Tramways are a vital component of urban mobility, providing efficient and sustainable public transportation in city centers. These electrically powered vehicles run on tracks embedded in the road, facilitating smooth and reliable transit. Cities such as Amsterdam and Melbourne showcase extensive tram networks, reducing traffic congestion and minimizing carbon emissions. The integration of tramways enhances accessibility by connecting key areas like business districts and cultural hubs while promoting eco-friendly travel. Data indicates that tram systems can transport high passenger volumes, supporting millions of daily commuters. Investment in tram infrastructure stimulates economic growth and improves urban livability by offering an alternative to private car usage.
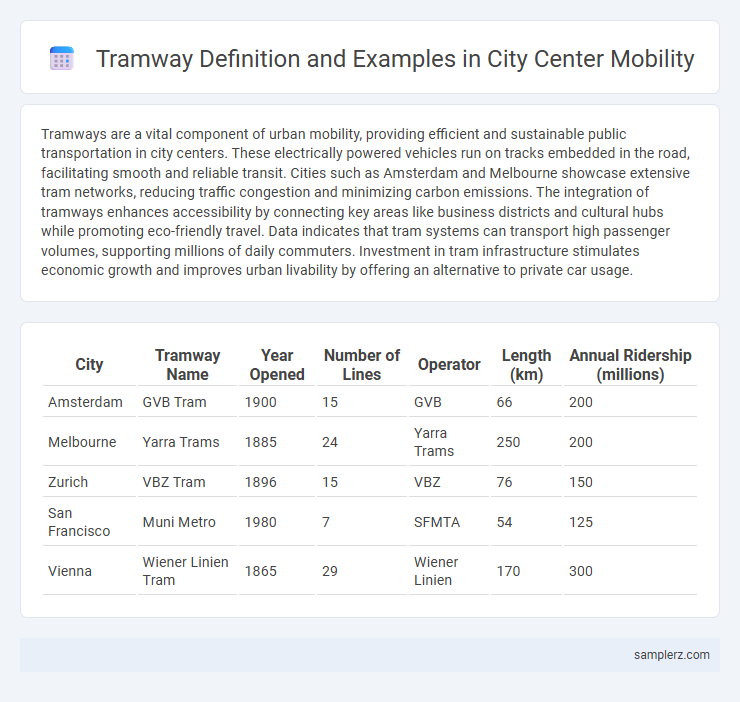
Table of Comparison
| City | Tramway Name | Year Opened | Number of Lines | Operator | Length (km) | Annual Ridership (millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amsterdam | GVB Tram | 1900 | 15 | GVB | 66 | 200 |
| Melbourne | Yarra Trams | 1885 | 24 | Yarra Trams | 250 | 200 |
| Zurich | VBZ Tram | 1896 | 15 | VBZ | 76 | 150 |
| San Francisco | Muni Metro | 1980 | 7 | SFMTA | 54 | 125 |
| Vienna | Wiener Linien Tram | 1865 | 29 | Wiener Linien | 170 | 300 |
Introduction to Tramway Systems in Urban Centers
Tramway systems in urban centers provide efficient, environmentally friendly transportation by reducing traffic congestion and lowering carbon emissions. Cities like Amsterdam and Melbourne showcase well-integrated tram networks that enhance accessibility and connect key commercial and residential areas. Modern tramways incorporate advanced technology such as energy-efficient vehicles and real-time passenger information systems to improve urban mobility and sustainability.
Historical Evolution of City Center Tramways
City center tramways trace their origins to the late 19th century, evolving from horse-drawn carriages to electrified systems by the early 20th century, significantly shaping urban mobility. The transition to electric tramways catalyzed economic growth and enhanced public transit efficiency in metropolitan areas such as San Francisco, Prague, and Melbourne. Modern tram systems integrate advanced technologies like GPS and real-time tracking to optimize routes and reduce congestion in historic downtown districts.
Key Features of Modern Tramways in Downtown Areas
Modern tramways in downtown areas feature energy-efficient electric propulsion systems that reduce urban air pollution and noise levels. Their compact design allows seamless integration with existing city infrastructure, supporting high passenger capacity and frequent service intervals to alleviate traffic congestion. Advanced signaling technologies enhance safety and operational reliability, while low-floor platforms ensure accessibility for all users.
Iconic Tramway Networks: Global City Center Examples
Iconic tramway networks in city centers like Melbourne, San Francisco, and Prague demonstrate efficient urban mobility by combining historic charm with modern transit technologies. Melbourne's extensive network spans over 250 kilometers, operating iconic W-class trams that serve as both transportation and cultural symbols. Prague's tram system, with over 140 kilometers of tracks, integrates seamlessly into its historic urban landscape, providing high-frequency service that reduces downtown congestion.
Benefits of Tramways for Urban Mobility
Tramways in city centers enhance urban mobility by providing efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly public transportation that reduces traffic congestion and lowers carbon emissions. Their high passenger capacity and frequent service improve accessibility, encouraging a shift from private car use to sustainable transit. Integrating tram networks with other transport modes fosters seamless connectivity, boosting economic activity and urban development.
Integrating Tramways with Other Public Transport Modes
Integrating tramways with buses, metros, and bike-sharing systems enhances urban mobility by creating seamless multi-modal transit networks in city centers. Real-time data sharing and unified ticketing systems improve passenger convenience and reduce transfer times, boosting overall public transport efficiency. Cities like Amsterdam and Strasbourg demonstrate successful integration through dedicated tram-bus interchange hubs and synchronized schedules.
Case Study: Successful Tramway Implementation in City Centers
The Montpellier tramway in France exemplifies successful urban mobility transformation, reducing car traffic by 20% and boosting public transit ridership by 35%. Its integration with pedestrian zones and bike-sharing systems enhances accessibility and lowers carbon emissions by approximately 15,000 tons annually. This case highlights the effectiveness of seamless multi-modal connectivity and dedicated tram lanes in revitalizing city centers.
Environmental Impact of Tramways in Dense Urban Areas
Tramways in dense urban areas significantly reduce air pollution by lowering reliance on fossil-fuel vehicles, cutting greenhouse gas emissions by up to 40% compared to buses. Their electric power enables near-zero local emissions, improving air quality and public health in city centers. Efficient energy use and reduced noise pollution further enhance urban sustainability and quality of life.
Challenges in Developing City Center Tramway Lines
Developing tramway lines in city centers faces challenges such as limited space for tracks and stations, disruption to existing traffic systems, and high construction costs due to complex underground utilities. Balancing the need for modern infrastructure with preserving historical sites requires meticulous planning and stakeholder engagement. Ensuring accessibility and minimizing environmental impact remain critical factors in sustainable tramway development.
Future Trends in City Center Tramway Mobility
City center tramway mobility is evolving with the integration of smart technologies and sustainable energy sources, such as electric and hydrogen-powered trams, reducing urban carbon footprints. Advanced traffic management systems utilize real-time data and AI algorithms to optimize tram schedules and enhance passenger flow, promoting efficient and reliable public transportation. Urban planners are increasingly prioritizing multimodal connectivity by linking tram networks with bike-sharing and pedestrian pathways, encouraging seamless and eco-friendly mobility solutions for future cities.
example of tramway in city center Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com