The cyclo, a traditional pedal-propelled rickshaw, exemplifies sustainable urban mobility by combining human power with practical transportation. Its design features a front-mounted cycle mechanism that enables the driver to pedal, propelling the vehicle forward while carrying passengers or goods. This mode of transport is widely used in Southeast Asian cities like Hanoi and Phnom Penh, where narrow streets and heavy traffic make motorized vehicles less efficient. Cyclo operations rely on efficient pedal propulsion systems that maximize energy transfer from the driver to the wheels. Components such as chain drives, sprockets, and pedals are optimized for smooth motion and durability under urban conditions. Data on cyclo usage highlights its role in reducing emissions and providing affordable transport, supporting sustainable mobility goals in densely populated areas.
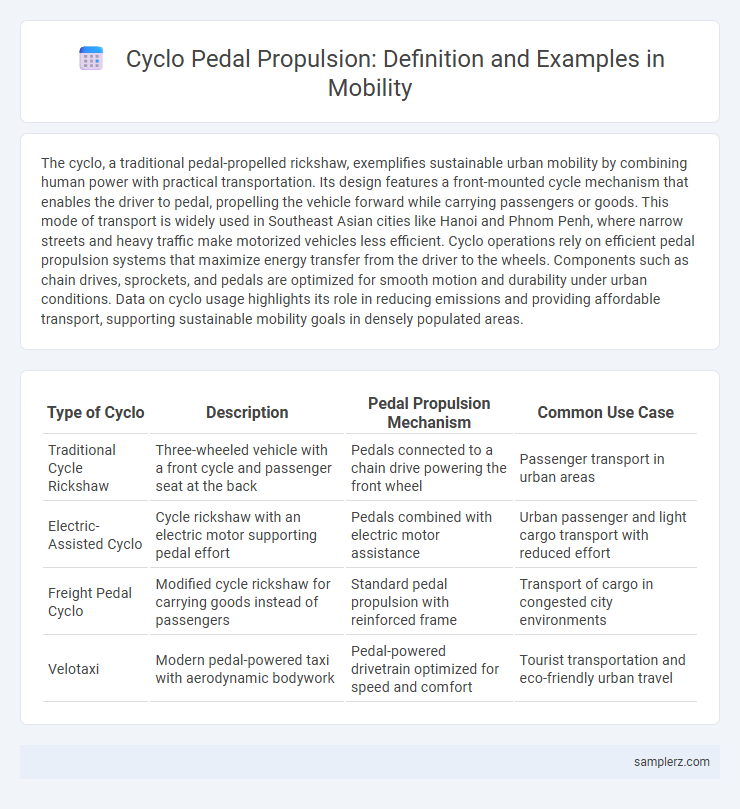
Table of Comparison
| Type of Cyclo | Description | Pedal Propulsion Mechanism | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Cycle Rickshaw | Three-wheeled vehicle with a front cycle and passenger seat at the back | Pedals connected to a chain drive powering the front wheel | Passenger transport in urban areas |
| Electric-Assisted Cyclo | Cycle rickshaw with an electric motor supporting pedal effort | Pedals combined with electric motor assistance | Urban passenger and light cargo transport with reduced effort |
| Freight Pedal Cyclo | Modified cycle rickshaw for carrying goods instead of passengers | Standard pedal propulsion with reinforced frame | Transport of cargo in congested city environments |
| Velotaxi | Modern pedal-powered taxi with aerodynamic bodywork | Pedal-powered drivetrain optimized for speed and comfort | Tourist transportation and eco-friendly urban travel |
Introduction to Cyclo Vehicles in Pedal Propulsion
Cyclo vehicles represent a unique form of pedal propulsion combining human power with a three-wheeled design to enhance urban mobility and reduce traffic congestion. Typically composed of a powered front wheel steered by handlebars and rear passenger seating, cyclos leverage mechanical advantage through gear systems to maximize pedaling efficiency. Their eco-friendly operation and compact structure make them an effective solution for short-distance transit in densely populated cities.
Historical Evolution of Pedal-Powered Cyclo
The historical evolution of the pedal-powered cyclo traces back to the late 19th century when early models integrated bicycle technology with three-wheeled designs for passenger transport, enhancing urban mobility in densely populated Asian cities. Innovations in pedal mechanics and chassis design throughout the 20th century improved efficiency, durability, and rider comfort, solidifying the cyclo's role as a sustainable, eco-friendly transportation mode. This evolution reflects broader trends in human-powered vehicles, emphasizing simplicity, affordability, and environmental benefits in urban transit systems.
Key Features of Pedal-Propelled Cyclo Design
Pedal-propelled cyclo designs feature a lightweight frame constructed from durable materials such as steel or aluminum, optimizing strength and agility for urban mobility. Ergonomically designed handlebars and adjustable seats enhance rider comfort and control during extended travel. The drivetrain includes a reliable chain or belt system paired with multi-speed gearing, allowing efficient energy transfer and adaptability to varied terrain.
Popular Regions Utilizing Cyclo for Transportation
Cyclo pedal propulsion remains widely utilized in Southeast Asia, especially in Vietnam and Cambodia, where it serves as an eco-friendly and cost-effective urban transport option. In cities like Hanoi and Phnom Penh, cyclos navigate narrow streets and congested areas, providing efficient mobility for both locals and tourists. The cyclo system supports sustainable transport initiatives by reducing carbon emissions and promoting healthier commuting practices.
Environmental Benefits of Pedal-Driven Cyclo
Pedal-driven cyclos significantly reduce carbon emissions by relying solely on human power instead of fossil fuels, contributing to cleaner urban air quality. Their zero noise pollution enhances city environments, promoting quieter and more peaceful streets. Efficient energy use in pedal propulsion lowers overall environmental impact compared to motor vehicles, supporting sustainable urban transportation systems.
Comparative Analysis: Cyclo vs. Other Pedal-Powered Transport
The cyclo, a pedal-powered tricycle commonly used in Southeast Asia, offers enhanced stability and cargo capacity compared to traditional bicycles, making it ideal for urban transport and short-distance goods delivery. Its unique design distributes weight evenly across three wheels, reducing rider fatigue and increasing load efficiency relative to standard two-wheel pedal-powered vehicles. While slower than some pedal-powered options due to added weight and drag, the cyclo's versatility and comfort provide distinct advantages in crowded city environments and congested streets.
Innovations in Modern Cyclo Pedal Propulsion
Innovations in modern cyclo pedal propulsion include the integration of lightweight aluminum frames and energy-efficient gear systems that enhance rider comfort and performance. Advances in electric-assist motors and regenerative braking technology have transformed traditional cyclo designs, making urban mobility more sustainable and accessible. Smart sensors and app connectivity allow real-time monitoring of speed, distance, and battery life, optimizing the overall riding experience.
Economic Impact of Cyclo-Based Mobility
Cyclo-based mobility significantly boosts local economies by providing affordable transportation options and creating numerous jobs in manufacturing, maintenance, and driving services. This pedal-propelled vehicle reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering transportation costs and environmental impact for low-income communities. Increased cyclo usage stimulates microenterprise growth, enhancing economic resilience and promoting sustainable urban mobility models.
Challenges Facing Pedal-Propelled Cyclo Adoption
Pedal-propelled cyclos face significant challenges in urban mobility, including limited speed and range compared to motorized vehicles, which restrict their practicality for long commutes. Infrastructure constraints such as inadequate dedicated lanes and traffic congestion increase safety risks and reduce operational efficiency. Additionally, the physical effort required for pedaling limits rider endurance and appeal, especially in hilly or densely populated cities.
Future Prospects for Cyclo in Urban Mobility
Cyclo pedal propulsion systems offer promising advancements in urban mobility with their eco-friendly, zero-emission design and efficient energy use. Integrating smart electric assists and lightweight materials enhances performance, making cyclos viable for short-distance city commutes and last-mile connectivity. Future prospects include widespread adoption in congested urban areas, improving sustainability and reducing traffic congestion while promoting active lifestyles.
example of cyclo in pedal propulsion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com