A caucus in an assembly refers to a meeting of members from a specific political party or faction to discuss policies, select candidates, or coordinate legislative strategy. In the United States Congress, the Congressional Black Caucus is an example where African American members convene to address issues affecting their communities and influence legislative priorities. Similarly, the Democratic and Republican caucuses organize members to unify voting on bills and shape the party agenda within the legislative body. State assemblies often utilize caucuses to consolidate party power and streamline decision-making processes. The New York State Assembly has various caucuses, such as the Women's Caucus, where female legislators collaborate on gender-related legislation and advocacy. These caucuses serve as influential entities within larger assemblies, driving policy development and enhancing the representation of specific interest groups.
Table of Comparison
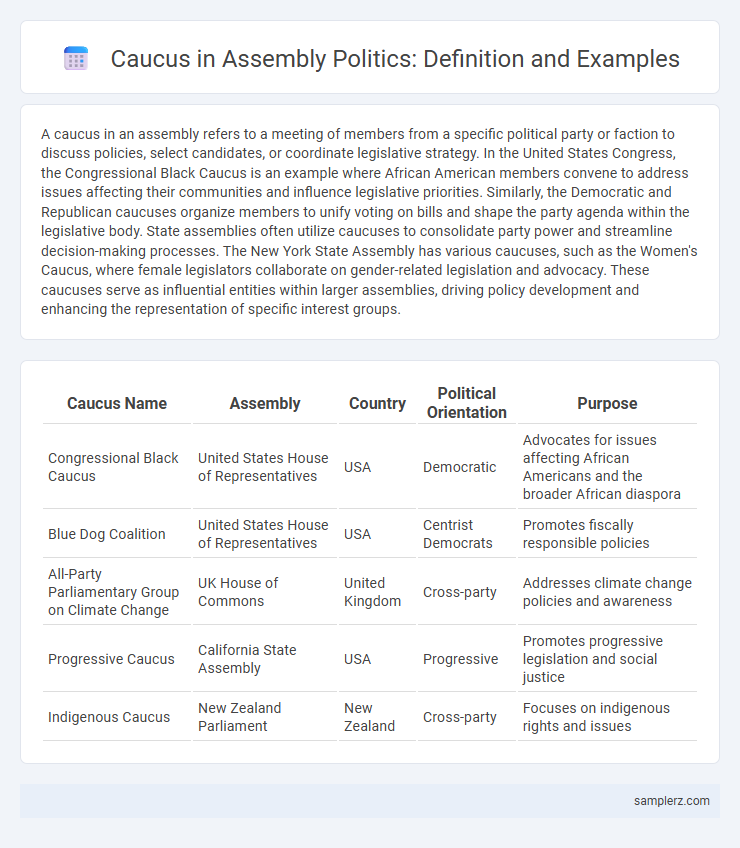
| Caucus Name | Assembly | Country | Political Orientation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congressional Black Caucus | United States House of Representatives | USA | Democratic | Advocates for issues affecting African Americans and the broader African diaspora |
| Blue Dog Coalition | United States House of Representatives | USA | Centrist Democrats | Promotes fiscally responsible policies |
| All-Party Parliamentary Group on Climate Change | UK House of Commons | United Kingdom | Cross-party | Addresses climate change policies and awareness |
| Progressive Caucus | California State Assembly | USA | Progressive | Promotes progressive legislation and social justice |
| Indigenous Caucus | New Zealand Parliament | New Zealand | Cross-party | Focuses on indigenous rights and issues |
Definition and Purpose of a Caucus in an Assembly
A caucus in an assembly is a meeting of members belonging to the same political party or faction to discuss strategy, policy positions, and legislative agendas. Its primary purpose is to coordinate voting decisions, strengthen party unity, and facilitate communication among members. Caucuses also play a crucial role in selecting leadership candidates and shaping the legislative priorities within the assembly.
Historical Examples of Caucuses in Political Assemblies
The Congressional Black Caucus, established in 1971, represents a significant historical example of a political caucus that amplifies African American voices within the U.S. Congress. The Tea Party Caucus, emerging around 2009, played a pivotal role in shaping conservative fiscal policies during the early 2010s. In the United Kingdom, the 1922 Committee functions as a powerful backbenchers' group influencing the selection of Conservative Party leaders and parliamentary strategy.
The Role of Caucuses in Legislative Decision-Making
Caucuses in legislative assemblies serve as critical platforms where members with shared interests or policy goals strategize and coordinate voting to influence legislative outcomes effectively. These groups enhance collective bargaining power, allowing them to shape agendas, prioritize bills, and negotiate amendments within committees and on the assembly floor. By consolidating expertise and aligning political objectives, caucuses play a decisive role in steering legislative decision-making and fostering policy consensus.
Notable Party Caucuses in National Parliaments
Notable party caucuses in national parliaments include the Congressional Black Caucus in the United States House of Representatives, which advocates for African American community interests. The Parliamentary Labour Party caucus in the UK represents Labour Party members, shaping internal party policy and strategy. In Canada, the Liberal Caucus in the House of Commons functions as a key decision-making body for the Liberal Party, coordinating legislative priorities.
Case Study: The Congressional Black Caucus in the U.S. House
The Congressional Black Caucus (CBC) in the U.S. House of Representatives advocates for policies addressing the interests of African American communities, including voting rights, economic equity, and criminal justice reform. Comprised of over 50 members, the CBC wields significant influence by forming strategic coalitions and advancing legislative agendas that promote social justice and civil rights. Their efforts have led to key legislative successes such as the Voting Rights Act reauthorization and initiatives targeting health disparities in Black populations.
Influence of Ideological Caucuses on Policy Formation
Ideological caucuses in legislative assemblies, such as the Progressive Caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives, significantly shape policy formation by consolidating members around shared political beliefs and strategic goals. These caucuses leverage collective bargaining power to influence committee assignments, push progressive agendas on healthcare, climate change, and social justice, and mobilize votes on key legislation. Their cohesive stance often compels broader party negotiations, steering legislative priorities to align more closely with their ideological objectives.
Caucuses and Coalition Building in Multi-Party Systems
Caucuses in multi-party assemblies serve as critical platforms where legislators with shared interests or policy goals collaborate to influence legislative agendas and negotiate power dynamics. These groups facilitate coalition building by aligning diverse party members around common issues, enhancing strategic bargaining and legislative effectiveness. Effective caucuses often determine the success of coalition governments by consolidating fragmented party positions into unified policy stances.
Challenges Faced by Minority Caucuses in Assemblies
Minority caucuses in legislative assemblies frequently encounter limited access to key committee assignments, which restricts their influence on policymaking processes. They often struggle with underrepresentation, leading to diminished voice and resources compared to majority caucuses. These challenges hinder the ability to advance legislative agendas and effectively represent their constituents' interests.
Comparative Analysis: Caucuses vs. Committees
Caucuses, such as the Congressional Black Caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives, serve as informal groups that unify legislators around shared interests or identities, contrasting with committees that have formal legislative authority and structured membership. Unlike committees, which draft, review, and amend legislation within specific policy domains, caucuses primarily influence policy through advocacy and networking, often shaping agenda setting and party positions. The effectiveness of caucuses lies in their ability to mobilize members across party lines, whereas committees function through procedural rules and hierarchical leadership to manage legislative processes.
Recent Developments: Virtual Caucuses in Modern Assemblies
Virtual caucuses have transformed political assemblies by enabling real-time collaboration among geographically dispersed legislators, leveraging platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams. Recent developments highlight increased participation rates and enhanced policy coordination, evidenced in the 2023 U.S. Congressional caucuses where virtual meetings streamlined agenda-setting processes. This digital shift improves transparency and responsiveness in legislative decision-making, reshaping traditional caucus dynamics in contemporary governance.
example of caucus in assembly Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com