A funicular is a type of cable railway system designed to move passengers up and down steep hillsides efficiently. Typically consisting of two counterbalanced cars connected by a cable, funiculars operate on tracks laid on inclined slopes, providing safe and reliable transportation in challenging terrains. One well-known example is the Peak Tram in Hong Kong, which ascends Victoria Peak and serves both commuters and tourists. Funiculars are strategically utilized in urban areas with significant elevation changes, where traditional transport systems face limitations. The hillside location demands robust engineering and durable cable mechanisms to ensure stability and passenger safety. These systems contribute to reducing traffic congestion and promoting sustainable mobility in hilly regions by offering an energy-efficient alternative to road vehicles.
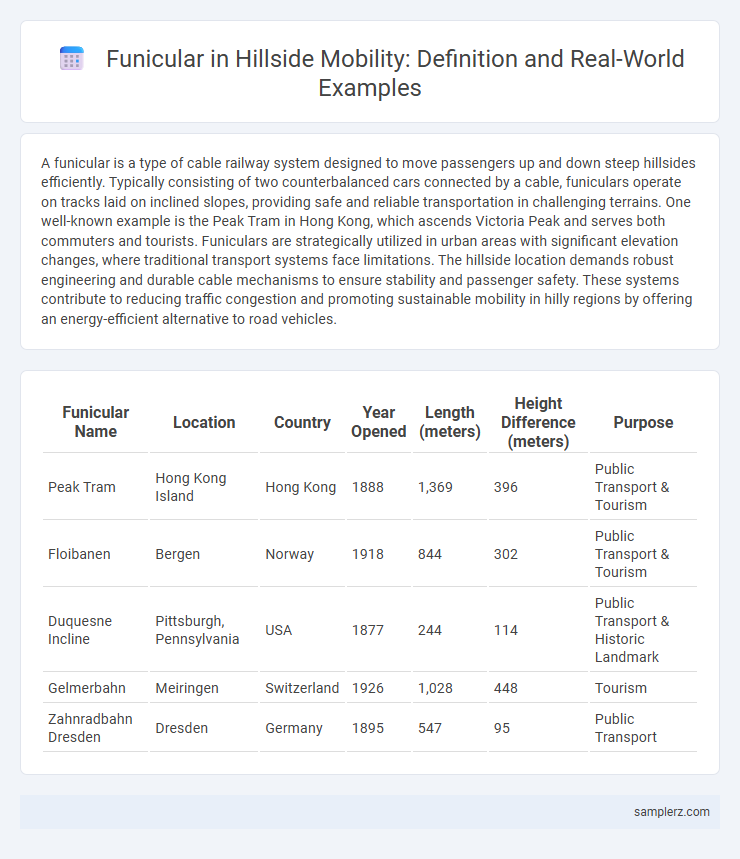
Table of Comparison
| Funicular Name | Location | Country | Year Opened | Length (meters) | Height Difference (meters) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Tram | Hong Kong Island | Hong Kong | 1888 | 1,369 | 396 | Public Transport & Tourism |
| Floibanen | Bergen | Norway | 1918 | 844 | 302 | Public Transport & Tourism |
| Duquesne Incline | Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania | USA | 1877 | 244 | 114 | Public Transport & Historic Landmark |
| Gelmerbahn | Meiringen | Switzerland | 1926 | 1,028 | 448 | Tourism |
| Zahnradbahn Dresden | Dresden | Germany | 1895 | 547 | 95 | Public Transport |
Introduction to Funiculars: Revolutionizing Hillside Mobility
Funiculars are cable-driven railways that efficiently navigate steep slopes by using counterbalanced cars, transforming hillside transportation. These systems drastically reduce travel time on inclines while minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional roadways. Modern funiculars integrate advanced safety mechanisms and energy-efficient technologies, making them a sustainable option for urban and rural hillside mobility.
How Funiculars Work: The Science Behind Steep-Slope Transport
Funiculars operate using a system of counterbalanced cars connected by a cable, which moves over a pulley at the top of the incline, efficiently transporting passengers up and down steep hillsides. The weight of the descending car helps pull the ascending car, minimizing energy consumption and providing a stable, safe ride on slopes often exceeding 45 degrees. This engineering principle leverages gravitational force and mechanical advantage, making funiculars a sustainable and reliable mode of hillside mobility.
Iconic Funicular Examples on Hillsides Worldwide
The Peak Tram in Hong Kong stands out as a historic and iconic funicular railway, ascending steep hillsides to offer panoramic city views. Switzerland's Gelmerbahn ranks among the steepest funiculars globally, climbing alpine slopes with a gradient of up to 106%. Italy's Funicolare Centrale in Amalfi provides essential hillside mobility, combining heritage charm with practical transport across Mediterranean terrain.
Urban Integration: Funiculars in Modern Cities
Funicular systems seamlessly integrate into urban landscapes by utilizing hillside terrain to connect neighborhoods with minimal environmental disruption. These railways provide efficient, eco-friendly transit solutions that reduce road congestion in densely populated cities. Modern designs incorporate accessibility features and smart technology, enhancing connectivity while preserving the natural slope and urban aesthetics.
Historic Funiculars: Preserving Heritage on the Hillside
Historic funiculars on hillsides offer unique solutions for steep terrain mobility, combining engineering ingenuity with cultural heritage preservation. These rail systems, often over a century old, continue to provide efficient, sustainable transportation while attracting tourism and maintaining the character of hillside communities. Iconic examples like the Lyon Funicular in France and the Valparaiso Funiculars in Chile showcase the integration of heritage conservation with modern mobility needs.
Environmental Benefits of Funicular Systems
Funicular systems on hillsides significantly reduce carbon emissions by utilizing electric-powered motors instead of fossil fuels, contributing to cleaner air quality. Their design minimizes land disruption and preserves natural vegetation, promoting biodiversity and preventing soil erosion. Efficient energy use and regenerative braking technologies further enhance their environmental sustainability compared to conventional hillside transportation.
Funicular Design Innovations for Challenging Landscapes
Funicular design innovations for challenging hillside landscapes incorporate advanced cable systems and adaptive track alignments to ensure stability and safety on steep gradients. Modern funiculars feature dynamic weight balancing and automated tension control, optimizing energy efficiency and reducing wear on mechanical components. Integration of smart monitoring technologies enables real-time adjustments, allowing seamless operation despite variable terrain and weather conditions.
Enhancing Tourism: Hillside Funiculars as Attractions
Hillside funiculars enhance tourism by providing unique access to scenic viewpoints and historic sites, creating memorable travel experiences that attract visitors year-round. These rail systems offer smooth, reliable transportation on steep terrain, enabling tourists to explore natural landscapes and cultural landmarks with ease. Their architectural charm and panoramic routes often become iconic attractions that boost local economies and promote sustainable tourism development.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Funiculars for All
Funicular railways on hillsides enhance accessibility by providing a reliable and safe transportation option for people with mobility impairments, seniors, and families with strollers. These systems are designed with inclusive features such as level boarding, spacious cabins, and audio-visual aids to accommodate diverse passenger needs. Funiculars also promote eco-friendly urban mobility by connecting steep terrains that are otherwise challenging to access, supporting inclusive and sustainable transport networks.
Future Trends in Funicular Mobility on Hillsides
Future trends in funicular mobility on hillsides focus on integrating advanced automation and energy-efficient technologies to enhance safety and sustainability. Electrification combined with regenerative braking systems allows funiculars to reduce energy consumption while maintaining reliable service on steep terrains. Smart monitoring platforms leveraging IoT sensors improve maintenance schedules and real-time operational control, paving the way for smarter hillside transit solutions.
example of funicular in hillside Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com