A gondola in aerial lift systems refers to an enclosed cabin suspended from a continuously moving cable, designed to transport passengers efficiently across varied terrains. These gondolas typically accommodate 4 to 15 people per cabin, providing protection from weather while offering scenic views. Key data points include cable speed, cabin capacity, and system length, which influence the overall transport capacity and passenger flow rates. Modern aerial lift gondolas incorporate advanced manufacturing materials and engineering designs to optimize safety and performance. Entities such as Doppelmayr and Leitner-Poma are leading manufacturers specializing in these systems globally. Data on operational metrics, including average speed reaching 6 meters per second and typical route lengths extending several kilometers, highlight their utility in ski resorts, urban transit, and tourist locations.
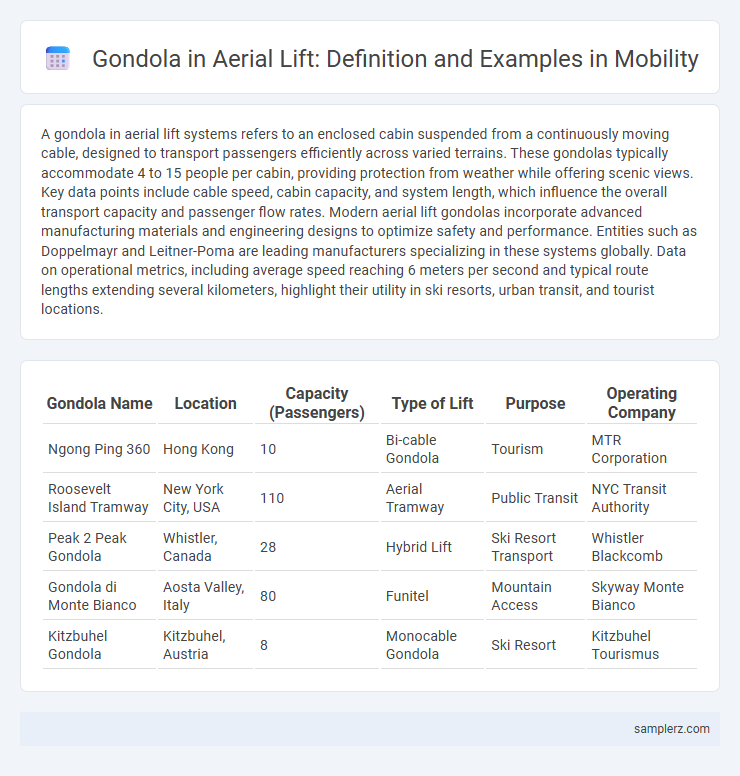
Table of Comparison
| Gondola Name | Location | Capacity (Passengers) | Type of Lift | Purpose | Operating Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ngong Ping 360 | Hong Kong | 10 | Bi-cable Gondola | Tourism | MTR Corporation |
| Roosevelt Island Tramway | New York City, USA | 110 | Aerial Tramway | Public Transit | NYC Transit Authority |
| Peak 2 Peak Gondola | Whistler, Canada | 28 | Hybrid Lift | Ski Resort Transport | Whistler Blackcomb |
| Gondola di Monte Bianco | Aosta Valley, Italy | 80 | Funitel | Mountain Access | Skyway Monte Bianco |
| Kitzbuhel Gondola | Kitzbuhel, Austria | 8 | Monocable Gondola | Ski Resort | Kitzbuhel Tourismus |
Introduction to Gondola Aerial Lifts
Gondola aerial lifts are a type of cable transport system commonly used in mountainous regions and urban areas for efficient passenger mobility. These lifts consist of enclosed cabins suspended from a continuously moving cable, providing a safe and weather-resistant mode of transportation. Key examples include ski resort gondolas and urban aerial transit systems that enhance accessibility and reduce traffic congestion.
History and Evolution of Gondola Systems
The history of gondola systems dates back to the early 20th century, with the first successful installation in 1908 in the Italian Alps, revolutionizing mountain transportation. Over the decades, technological advancements transformed gondolas from basic cable cars to high-speed, detachable systems capable of carrying dozens of passengers with enhanced safety and efficiency. Modern gondola lifts integrate aerodynamic cabins, computerized control systems, and energy-efficient motors, making them vital for urban mobility and ski resort accessibility worldwide.
Key Features of Gondola Lifts
Gondola lifts feature enclosed cabins suspended from continuously moving steel cables, providing efficient and weather-protected transportation over varied terrains. Their key components include aerodynamic cabins for passenger comfort, automated boarding systems, and advanced grip technology ensuring smooth cable attachment and detachment. These lifts excel in high-capacity transit with minimal environmental impact, commonly used in ski resorts, urban transit, and tourist destinations.
Popular Urban Gondola Examples Worldwide
Popular urban gondolas such as the Roosevelt Island Tramway in New York City, Medellin Metrocable in Colombia, and Portland Aerial Tram in Oregon showcase innovative aerial lift systems enhancing mobility in challenging terrains. These gondolas integrate seamlessly into public transit networks, offering efficient, eco-friendly solutions that reduce traffic congestion and provide stunning city views. Urban gondolas exemplify modern transportation advancements delivering accessible and reliable alternatives in densely populated areas worldwide.
Notable Mountain Gondola Installations
Notable mountain gondola installations include the Peak 2 Peak Gondola in Whistler Blackcomb, Canada, spanning 4.4 kilometers and holding the record for the longest free span between ropeway towers. The Aiguille du Midi cable car in the French Alps transports up to 1,000 passengers per hour to 3,842 meters, providing access to Mont Blanc's high altitude terrain. Val Thorens' Saint-Martin 3S Gondola combines speed and capacity, moving skiers efficiently across the Trois Vallees, one of the world's largest ski areas.
Technological Innovations in Gondola Aerial Lifts
Technological innovations in gondola aerial lifts include advanced grip systems that enhance safety and efficiency while allowing smooth boarding and disembarking. Modern gondolas feature energy-efficient electric motors and aerodynamic cabin designs that reduce wind resistance and noise. Integration of IoT sensors enables real-time monitoring of mechanical components, ensuring predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime in urban mobility solutions.
Environmental Benefits of Gondola Transportation
Gondola transportation significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing electric power instead of fossil fuels, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional vehicles. This aerial lift system minimizes land disruption and habitat fragmentation since it operates above ground, preserving natural landscapes and biodiversity. Energy-efficient gondolas also lower noise pollution, contributing to cleaner urban and rural environments.
Gondolas as a Solution for Urban Mobility
Gondolas in aerial lift systems offer an efficient and sustainable solution for urban mobility by providing continuous, elevated transit that bypasses congested roads. These cable-propelled vehicles minimize traffic delays, reduce carbon emissions, and connect hard-to-reach areas like hills or riverside neighborhoods. Cities such as Medellin and La Paz successfully utilize gondola networks to integrate underserved communities into the urban fabric while enhancing overall transit accessibility.
Safety and Accessibility in Gondola Systems
Gondola systems in aerial lifts prioritize safety through advanced restraint mechanisms, emergency evacuation protocols, and real-time monitoring technologies that ensure passenger protection throughout the ride. Accessibility features such as low-floor cabins, wide doors, and wheelchair-compatible designs facilitate easy boarding for individuals with mobility challenges. These combined safety and accessibility measures make gondola transportation a reliable and inclusive option for urban mobility and recreational activities.
Future Trends in Gondola Aerial Lift Development
Future trends in gondola aerial lift development emphasize enhanced energy efficiency through regenerative braking systems and integration with smart grid technology. Advances in autonomous operation and real-time monitoring improve safety and optimize passenger flow in urban mobility networks. Lightweight composite materials and aerodynamic cabin designs contribute to reduced operational costs and increased environmental sustainability in modern aerial lift systems.
example of gondola in aerial lift Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com