Recall in a political mandate refers to the process by which constituents remove an elected official from office before their term ends. This mechanism empowers voters to hold politicians accountable and ensure they adhere to their campaign promises. Recall elections vary by jurisdiction but typically require a petition with a specific number of signatures to initiate the process. The recall process directly impacts the legitimacy and stability of political mandates by allowing the electorate to challenge officials who fail to meet public expectations. Data shows that recall elections are more common in local and state governments, particularly in the United States, where mandates are strictly enforced by voter engagement. The effectiveness of recall as a political tool depends on legal frameworks and voter participation rates within the affected region.
Table of Comparison
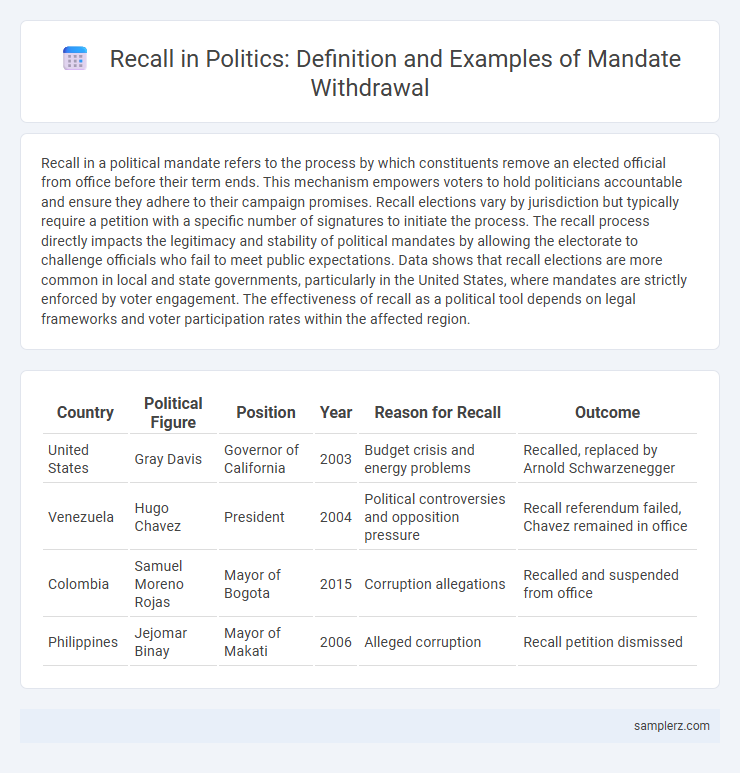
| Country | Political Figure | Position | Year | Reason for Recall | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Gray Davis | Governor of California | 2003 | Budget crisis and energy problems | Recalled, replaced by Arnold Schwarzenegger |
| Venezuela | Hugo Chavez | President | 2004 | Political controversies and opposition pressure | Recall referendum failed, Chavez remained in office |
| Colombia | Samuel Moreno Rojas | Mayor of Bogota | 2015 | Corruption allegations | Recalled and suspended from office |
| Philippines | Jejomar Binay | Mayor of Makati | 2006 | Alleged corruption | Recall petition dismissed |
Defining Recall in Political Mandate
Recall in a political mandate refers to the process allowing voters to remove elected officials from office before their term ends. This mechanism serves as a direct democratic tool to hold representatives accountable for misconduct, poor performance, or loss of public trust. States like California and Wisconsin have established legal frameworks enabling constituents to initiate recall elections through petition drives, exemplifying recall's role in maintaining political accountability.
Historical Examples of Recall in Government
The 2003 Texas gubernatorial recall election targeting Governor Rick Perry marked a significant historical example of recall in government, showcasing the use of this democratic mechanism to challenge executive leadership. Similarly, the 1921 North Dakota recall of Governor Lynn Frazier remains notable as one of the earliest successful uses of recall to remove a sitting governor due to policy disagreements during an economic crisis. These cases illustrate recall's function as a vital tool for political accountability and public influence over elected officials' mandates.
Landmark Recall Elections Worldwide
The 2003 California gubernatorial recall election, which resulted in the removal of Governor Gray Davis and the election of Arnold Schwarzenegger, stands as a landmark case in recall mandates. In 2012, Venezuela's recall referendum aimed to remove President Hugo Chavez, showcasing the political volatility surrounding recall processes in Latin America. Switzerland's frequent use of recall mechanisms at local levels highlights the country's commitment to direct democracy and political accountability.
Notable Recall Cases in Local Politics
Notable recall cases in local politics include the 2003 recall of California Governor Gray Davis, which marked a significant precedent in the use of recall elections to challenge executive mandates. Another example is the 2011 recall of Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker, centered on controversial labor reforms that mobilized widespread public protest. These cases illustrate the potent use of recall mechanisms to directly hold elected officials accountable at the local and state levels.
The Legal Process of Mandate Recall
The legal process of mandate recall involves submitting a formal petition signed by a required percentage of registered voters, typically ranging from 10% to 30%, depending on jurisdiction. Once the petition meets verification standards, a recall election is scheduled for voters to decide whether to remove the elected official before their term ends. Key examples include California's recall procedures, which mandate strict timelines and verification protocols to ensure the legitimacy of the initiative.
Recall Campaigns: Successes and Failures
Recall campaigns have demonstrated varied outcomes, such as the successful 2003 California gubernatorial recall that ousted Governor Gray Davis, contrasting with the unsuccessful 2012 recall attempt of Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker. Factors influencing these results include voter mobilization, public opinion shifts, and campaign resource allocation. Analyzing these cases reveals critical insights into the strategic dynamics and political impact of recall efforts in democratic mandates.
Voter Participation in Mandate Recall
Voter participation in mandate recall elections typically fluctuates between 30% and 60%, significantly impacting the legitimacy of the recall outcome. Higher voter turnout often correlates with increased public engagement and stronger democratic accountability, while low participation may question the representativeness of the recall decision. Factors such as public awareness, media coverage, and the political climate heavily influence voter mobilization during these recall processes.
Impact of Recall on Political Accountability
The recall of California Governor Gray Davis in 2003 demonstrated the significant impact of recall mechanisms on political accountability by allowing voters to remove officials before their term ends. This process increased responsiveness, compelling elected representatives to prioritize constituent interests and maintain integrity to avoid early dismissal. Recall elections serve as a direct democratic tool, reinforcing the balance of power and deterring corruption or poor governance.
Challenges in Implementing Recall Mechanisms
Challenges in implementing recall mechanisms often include legal ambiguities, high procedural costs, and the risk of political manipulation. Voter fatigue and low public awareness further complicate organizing successful recall campaigns. These obstacles can undermine the effectiveness of recall as a tool for democratic accountability.
Future Trends in Political Recall Practices
Emerging trends in political recall practices highlight increased use of digital platforms to facilitate voter petitions and mobilize support efficiently. Data analytics and social media monitoring are becoming essential tools for campaigns aiming to anticipate recall triggers and shape public opinion proactively. Legal reforms in several democracies are pushing for clearer regulations to balance accountability with stability in elected mandates.
example of recall in mandate Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com