The draisine is an early form of railway vehicle designed for track inspection and maintenance. Originating in the early 19th century, it was typically a lightweight, human-powered or horse-drawn vehicle running on railway tracks. The invention of the draisine marked a significant advancement in railway history, especially for its role in enabling efficient track monitoring and repairs during the expansion of rail networks. In railway history, the draisine is recognized for improving operational safety and maintenance practices. This vehicle allowed workers to traverse tracks quickly, detecting defects and performing repairs without disrupting regular train schedules. The draisine's use laid the foundation for modern railway maintenance equipment and methods, contributing to the development of safer and more reliable rail transport systems worldwide.
Table of Comparison
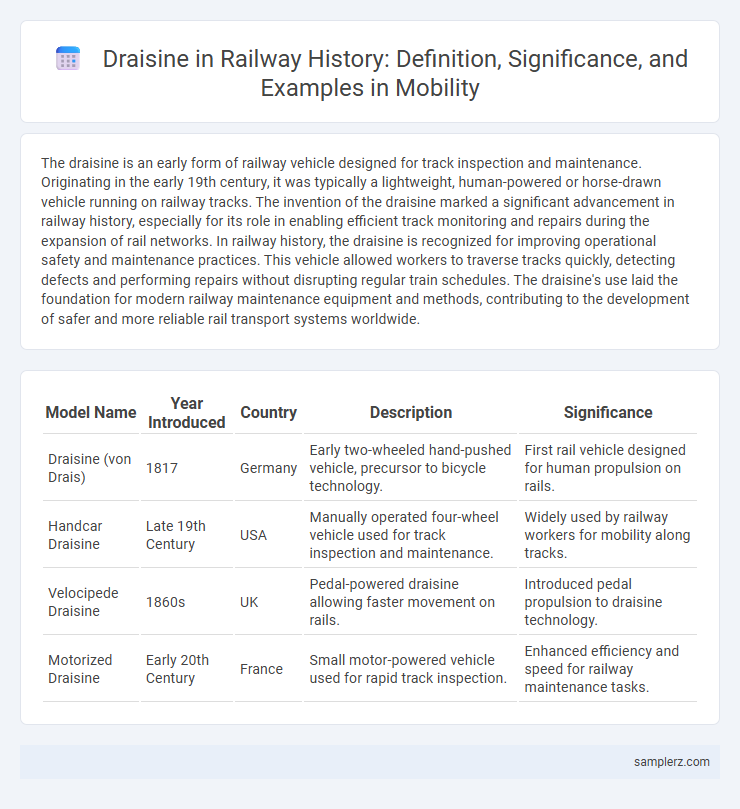
| Model Name | Year Introduced | Country | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Draisine (von Drais) | 1817 | Germany | Early two-wheeled hand-pushed vehicle, precursor to bicycle technology. | First rail vehicle designed for human propulsion on rails. |
| Handcar Draisine | Late 19th Century | USA | Manually operated four-wheel vehicle used for track inspection and maintenance. | Widely used by railway workers for mobility along tracks. |
| Velocipede Draisine | 1860s | UK | Pedal-powered draisine allowing faster movement on rails. | Introduced pedal propulsion to draisine technology. |
| Motorized Draisine | Early 20th Century | France | Small motor-powered vehicle used for rapid track inspection. | Enhanced efficiency and speed for railway maintenance tasks. |
Early Innovations: The Birth of the Draisine
The draisine, invented by Karl Drais in 1817, marked a pivotal innovation in railway history as the first human-powered rail vehicle, laying the foundation for modern mobility. This early invention featured a wooden frame with two wheels and was propelled by the rider's feet pushing against the ground, representing a significant advancement in efficient land transport before the steam locomotive era. The draisine's design influenced subsequent developments in rail transport technology, demonstrating the potential for mechanized mobility on tracks.
Mechanism and Design Features of Historical Draisines
Historical draisines in railway history featured a simple yet effective mechanism consisting of a manually operated lever or foot-pumping system that propelled the vehicle along tracks, enabling efficient inspection and maintenance of rail lines. The lightweight wooden or metal frame combined with flanged wheels ensured smooth movement on narrow gauge rails while maintaining stability and ease of use. Early draisine designs often included minimal suspension and basic seating, prioritizing functionality over comfort in railway mobility solutions.
Baron Karl Drais and the Origins of Rail Draisines
Baron Karl Drais invented the earliest form of draisine in 1817, marking a significant development in the history of railway mobility. His invention, originally called the "laufmaschine," was a precursor to rail draisines used for track inspection and maintenance. This lightweight, human-powered vehicle laid the groundwork for later mechanized rail vehicles designed to enhance railway efficiency and safety.
Draisines in 19th Century European Railways
Draisines, early human-powered railway vehicles, played a crucial role in 19th-century European railway history by enabling efficient track inspection and maintenance. These lightweight, pedal-powered carts allowed railway workers to travel quickly along tracks, improving the speed and safety of railway operations. Their use laid foundational practices for modern railway maintenance and mobility logistics during the industrial expansion of European rail networks.
The Draisine’s Role in Track Inspection and Maintenance
The draisine revolutionized railway track inspection and maintenance by allowing workers to quickly traverse rails for efficient monitoring of track conditions, detecting defects such as cracks or misalignments early. Its lightweight design and manual propulsion enabled access to remote or difficult sections of track, significantly improving the speed and accuracy of routine inspections. This innovation ultimately contributed to enhanced railway safety and reduced downtime caused by track failures.
Evolution from Draisine to Modern Rail Trolley
The draisine, invented by Karl Drais in 1817, marked the inception of human-powered rail vehicles, enabling effortless movement along railway tracks for maintenance and inspection purposes. Evolving from this early model, modern rail trolleys now incorporate motorized systems, lightweight materials like aluminum, and ergonomic designs to enhance efficiency and operator comfort. These advancements have transformed draisines from simple mechanical devices into sophisticated tools essential for railway infrastructure maintenance and rapid personnel transport.
Notable Historical Draisine Models and Uses
Notable historical draisine models include the early 19th-century steam-powered vehicles such as Richard Trevithick's 1803 steam locomotive prototype, which laid foundational engineering principles for railway mobility. The German Draisines, utilized extensively in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, featured pedal-powered inspection and maintenance vehicles crucial for track surveillance and rapid-response repairs. These draisines exemplify early innovations in railway history, showcasing the evolution from manual propulsion to mechanized mobility solutions on rail infrastructure.
The Spread of Draisines Beyond Europe
The draisine, an early human-powered rail vehicle invented by Baron Karl Drais in 1817, revolutionized railway transport and spread rapidly beyond Europe to North America and Asia in the 19th century. In the United States, draisines were adapted for track inspection and maintenance, facilitating the expansion of railroads across vast territories. Asian countries integrated draisines into local transport systems, highlighting their importance in the global development of railway mobility.
Draisines in Wartime Railway Operations
Draisines played a crucial role in wartime railway operations by enabling rapid reconnaissance and transportation of personnel along front-line tracks. These lightweight, hand-powered or motorized vehicles allowed military units to inspect damaged rails, deliver messages, and maintain supply lines under combat conditions. Their agility and speed significantly enhanced operational mobility and communication efficiency during conflicts.
Legacy and Preservation of Historical Draisines
Historical draisines, early hand-powered railway vehicles, hold significant legacy as precursors to modern rail maintenance equipment. Preservation efforts by railway museums and heritage railways ensure these draisines remain operational or on display, highlighting their role in the evolution of railway mobility. Restored draisines serve educational purposes, illustrating 19th-century innovation and the development of rail infrastructure.
example of draisine in railway history Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com