A straw poll in a political convention is an informal vote used to gauge the preferences of attendees. For example, during the 2016 Republican National Convention, a straw poll was conducted among delegates to show early support for presidential candidates. These polls provide insight into candidate popularity but do not carry official decision-making power. Straw polls help campaigns assess momentum and adjust strategies based on delegate sentiment. The results can influence media coverage and donor confidence by revealing which candidates have strong grassroots support. Though non-binding, they remain a key aspect of political conventions for measuring preliminary opinion.
Table of Comparison
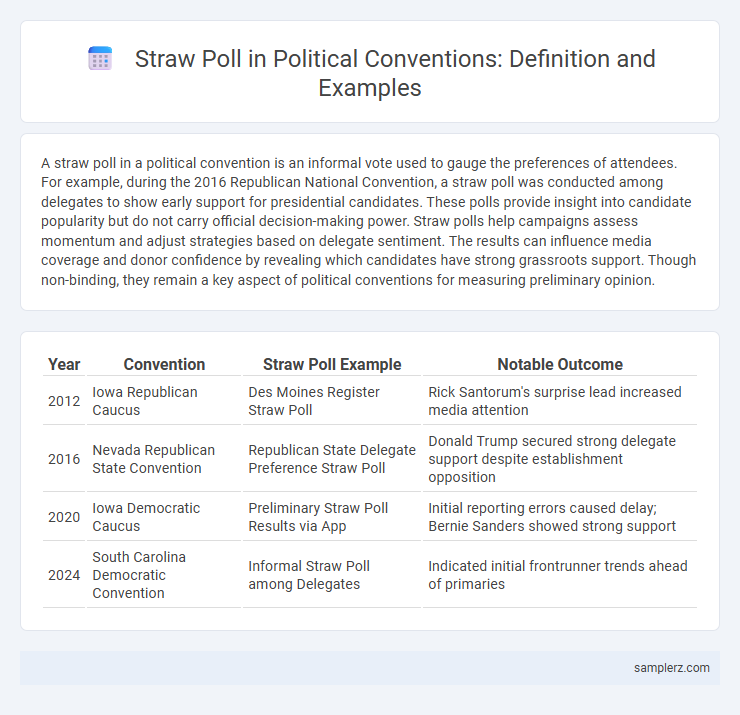
| Year | Convention | Straw Poll Example | Notable Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | Iowa Republican Caucus | Des Moines Register Straw Poll | Rick Santorum's surprise lead increased media attention |
| 2016 | Nevada Republican State Convention | Republican State Delegate Preference Straw Poll | Donald Trump secured strong delegate support despite establishment opposition |
| 2020 | Iowa Democratic Caucus | Preliminary Straw Poll Results via App | Initial reporting errors caused delay; Bernie Sanders showed strong support |
| 2024 | South Carolina Democratic Convention | Informal Straw Poll among Delegates | Indicated initial frontrunner trends ahead of primaries |
Introduction to Straw Polls in Political Conventions
Straw polls in political conventions serve as informal surveys to gauge delegate support for candidates before official voting begins. These polls provide early indicators of candidate popularity and campaign momentum among party members. Their results influence campaign strategies and media coverage during the convention process.
Historical Significance of Straw Polls
Straw polls in political conventions have historically served as early indicators of candidate viability and public sentiment, often shaping subsequent campaign strategies. The 1976 Iowa Straw Poll, for instance, propelled Jimmy Carter from obscurity to national prominence, demonstrating the poll's impact on momentum building. These informal votes provide unique insights into grassroots preferences and influence delegate decisions long before formal nominations occur.
Notable Examples of Straw Polls at National Conventions
Notable examples of straw polls at national conventions include the Iowa Straw Poll, which has historically served as a key early indicator of candidate viability in presidential races. The 2011 Iowa Straw Poll, won by Michele Bachmann, demonstrated the influence such informal gatherings can have on campaigns despite lacking official delegate weight. These polls often capture grassroots enthusiasm and can significantly impact fundraising and media coverage heading into primary seasons.
Impact of Straw Polls on Delegate Decision-Making
Straw polls at political conventions often serve as informal gauges of candidate support, influencing undecided delegates by signaling momentum and popular backing. These polls can sway delegate decision-making by providing a snapshot of grassroots enthusiasm, which may affect perceptions of electability and party unity. While non-binding, the outcomes of straw polls frequently shape media narratives and strategic endorsements that impact delegate commitments.
Real-Life Straw Poll Results: Key Case Studies
Real-life straw polls at political conventions, such as the 2011 Ames Straw Poll, effectively gauge candidate popularity by capturing grassroots support early in the election cycle. The 2016 Iowa Straw Poll highlighted Donald Trump's dominant favorability, influencing subsequent primary strategies and media narratives. These case studies demonstrate how straw poll results serve as critical indicators of campaign momentum and voter sentiment within party ranks.
Famous Upsets: Straw Polls vs. Final Outcomes
The 2016 Iowa Straw Poll showcased Ted Cruz's strong early support, yet Donald Trump ultimately secured the Republican nomination, highlighting the gap between straw poll results and final outcomes. Straw polls often capture enthusiasm but may not predict long-term voter alignment, as seen in Ron Paul's 2012 Iowa Straw Poll victory that did not translate into broad delegate support. These famous upsets emphasize the need to view straw polls as indicative snapshots rather than definitive forecasts in political conventions.
Methodology: How Straw Polls Are Conducted at Conventions
Straw polls at political conventions are conducted by gathering delegates or attendees who cast informal votes to gauge candidate support, typically using paper ballots or electronic voting systems. These polls are unbinding and designed to quickly capture preferences, with organizers ensuring anonymity to encourage honest responses. Results help campaigns assess momentum but are not official nominations, emphasizing the importance of transparent procedures and representative sampling in the methodology.
Reactions and Controversies Surrounding Straw Polls
Straw polls at political conventions often trigger intense reactions, with candidates and attendees questioning their accuracy and representativeness. These informal votes can spark controversies over potential manipulation, voter suppression, or the impact on media narratives and campaign momentum. Critics argue that straw polls sometimes distort public opinion, influencing delegate behavior disproportionately during the nomination process.
Influence of Straw Polls on Media Coverage and Public Perception
Straw polls at political conventions significantly shape media coverage by providing early indicators of candidate support, often influencing journalist narratives and headline prominence. These polls create a feedback loop wherein candidates with strong straw poll performances receive increased media attention, which can sway public perception and boost campaign momentum. As a result, straw polls serve as powerful tools in framing electoral viability before formal primary voting begins.
Lessons Learned from Straw Polls in Political History
Straw polls, such as the Ames Straw Poll in 2011, highlight the importance of early voter enthusiasm but often fail to predict primary outcomes accurately due to limited demographic representation and strategic campaigning. Historical analysis reveals that while straw polls can boost candidate visibility and fundraising, they should not be solely relied upon for forecasting election results. Political strategists use lessons from straw polls to refine voter outreach and gauge grassroots support without overestimating their predictive value.
example of straw poll in convention Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com