanging support for pet projects to secure broad approval for major bills, exemplified by the 2021 U.S. infrastructure law where members backed highway funding in exchange for investments in local transit initiatives. This practice enables the passage of comprehensive legislation by aligning diverse regional interests and legislative priorities through strategic vote trading. Such examples highlight how logrolling remains a powerful tool in navigating complex political landscapes and achieving multifaceted policy goals.
example of logroll in bill Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com