A funicular is a type of cable railway system specifically designed for steep inclines, often found in mountainous regions. This transportation method uses two counterbalanced cars attached to a cable, which moves them simultaneously up and down the slope. The rail tracks are fixed on the mountainside, enabling efficient and safe transit over rugged terrain. One famous example of a funicular in a mountainous area is the Peak Tram in Hong Kong, which connects the Central district with Victoria Peak. Another notable example is the Gelmerbahn funicular in Switzerland, known for being one of the steepest funicular railways in Europe. These funiculars function by utilizing gravity and counterweight principles, effectively addressing the challenges of vertical mobility in terrains where conventional vehicles are impractical.
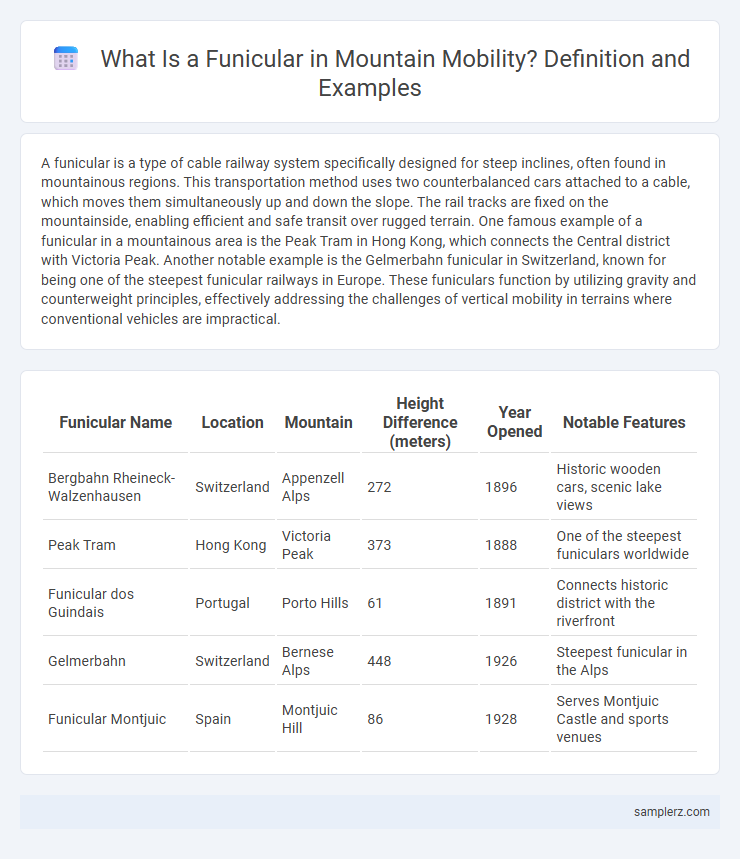
Table of Comparison
| Funicular Name | Location | Mountain | Height Difference (meters) | Year Opened | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bergbahn Rheineck-Walzenhausen | Switzerland | Appenzell Alps | 272 | 1896 | Historic wooden cars, scenic lake views |
| Peak Tram | Hong Kong | Victoria Peak | 373 | 1888 | One of the steepest funiculars worldwide |
| Funicular dos Guindais | Portugal | Porto Hills | 61 | 1891 | Connects historic district with the riverfront |
| Gelmerbahn | Switzerland | Bernese Alps | 448 | 1926 | Steepest funicular in the Alps |
| Funicular Montjuic | Spain | Montjuic Hill | 86 | 1928 | Serves Montjuic Castle and sports venues |
Introduction to Mountain Funiculars
Mountain funiculars efficiently transport passengers on steep inclines by using counterbalanced cars connected by cables, minimizing energy consumption. These rail systems are often found in tourist destinations, providing scenic and reliable access to mountain peaks and ski resorts. Engineering design ensures safety and smooth operation despite challenging terrain and elevation changes.
Historical Overview of Mountain Funiculars
Mountain funiculars, such as the Gelmerbahn in Switzerland, date back to the 19th century, revolutionizing alpine transportation by enabling steep ascents. Early designs relied on water counterbalancing systems, exemplified by the Seilbahn Reichenbachfalle, highlighting engineering ingenuity in challenging terrains. These historical funiculars paved the way for modern, efficient cable-driven transport solutions integral to mountain mobility today.
Key Features of Mountain Funicular Systems
Mountain funicular systems feature dual counterbalanced cars connected by a cable, which ensures energy efficiency and smooth operation on steep inclines often exceeding 30 degrees. The tracks are typically designed with strong anchorage and rail profiles optimized for rugged terrain, enabling safe and reliable ascent and descent. Advanced braking systems and automated control ensure passenger safety while providing panoramic views, making mountain funiculars a preferred mode of sustainable transport in challenging topographies.
Iconic Mountain Funiculars Around the World
Iconic mountain funiculars such as the Gelmerbahn in Switzerland, the Peak Tram in Hong Kong, and the Montmartre Funicular in Paris provide efficient and scenic transport up steep inclines. These engineering marvels combine cable traction with steep gradients, enabling passenger access to breathtaking mountain vistas while reducing environmental impact. Funiculars remain essential in preserving natural landscapes while enhancing mobility in mountainous regions worldwide.
Engineering Marvels: How Mountain Funiculars Operate
Mountain funiculars exemplify engineering marvels by utilizing counterbalanced cars connected by cables that efficiently ascend steep slopes, minimizing energy consumption. These systems employ precisely engineered tracks and powerful winches to ensure safe, smooth operation on rugged terrain. Advanced braking mechanisms and automated controls maintain stability and passenger safety throughout the journey on inclines often exceeding 45 degrees.
Notable European Mountain Funiculars
Notable European mountain funiculars include the Gelmerbahn in Switzerland, renowned for its steep incline and panoramic alpine views, and the Montjuic Funicular in Spain, which connects the city of Barcelona to the Montjuic hill, offering scenic urban and natural landscapes. Another key example is the Funiculaire de Montmartre in France, facilitating access to the Sacre-Coeur Basilica atop the Montmartre hill in Paris. These funiculars exemplify efficient, eco-friendly transportation solutions integrating mountainous terrain with tourism and urban mobility needs.
Safety and Sustainability in Mountain Funicular Design
Mountain funiculars prioritize advanced safety systems such as automated braking and real-time monitoring to ensure passenger protection on steep slopes. Sustainable design incorporates energy-efficient regenerative braking and environmentally friendly construction materials to reduce ecological impact. These innovations maintain reliable transport while preserving fragile mountain ecosystems.
Scenic Journeys: Funiculars Offering Breathtaking Mountain Views
Funicular railways such as the Gelmerbahn in Switzerland provide exhilarating mountain journeys with panoramic views of alpine landscapes, combining efficient mobility with unique sightseeing opportunities. These steeply inclined railways enhance accessibility to remote peaks, offering tourists and adventurers seamless transportation while showcasing pristine natural beauty. The blend of engineering innovation and scenic vistas makes funiculars ideal for immersive mountain travel experiences.
The Role of Funiculars in Mountain Tourism
Funicular railways are essential in mountain tourism as they provide a safe, efficient means of ascending steep slopes, connecting tourists from base stations to scenic viewpoints or ski resorts. These cable-driven systems minimize environmental impact by reducing the need for extensive road construction and vehicle traffic in fragile alpine ecosystems. Funiculars also enhance accessibility, enabling visitors of all ages and physical abilities to explore mountainous regions comfortably and sustainably.
Future Innovations in Mountain Funicular Mobility
Future innovations in mountain funicular mobility include advanced magnetic levitation systems that reduce friction and enhance speed while maintaining energy efficiency. Integration of smart sensors and AI enables real-time monitoring and adaptive control, improving safety and operational reliability on steep terrains. Sustainable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are increasingly incorporated to minimize environmental impact and promote eco-friendly mountain transportation.
example of funicular in mountain Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com