A Quango, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organization, plays a significant role in political administration by operating independently while receiving government funding. An example of a Quango in administration is the UK's Environment Agency, which manages environmental protection and regulation across England. This entity implements government policies on water management, flood defense, and pollution control with a degree of operational autonomy. In political administration, Quangos balance governmental oversight and independent decision-making, which enhances efficiency and specialized expertise. Another example includes the Arts Council England, responsible for distributing public funds to support arts and culture, ensuring alignment with government cultural policies. These bodies contribute to public service delivery without direct political interference, optimizing governance through focused mandates.
Table of Comparison
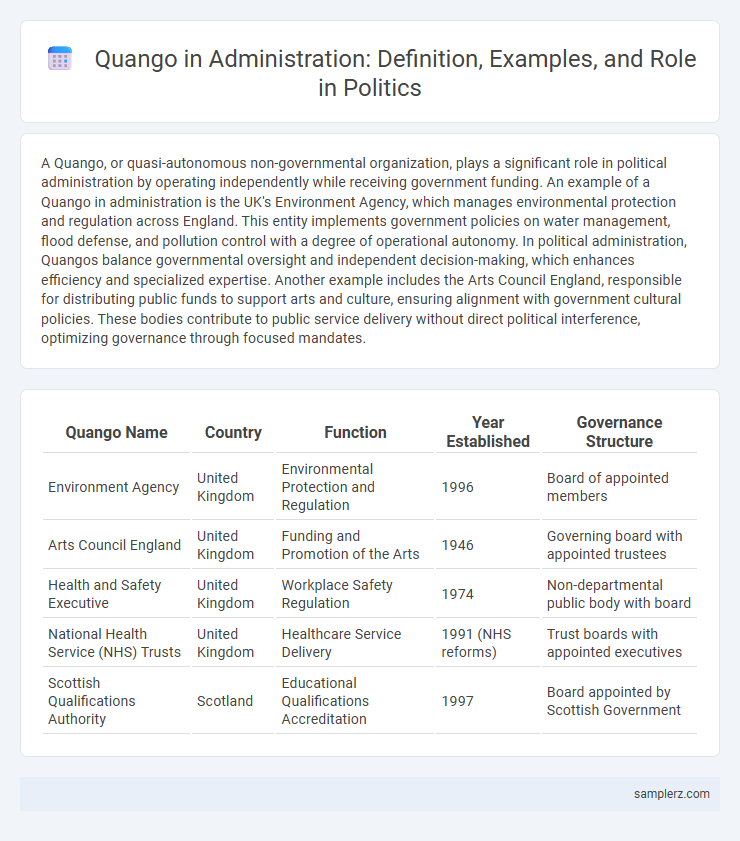
| Quango Name | Country | Function | Year Established | Governance Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environment Agency | United Kingdom | Environmental Protection and Regulation | 1996 | Board of appointed members |
| Arts Council England | United Kingdom | Funding and Promotion of the Arts | 1946 | Governing board with appointed trustees |
| Health and Safety Executive | United Kingdom | Workplace Safety Regulation | 1974 | Non-departmental public body with board |
| National Health Service (NHS) Trusts | United Kingdom | Healthcare Service Delivery | 1991 (NHS reforms) | Trust boards with appointed executives |
| Scottish Qualifications Authority | Scotland | Educational Qualifications Accreditation | 1997 | Board appointed by Scottish Government |
Defining Quangos in Modern Political Systems
Quangos, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations, function as crucial intermediaries in modern political systems, combining government oversight with independent operational roles. An example of a quango is the UK's Environment Agency, which manages environmental regulation and flood control with governmental funding yet operates at arm's length from direct political control. These entities enhance administrative efficiency by balancing public accountability with specialized expertise in policy implementation.
The Role of Quangos in Public Administration
Quangos such as the UK's Arts Council England exemplify the role of quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations in public administration by managing specific public services independently while remaining funded and overseen by the government. These bodies enhance administrative efficiency by delivering specialized expertise outside traditional ministerial departments, often focusing on cultural, health, or regulatory sectors. Their semi-autonomous status allows for flexibility and responsiveness, balancing public accountability with operational independence in policy implementation.
Notable Quango Examples in the United Kingdom
Notable Quangos in the United Kingdom include the Environment Agency, responsible for environmental protection and regulation across England, and the Arts Council England, which funds and promotes arts and culture nationwide. The Health and Safety Executive oversees workplace health and safety standards, playing a critical role in public safety. These bodies operate with a degree of governmental oversight but maintain operational independence, illustrating the diverse functions Quangos serve in UK public administration.
Quangos and Their Impact on Policy Implementation
Quangos, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations, play a crucial role in bridging government objectives and public service delivery, exemplified by entities like the UK's Environment Agency. These organizations operate with a degree of independence from direct political control, allowing for specialized expertise and flexibility in policy implementation, which can enhance efficiency and responsiveness. However, their impact often sparks debate over accountability and transparency in governance, influencing the overall effectiveness of public administration.
Quangos in Health and Education Administration
Quangos such as the National Health Service (NHS) trusts play a crucial role in managing public healthcare delivery, ensuring efficient allocation of resources and quality patient care. In education administration, bodies like Ofsted oversee school inspections and standards, directly influencing educational outcomes and policy implementation. These semi-autonomous organizations operate with government funding but maintain operational independence to enhance public service effectiveness.
Regulatory Functions of Quangos in Governance
Quangos such as the UK's Environment Agency exemplify regulatory functions by enforcing environmental legislation and overseeing compliance with pollution control standards. These semi-autonomous bodies operate independently from direct government control, ensuring impartial regulation and implementation of policies within specific sectors. Their role enhances governance by providing specialized oversight, reducing bureaucratic inefficiencies, and maintaining accountability in public administration.
Quangos and Public Sector Accountability
Quangos, or Quasi-Autonomous Non-Governmental Organizations, serve as pivotal bodies within public administration, bridging government directives and independent oversight. Entities like the UK's Arts Council exemplify Quangos, operating with delegated authority to manage public funds while maintaining a degree of operational independence that complicates direct accountability. The challenge in public sector accountability arises as Quangos balance governmental policy implementation with transparency requirements, necessitating robust monitoring mechanisms to ensure effective governance and prevent misuse of resources.
Comparing Quangos Across Different Countries
Quangos, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations, vary significantly across countries in terms of structure and function; for example, the UK's Environment Agency operates with regulatory authority over environmental issues, while Germany's Bundesagentur fur Arbeit manages employment services with closer state integration. In contrast, Canadian quangos like the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) serve as independent regulatory bodies with a strong focus on public policy enforcement. These differences highlight how governmental delegation and accountability mechanisms shape quango operations in various administrative contexts.
Debates and Criticism Surrounding Quangos
Quangos, such as the UK's Arts Council England, face ongoing debates regarding their transparency and accountability in public administration. Critics argue that quangos often operate with insufficient oversight, leading to concerns over mismanagement and politicization of resources. These debates emphasize the need for reforms to balance independent expertise with democratic accountability in governance structures.
Future Trends in Quango Administration
Quangos such as the Environment Agency exemplify semi-autonomous governmental bodies tasked with regulatory oversight and policy implementation. Future trends in quango administration emphasize increased digital transformation and data-driven decision-making to improve transparency and efficiency. Enhanced public accountability measures and greater integration with central government agencies are also anticipated to address concerns over autonomy and effectiveness.
example of Quango in administration Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com