Tram-trains are innovative urban mobility solutions that combine the features of trams and trains to facilitate seamless travel within and around city beltways. These vehicles operate on both tramway tracks within urban areas and traditional railway lines, enabling efficient connectivity between city centers and suburban or regional destinations. Examples of tram-train systems can be found in cities like Karlsruhe, Germany, where the network enhances public transport coverage and reduces reliance on private vehicles. The integration of tram-trains into beltway routes provides a strategic advantage by linking key transit hubs and peripheral neighborhoods, optimizing passenger flow and reducing congestion. Data from cities employing tram-train technology show significant improvements in transit ridership and reduced travel times compared to conventional transport modes. Such systems support sustainable urban development by promoting multimodal transport networks that lower carbon emissions and improve accessibility.
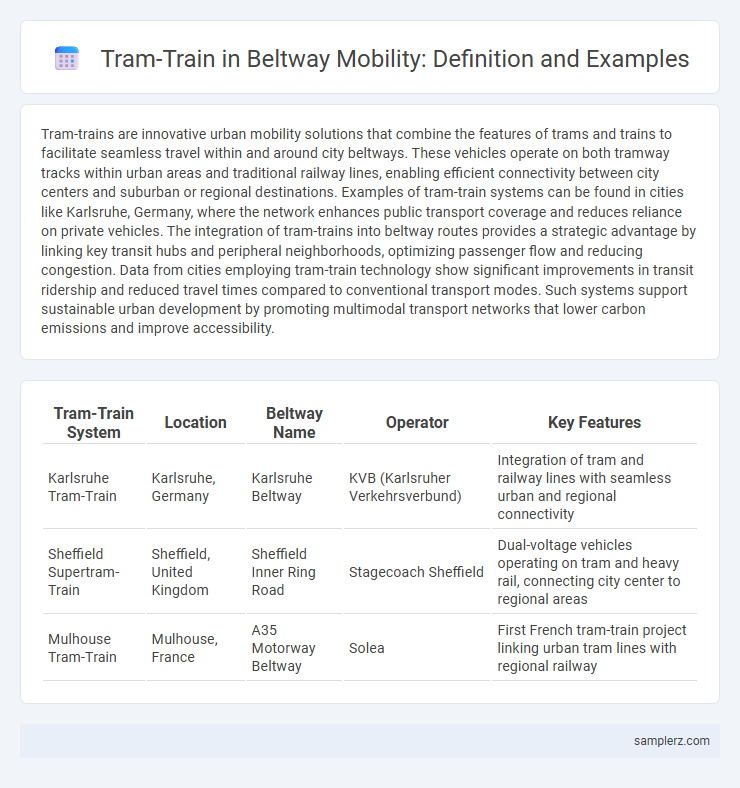
Table of Comparison
| Tram-Train System | Location | Beltway Name | Operator | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karlsruhe Tram-Train | Karlsruhe, Germany | Karlsruhe Beltway | KVB (Karlsruher Verkehrsverbund) | Integration of tram and railway lines with seamless urban and regional connectivity |
| Sheffield Supertram-Train | Sheffield, United Kingdom | Sheffield Inner Ring Road | Stagecoach Sheffield | Dual-voltage vehicles operating on tram and heavy rail, connecting city center to regional areas |
| Mulhouse Tram-Train | Mulhouse, France | A35 Motorway Beltway | Solea | First French tram-train project linking urban tram lines with regional railway |
Introduction to Tram-Train Systems in Beltways
Tram-train systems in beltways integrate light rail vehicles with existing urban rail networks, enabling seamless transit across city outskirts and central areas. These systems enhance connectivity by allowing trams to operate on both tram tracks and standard railway lines, reducing transfer times and increasing frequency. Key examples, such as the Karlsruhe model in Germany, demonstrate improved commuter flow and decreased traffic congestion within metropolitan beltway regions.
Key Features of Beltway Tram-Train Integration
Beltway tram-train integration combines urban light rail flexibility with regional train capacity, enabling seamless travel across metropolitan and suburban areas. Key features include shared tracks for both tram and train vehicles, multi-modal transfer hubs, and synchronized scheduling to minimize wait times. This integration enhances connectivity, reduces traffic congestion, and promotes sustainable urban mobility.
Case Study: Successful Tram-Train Routes on Urban Beltways
The Karlsruhe Model in Germany exemplifies a successful tram-train route integrating urban beltways by seamlessly connecting suburban areas with the city center using existing railway infrastructure, significantly reducing commute times and traffic congestion. This approach combines light rail flexibility with heavy rail capacity, optimizing passenger flow and fostering sustainable urban mobility. Effective coordination between municipal transit authorities and regional rail operators ensures high service frequency and reliability on beltway corridors.
Infrastructure Requirements for Beltway Tram-Train Operations
Beltway tram-train operations demand robust infrastructure featuring dual-gauge tracks to accommodate both tram and train vehicles, ensuring seamless transition between urban tram lines and regional rail networks. Advanced signaling systems and dedicated transfer stations are essential to manage high passenger flows and maintain precise scheduling within the beltway perimeter. Electrification standards must be unified across the infrastructure to support efficient energy use and reduce operational interruptions in mixed tram-train corridors.
Technological Innovations in Beltway Tram-Train Networks
Beltway tram-train networks integrate cutting-edge technologies such as real-time traffic management systems and energy-efficient regenerative braking to enhance urban mobility. Advanced signaling and automation enable seamless transitions between tram and train infrastructures, optimizing route flexibility and reducing transit times. These innovations contribute to sustainable transport solutions by lowering emissions and improving connectivity within metropolitan beltways.
Passenger Benefits of Tram-Train on Beltways
Tram-trains on beltways enhance passenger convenience by providing seamless transfers between urban and suburban areas without changing vehicles, reducing overall travel time and increasing route flexibility. The integration of tram-train systems on beltways supports frequent service intervals and greater reliability, improving passenger satisfaction and accessibility. Access to multiple stops along the beltway encourages increased ridership by connecting residential, commercial, and recreational zones efficiently.
Environmental Impact of Tram-Train Systems in Beltway Mobility
Tram-train systems integrated into beltway mobility significantly reduce carbon emissions by combining the efficiency of electric trams with the flexibility of trains, cutting reliance on fossil fuel-powered vehicles. These systems enhance air quality by lowering particulate matter and nitrogen oxide levels around urban beltways, contributing to healthier environments. Noise pollution is also diminished due to quieter electric propulsion, making tram-trains a sustainable alternative for high-density, ring-road transit solutions.
Challenges in Implementing Tram-Train on Existing Beltways
Implementing tram-train systems on existing beltways poses significant challenges including the integration of differing track gauges and signaling systems, which complicates infrastructure compatibility. Spatial limitations within urban beltways often restrict necessary modifications, leading to potential disruptions in traffic flow and raising safety concerns. Coordinating schedules between tram-train services and existing transit operations requires sophisticated traffic management to minimize delays and ensure seamless connectivity.
Comparison: Tram-Train vs. Traditional Transit on Beltways
Tram-train systems on beltways offer higher flexibility and direct connectivity by operating seamlessly on both urban tram tracks and mainline railways, unlike traditional transit which typically requires transfers between modes. Their integration into existing infrastructure reduces travel times and increases route options, enhancing overall commuter experience around city loops. Cost efficiency in construction and operation also surpasses many traditional transit systems on beltways, making tram-trains a viable alternative for urban mobility.
Future Prospects for Tram-Train Expansion in Beltway Corridors
Tram-train systems in beltway corridors demonstrate significant potential for urban mobility enhancement through seamless integration of tram and rail networks, reducing congestion and promoting sustainable transit. Future prospects include expanding these systems to connect peripheral suburbs with city centers, leveraging existing rail infrastructure for cost-effective scalability. Advancements in signaling technology and battery-powered tram-trains are expected to increase operational efficiency and environmental benefits in beltway expansions.
example of tram-train in beltway Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com