The autoped is an early example of personal mobility devices, introduced in the 1910s as one of the first motorized scooters. It features a compact design with a small gasoline engine mounted on a narrow platform, allowing users to stand and travel short distances efficiently. This device was ideal for urban promenades, providing a convenient and innovative means of transport along paved walkways. The autoped's lightweight structure and modest speed made it suitable for leisurely travel in pedestrian zones and parks. Its electric or gas-powered motor represented a significant advancement in micro-mobility, predating modern electric scooters commonly used today. Historic promenades often showcased such devices, marking the early integration of motorized personal transport in public recreational spaces.
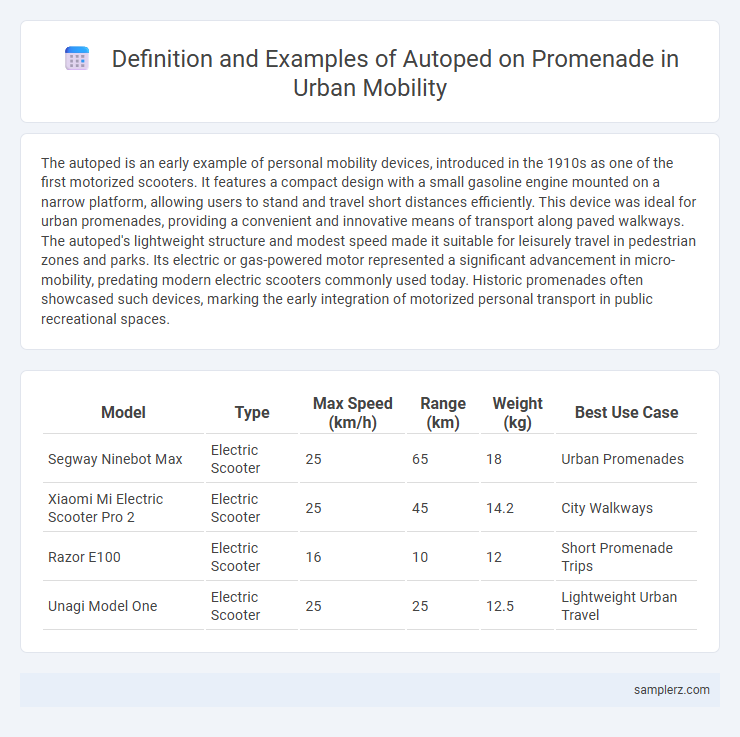
Table of Comparison
| Model | Type | Max Speed (km/h) | Range (km) | Weight (kg) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segway Ninebot Max | Electric Scooter | 25 | 65 | 18 | Urban Promenades |
| Xiaomi Mi Electric Scooter Pro 2 | Electric Scooter | 25 | 45 | 14.2 | City Walkways |
| Razor E100 | Electric Scooter | 16 | 10 | 12 | Short Promenade Trips |
| Unagi Model One | Electric Scooter | 25 | 25 | 12.5 | Lightweight Urban Travel |
Introduction to Autopeds in Urban Promenades
Autopeds offer an innovative solution for urban promenades, combining compact design and electric propulsion to enhance mobility on crowded walkways. Their lightweight frames and low speeds ensure pedestrian safety while providing efficient short-distance travel. Increasingly integrated into city planning, autopeds support sustainable transportation goals and reduce reliance on traditional vehicles in pedestrian zones.
Historical Evolution of Autopeds on Promenades
Autopeds first appeared on promenades in the early 20th century, representing a significant innovation in personal mobility with their lightweight frames and gasoline-powered engines. These early models evolved from simple motorized bicycles to more sophisticated, reliable machines that allowed users to navigate crowded promenades efficiently. The historical evolution reflects advancements in engine technology and design, which enhanced speed, safety, and accessibility for urban commuters and leisure riders alike.
Types of Autopeds Commonly Seen in Promenade Areas
Electric and gas-powered autopeds are commonly seen in promenade areas, offering convenience and eco-friendly solutions for short-distance travel. Lightweight, foldable models are also popular due to their portability and ease of storage. Many autopeds feature adjustable speed settings and enhanced safety features, catering to diverse rider preferences in bustling pedestrian zones.
Safety Considerations for Autoped Riders
Autopeds used on promenades must adhere to strict safety considerations such as helmets, reflective gear, and speed limits to reduce accident risks. Ensuring well-maintained surfaces and clear signage improves rider visibility and prevents collisions with pedestrians. Riders should also be trained on safe maneuvering techniques specific to mixed pedestrian environments to enhance overall safety on shared pathways.
Promenade Infrastructure and Autoped Support
Promenade infrastructure designed for autoped support features smooth, wide pathways with durable, non-slip surfaces to ensure safety and ease of movement. Dedicated charging stations and clearly marked lanes enhance user convenience and promote efficient traffic flow. Strategic integration of ramps and rest areas further optimizes accessibility for autoped riders along the promenade.
Environmental Impact of Autopeds in Public Spaces
Autopeds operating on promenades contribute to reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles due to their electric propulsion systems, supporting cleaner urban air quality. Their compact design results in minimal noise pollution, preserving the tranquility of public spaces and enhancing the pedestrian experience. However, careful management of autoped traffic is essential to prevent overcrowding and ensure the safety and comfort of all promenade users.
Social Dynamics: Pedestrians and Autoped Users
On promenades, the interaction between pedestrians and autoped users shapes social dynamics by balancing shared space and personal mobility. Autoped users navigate smoothly alongside walkers, requiring mutual awareness to prevent collisions and ensure safety. This coexistence fosters a dynamic environment where inclusivity and respect for varied mobility preferences enhance overall social experience.
Regulations Governing Autoped Usage on Promenades
Regulations governing autoped usage on promenades typically restrict maximum speed limits to 15 km/h to ensure pedestrian safety and mandate the use of helmets and protective gear. Many local authorities require riders to keep to designated lanes or sections of promenades, preventing obstruction of foot traffic and reducing accident risks. Compliance with noise restrictions and emission standards, especially for electric models, is enforced to maintain the tranquil environment of promenades.
Case Studies: Successful Autoped Integration in Promenade Design
Case studies of autoped integration in promenades highlight effective urban mobility solutions that enhance user convenience and sustainability. In Barcelona's beachfront promenade, autoped lanes reduce pedestrian congestion and promote eco-friendly transport, supported by smart docking stations and real-time tracking apps. Similarly, Singapore's marina bay promenade incorporates autopeds with seamless connectivity to public transit, fostering multimodal travel and decreasing carbon emissions.
Future Trends for Autopeds in Promenade Mobility
Future trends for autopeds in promenade mobility emphasize enhanced battery efficiency, integration of smart navigation systems, and increased safety features such as collision avoidance sensors. Lightweight materials and IoT connectivity will enable seamless urban travel and real-time traffic data exchange, improving user experience. Autonomous autopeds with AI-driven route optimization promise to transform pedestrian zones, supporting sustainable and eco-friendly urban mobility solutions.
example of autoped in promenade Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com