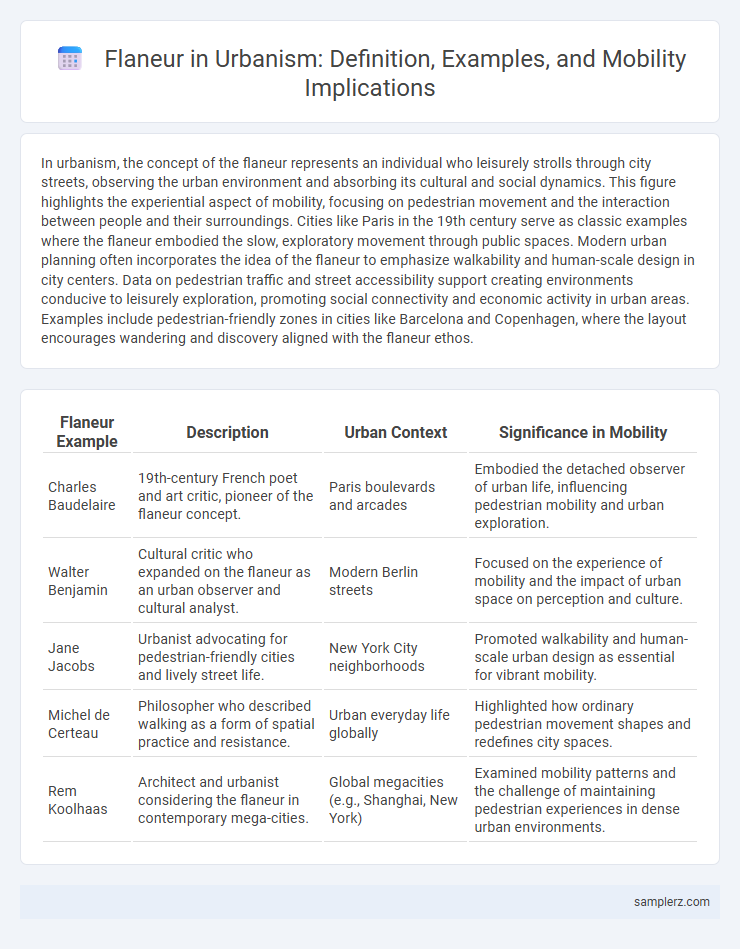
In urbanism, the concept of the flaneur represents an individual who leisurely strolls through city streets, observing the urban environment and absorbing its cultural and social dynamics. This figure highlights the experiential aspect of mobility, focusing on pedestrian movement and the interaction between people and their surroundings. Cities like Paris in the 19th century serve as classic examples where the flaneur embodied the slow, exploratory movement through public spaces. Modern urban planning often incorporates the idea of the flaneur to emphasize walkability and human-scale design in city centers. Data on pedestrian traffic and street accessibility support creating environments conducive to leisurely exploration, promoting social connectivity and economic activity in urban areas. Examples include pedestrian-friendly zones in cities like Barcelona and Copenhagen, where the layout encourages wandering and discovery aligned with the flaneur ethos.
Table of Comparison
| Flaneur Example | Description | Urban Context | Significance in Mobility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charles Baudelaire | 19th-century French poet and art critic, pioneer of the flaneur concept. | Paris boulevards and arcades | Embodied the detached observer of urban life, influencing pedestrian mobility and urban exploration. |
| Walter Benjamin | Cultural critic who expanded on the flaneur as an urban observer and cultural analyst. | Modern Berlin streets | Focused on the experience of mobility and the impact of urban space on perception and culture. |
| Jane Jacobs | Urbanist advocating for pedestrian-friendly cities and lively street life. | New York City neighborhoods | Promoted walkability and human-scale urban design as essential for vibrant mobility. |
| Michel de Certeau | Philosopher who described walking as a form of spatial practice and resistance. | Urban everyday life globally | Highlighted how ordinary pedestrian movement shapes and redefines city spaces. |
| Rem Koolhaas | Architect and urbanist considering the flaneur in contemporary mega-cities. | Global megacities (e.g., Shanghai, New York) | Examined mobility patterns and the challenge of maintaining pedestrian experiences in dense urban environments. |
Defining the Flâneur in Urban Mobility
The flaneur, originating from 19th-century Parisian urban culture, embodies a leisurely urban explorer who moves through city streets with no fixed destination, observing and experiencing the urban environment in a deeply sensory and reflective manner. In urban mobility studies, the flaneur represents a mode of mobility characterized by slow, meandering movement, emphasizing the experiential and social dimensions of the city over efficiency or speed. This concept highlights the importance of walkability, public spaces, and human-scale design in creating environments that encourage exploration, spontaneity, and meaningful engagement with the urban fabric.
Historical Roots of the Flâneur in City Life
The flaneur, a key figure in urbanism, emerged in 19th-century Paris as an observer and wanderer of city streets, embodying the experience of modern urban life. Rooted in the advent of arcades and boulevards, the flaneur's practice of leisurely strolling allowed for an intimate engagement with the evolving urban landscape. This historical archetype highlights the intersection of mobility, social observation, and the spatial dynamics of metropolitan environments.
The Flâneur and Pedestrian Exploration
The flaneur embodies the essence of pedestrian exploration, wandering urban streets with keen observation and unhurried pace. This mode of mobility highlights the dynamic relationship between individuals and city spaces, emphasizing sensory engagement and spontaneous discovery. Urban planners leverage the concept to design walkable environments that foster social interaction, cultural experiences, and enhanced spatial awareness.
Flâneur Perspectives on Urban Public Spaces
The flaneur embodies a unique perspective on urban public spaces by leisurely observing the rhythms and interactions within city life, emphasizing the experiential and sensory dimensions of mobility. This mode of pedestrian engagement reveals how urban design influences social encounters, spatial awareness, and the spontaneous discovery of cultural narratives in metropolitan settings. Understanding flaneur perspectives informs the creation of walkable, inclusive, and dynamically engaging environments that enhance public space vitality and urban connectivity.
Observing City Dynamics Through the Flâneur Lens
The flaneur exemplifies urban mobility by embodying the act of leisurely wandering through city streets while attentively observing social interactions and architectural rhythms. This practice reveals the intricate dynamics of urban life, such as pedestrian flows, cultural expressions, and spatial uses, providing valuable insights for urban planners and sociologists. Studying the flaneur's perspective enhances understanding of how mobility shapes and is shaped by the evolving urban environment.
Flânerie and the Evolution of Urban Transportation
Flanerie, the art of leisurely urban wandering, reflects the transformation of city spaces influenced by evolving transportation modes such as trams, subways, and bicycles. This practice highlights how mobility innovations reshape pedestrian experiences, enabling new patterns of exploration and social interaction within metropolitan environments. The integration of diverse transit systems fosters dynamic flaneur pathways, promoting a deeper connection between individuals and the urban fabric.
Gender and Inclusivity in the Flâneur Experience
The concept of the flaneur in urbanism traditionally centers on a male figure navigating the city with detached observation, often overlooking diverse gender experiences. Contemporary urban studies emphasize inclusive flanerie by recognizing women and non-binary individuals who engage with public spaces differently due to safety concerns and social dynamics. Inclusive urban design promotes accessible, safe environments that enable all genders to experience the city's textures freely and equitably.
The Flâneur's Role in Urban Placemaking
The flaneur navigates urban spaces as an observant wanderer, influencing urban placemaking by uncovering the nuanced human experiences within the city. This role highlights the importance of pedestrian movement and sensory engagement in shaping vibrant, walkable environments that foster community interaction. Urban planners integrate flaneur-inspired insights to design public spaces promoting social connectivity and cultural expression.
Flâneur-Inspired Urban Design Examples
Flaneur-inspired urban design prioritizes walkability and sensory engagement, with projects like Paris' Promenade Plantee showcasing elevated green pathways that encourage leisurely strolls and urban exploration. In Melbourne, the laneway revitalization fosters intimate pedestrian experiences through art, cafes, and diverse micro-urban environments modeled on the flaneur's appreciation for spontaneous discovery. These designs emphasize human-scale movement and visual connectivity, aligning with concepts of slow mobility and immersive city strolling characteristic of flaneur culture.
Digital Flâneur: Urban Strolling in the Modern Era
The Digital Flaneur navigates urban landscapes through augmented reality apps and real-time data, transforming traditional strolling into an immersive experience. Equipped with smartphones and wearable technology, they engage with the city's digital layers, uncovering hidden histories and social narratives embedded within urban infrastructures. This fusion of physical movement and digital interaction redefines modern urban exploration, blending technology with the timeless practice of wandering.
example of flâneur in urbanism Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com