In political elections, a slate refers to a group of candidates who run together under a unified platform or party banner. Each slate typically represents a specific political party or ideology, aiming to secure multiple offices in a single election cycle. Voters often select an entire slate to ensure consistent governance aligned with their values. An example of a slate in a ballot is seen in municipal elections where candidates for mayor, city council, and school board run collectively. For instance, the Progressive Party might field a slate including a mayoral candidate, several city council candidates, and a school board nominee. This slate strategy strengthens party visibility and voter turnout by presenting a cohesive choice.
Table of Comparison
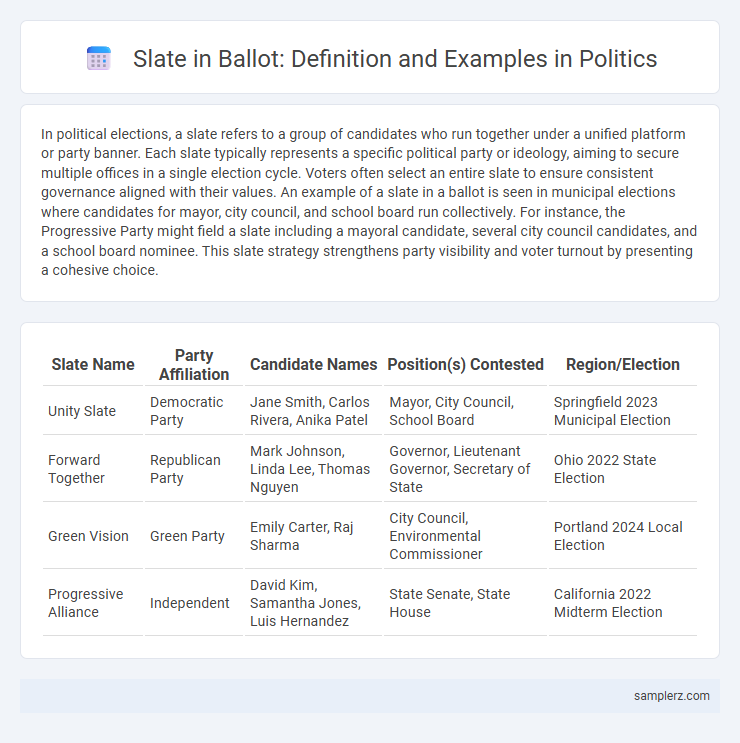
| Slate Name | Party Affiliation | Candidate Names | Position(s) Contested | Region/Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unity Slate | Democratic Party | Jane Smith, Carlos Rivera, Anika Patel | Mayor, City Council, School Board | Springfield 2023 Municipal Election |
| Forward Together | Republican Party | Mark Johnson, Linda Lee, Thomas Nguyen | Governor, Lieutenant Governor, Secretary of State | Ohio 2022 State Election |
| Green Vision | Green Party | Emily Carter, Raj Sharma | City Council, Environmental Commissioner | Portland 2024 Local Election |
| Progressive Alliance | Independent | David Kim, Samantha Jones, Luis Hernandez | State Senate, State House | California 2022 Midterm Election |
Definition and Importance of a Slate in Ballots
A slate in a ballot is a predetermined list of candidates presented by a political party or group for election, often used in local and organizational elections to streamline voter choice. This system enables voters to select a full group of aligned candidates efficiently, promoting cohesive policy agendas and party unity. Understanding the role of slates is crucial for analyzing electoral strategies and the dynamics of party influence in democratic processes.
Historical Examples of Slate Voting in Elections
Slate voting has played a pivotal role in several historical elections, such as the 1932 U.S. presidential race where Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal coalition appointed a unified slate of electors to secure victory. Similarly, in South African elections during apartheid, political parties presented slates to maintain control while marginalizing opposition voices. These examples demonstrate how slate voting strategically influences election outcomes by consolidating votes under a cohesive group of candidates aligned with specific political agendas.
How Political Parties Form Slates
Political parties form slates by strategically selecting a group of candidates who represent their platform and appeal to diverse voter demographics. This coordinated effort ensures unified campaigning and increases the chances of winning multiple seats in elections such as city councils, legislative bodies, or school boards. Parties analyze voter data and political trends to compile slates that maximize electoral success and reinforce party cohesion.
Slate Ballots in Primary vs. General Elections
Slate ballots in primary elections typically feature candidates aligned with a specific political faction or ideology within the same party, allowing voters to select a cohesive group that advances shared policy goals. In general elections, slate ballots may include candidates from different parties united by a common platform or electoral strategy, aiming to maximize coordinated voter turnout and influence broader governance outcomes. The strategic use of slate ballots in both contexts highlights their role in consolidating voter preferences and enhancing organizational power in diverse electoral systems.
Impact of Slate Voting on Election Outcomes
Slate voting significantly influences election outcomes by allowing organized groups to promote a unified set of candidates, increasing their chances of winning multiple seats simultaneously. This strategy often leads to the consolidation of power within political parties or factions, sometimes marginalizing independent candidates or minority voices. Research shows that slate voting can alter voter behavior, as supporters are more likely to cast ballots for a complete slate rather than individual candidates, thereby shaping legislative representation and policy direction.
Case Study: Slates in Local Government Elections
Slates in local government elections often consist of candidates who share similar political ideologies and campaign strategies, aiming to maximize voter turnout and influence council decisions. A notable case study is the 2018 San Francisco Board of Supervisors election, where slate campaigning increased coordination among candidates, enhancing their visibility and voter mobilization. Research indicates that slate endorsements can significantly affect election outcomes by consolidating resources and presenting a unified policy agenda to constituents.
Notable Slate Strategies Used Worldwide
Notable slate strategies used worldwide in politics often involve cohesive candidate grouping to maximize electoral success and streamline voter choices. In countries like Japan and South Korea, party slates are crafted to balance regional representation and ideological diversity, enhancing appeal across demographics. This approach also appears in U.S. municipal elections where slates promote unified policy platforms, increasing collective influence and voter recognition.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Slate Voting
Slate voting allows political parties or groups to present a unified list of candidates, ensuring cohesive policy implementation and simplifying voter choices. It can strengthen party loyalty and streamline the electoral process but may limit individual candidate evaluation and reduce diversity of representation. Critics argue that slate voting sometimes marginalizes independent candidates and diminishes voter autonomy.
Legal Regulations Governing Slate Ballots
Legal regulations governing slate ballots vary by jurisdiction, often requiring political parties or groups to submit a predefined list of candidates for election to ensure transparency and voter clarity. These regulations mandate the format, submission deadlines, and eligibility criteria for slate candidates to prevent fraud and promote fair competition. Compliance with such laws is critical for maintaining the integrity of the electoral process and upholding democratic principles.
Future Trends for Slate Usage in Politics
Political slates on ballots are evolving with digital platforms enabling more transparent and inclusive candidate grouping, enhancing voter engagement. Data analytics and AI-driven voter behavior insights are expected to streamline slate formation, targeting more personalized and strategic voter outreach. The increasing use of blockchain technology promises secure, tamper-proof electoral processes, potentially revolutionizing how political slates maintain integrity and public trust.
example of slate in ballot Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com