The blue slip is a Senate tradition used during the judicial nomination process. It allows senators from the nominee's home state to express approval or disapproval before the Senate Judiciary Committee holds confirmation hearings. This practice influences the progression of federal judicial appointments, impacting the balance of power within the judiciary. In recent examples, a blue slip refusal has resulted in stalled nominations for federal judgeships. Senators employ the blue slip to exert significant leverage over the executive branch's judicial selections. The data shows nominees often face delays or withdrawals when home-state senators return negative or no blue slips, highlighting its critical role in Senate confirmations.
Table of Comparison
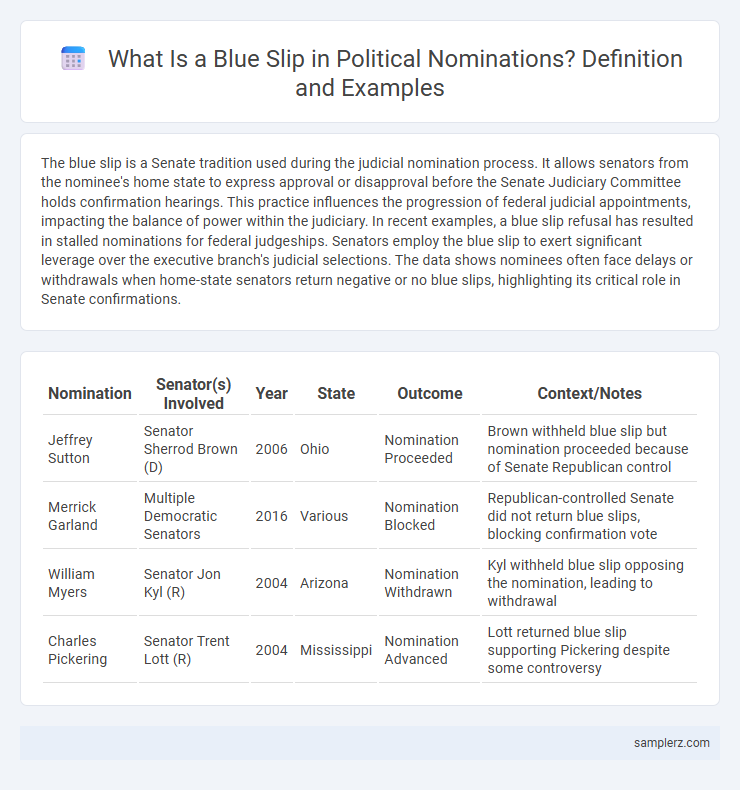
| Nomination | Senator(s) Involved | Year | State | Outcome | Context/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeffrey Sutton | Senator Sherrod Brown (D) | 2006 | Ohio | Nomination Proceeded | Brown withheld blue slip but nomination proceeded because of Senate Republican control |
| Merrick Garland | Multiple Democratic Senators | 2016 | Various | Nomination Blocked | Republican-controlled Senate did not return blue slips, blocking confirmation vote |
| William Myers | Senator Jon Kyl (R) | 2004 | Arizona | Nomination Withdrawn | Kyl withheld blue slip opposing the nomination, leading to withdrawal |
| Charles Pickering | Senator Trent Lott (R) | 2004 | Mississippi | Nomination Advanced | Lott returned blue slip supporting Pickering despite some controversy |
Understanding the Blue Slip Process in Judicial Nominations
The blue slip process serves as a Senate tradition allowing home-state senators to express approval or disapproval of a judicial nominee by returning a blue slip to the Judiciary Committee. This mechanism empowers senators to influence federal judicial appointments, often reflecting partisan or ideological considerations. While not a formal rule, the blue slip's role varies depending on committee leadership, impacting the pace and success of judicial nominations.
Historical Overview of the Blue Slip Tradition
The blue slip tradition dates back to the early 20th century as a Senate Judiciary Committee practice allowing senators to approve or oppose federal judicial nominees in their home states. Historically, this process granted significant influence to individual senators, often serving as a gatekeeping mechanism in judicial confirmations. Over time, the blue slip's application has fluctuated, reflecting shifts in Senate norms and political considerations surrounding judicial nominations.
Notable Blue Slip Examples in Senate History
Senate history reveals notable blue slip instances where senators blocked judicial nominations by withholding approval, such as Senator Strom Thurmond's opposition to Robert Bork's Supreme Court nomination in 1987. Another significant example includes Senator Chuck Grassley's use of blue slips to delay lower court nominees during the Obama administration. These cases highlight the blue slip's critical role in shaping judicial appointments and maintaining senatorial prerogative within the confirmation process.
Blue Slip Usage in Recent Nominations
Blue slip usage in recent nominations has been a strategic tool for senators to express approval or disapproval of judicial nominees from their states, significantly impacting the confirmation timeline. In the past decade, several high-profile nominations stalled due to negative or withheld blue slips, illustrating the influence of senatorial courtesy on the judicial appointment process. This practice underscores the Senate's role in balancing executive appointments with legislative oversight in shaping the federal judiciary.
Case Study: The Blue Slip and Supreme Court Appointments
The Blue Slip tradition allows U.S. Senators to approve or block judicial nominees from their home states, significantly impacting Supreme Court appointments. In the 2018 case of Justice Brett Kavanaugh's nomination, Senate Democrats used blue slips to express opposition, highlighting its role in the confirmation process. This practice underscores the political strategy involved in shaping the Supreme Court's composition and the balance of judicial power.
High-Profile Opposition Through Blue Slips
High-profile opposition through blue slips occurs when senators use this procedural tool to block or delay judicial nominations, especially for federal appellate and district court judges. This tactic is often employed to signal significant political or ideological resistance to a nominee's judicial philosophy or background. The blue slip tradition, although not a formal rule, grants individual senators substantial influence over the confirmation process in their home states, impacting the pace and success of nominations.
Blue Slip Controversies: Key Political Battles
Blue slip controversies have become a focal point in Senate Judiciary Committee battles, with senators using the tradition to block judicial nominees from their home states, intensifying partisan conflicts. Notable instances include the blockade of Merrick Garland's Supreme Court nomination in 2016, where Senate Republicans invoked procedural tactics linked to blue slip policies to delay hearings. These disputes highlight the evolving power dynamics in judicial appointments and the increasing politicization of blue slips as tools for Senate obstruction.
Blue Slip Influence on Lower Court Nominations
Blue slip influence significantly affects lower court nominations by allowing home-state senators to block or delay judicial appointments through withholding their approval. This senatorial courtesy grants substantial power to senators, shaping the composition and ideological balance of district and circuit courts. Nominees often face prolonged confirmation processes or withdrawal if blue slips are not returned, underscoring the critical role of this tradition in judicial appointments.
Partisan Dynamics in Blue Slip Decisions
Blue slips serve as a powerful tool in the U.S. Senate to influence judicial nominations, often reflecting partisan dynamics that shape confirmation processes. Senators from the nominee's home state use blue slips to express approval or opposition, with party alignment frequently determining whether a blue slip blocks or advances a nomination. This practice intensifies partisan strategies, as majority parties may choose to honor or disregard blue slips based on their legislative agenda and political objectives.
The Future of the Blue Slip in the Confirmation Process
The blue slip tradition allows senators to approve or block judicial nominees from their home state, significantly shaping the confirmation process. Its future remains uncertain as procedural changes and partisan strategies challenge the precedent, potentially reducing senatorial influence over nominations. Senate leadership's evolving stance on blue slips could reshape judicial confirmations, affecting the balance of power between the executive branch and the Senate.
example of blue slip in nomination Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com