Cyclecars were a popular form of urban mobility in the early 20th century, offering a compact and economical alternative to larger automobiles. These lightweight vehicles typically featured small engines, minimalistic designs, and affordable prices, making them ideal for navigating crowded city streets. Companies like the French manufacturer Morgan and the British maker Austin produced notable models that contributed to the growth of cyclecars in metropolitan areas. Modern urban mobility increasingly relies on electric cyclecars, combining eco-friendly technology with the traditional advantages of these compact vehicles. Electric cyclecars provide efficient short-distance travel, reduced emissions, and ease of parking in dense city environments. Data from recent urban studies show a rising trend in cyclecar adoption as cities prioritize sustainable transportation infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
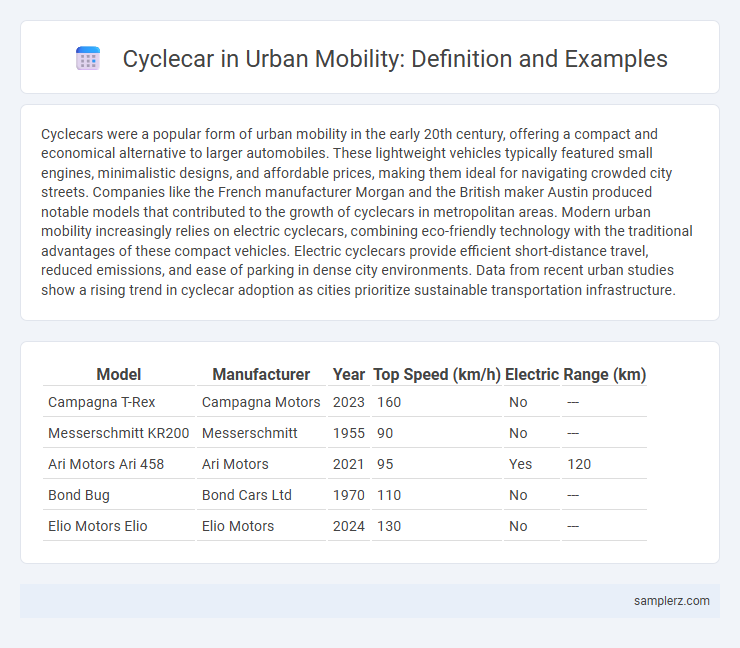
| Model | Manufacturer | Year | Top Speed (km/h) | Electric | Range (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campagna T-Rex | Campagna Motors | 2023 | 160 | No | --- |
| Messerschmitt KR200 | Messerschmitt | 1955 | 90 | No | --- |
| Ari Motors Ari 458 | Ari Motors | 2021 | 95 | Yes | 120 |
| Bond Bug | Bond Cars Ltd | 1970 | 110 | No | --- |
| Elio Motors Elio | Elio Motors | 2024 | 130 | No | --- |
Introduction to Cyclecars: Urban Mobility Solutions
Cyclecars offer a compact and efficient urban mobility solution, combining the agility of motorcycles with the comfort of small cars, making them ideal for navigating congested city streets. These lightweight vehicles typically feature a narrow profile and low emissions, supporting eco-friendly transportation and reducing traffic congestion in dense urban environments. Innovations in electric cyclecars further enhance their appeal by providing quiet, zero-emission transport options tailored for short city commutes.
Historical Evolution of Cyclecars in City Landscapes
Cyclecars emerged in the early 20th century as compact, affordable vehicles designed to navigate narrow city streets and congested urban environments. Their lightweight construction and small engines allowed for efficient maneuverability and reduced fuel consumption compared to traditional automobiles. This historical evolution highlights cyclecars' role in shaping early urban mobility by providing accessible personal transport before the rise of modern compact cars.
Popular Cyclecar Models Used in Urban Environments
Popular cyclecar models such as the Morgan 3 Wheeler and the Aixam City offer compact dimensions and efficient fuel consumption ideal for urban mobility. These lightweight vehicles provide excellent maneuverability and ease of parking, making them suitable for congested city streets. Their combination of agility and cost-effectiveness contributes to increased adoption of cyclecars in urban transportation systems.
Key Features of Cyclecars for City Commuting
Cyclecars designed for city commuting feature compact dimensions ideal for navigating tight urban streets and limited parking spaces, enhancing maneuverability in congested areas. These vehicles prioritize fuel efficiency and low emissions, supporting eco-friendly transportation and reducing overall commuting costs. Lightweight construction and efficient powertrains enable quick acceleration and nimble handling tailored to frequent stop-and-go city traffic.
Cyclecar Integration in Public Transport Networks
Cyclecar integration in public transport networks enhances urban mobility by providing flexible, low-emission last-mile connectivity, especially in congested city centers. These lightweight, compact vehicles can be easily parked and accessed at transit hubs, facilitating smooth transfers between buses, trains, and bicycles. Their affordability and efficiency support sustainable commuting, reducing reliance on traditional cars and easing traffic congestion.
Case Studies: Successful Cyclecar Deployment in Cities
Barcelona's implementation of cyclecar-sharing programs has significantly reduced urban congestion and emissions by providing compact, efficient vehicles tailored for narrow streets. In Tokyo, cyclecars have improved last-mile connectivity, seamlessly integrating with public transit to enhance commuter flexibility and reduce reliance on larger, polluting vehicles. These case studies demonstrate cyclecars' potential to transform urban mobility through increased accessibility and environmental benefits.
Environmental Impact of Urban Cyclecar Usage
Urban cyclecars significantly reduce carbon emissions by offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional cars, emitting approximately 60-70% less CO2 per kilometer. Their compact design contributes to lower traffic congestion and minimizes urban noise pollution, enhancing overall city air quality. Electric-powered cyclecars further decrease reliance on fossil fuels, supporting sustainable urban mobility and reducing environmental footprints in densely populated areas.
Urban Infrastructure Adaptations for Cyclecars
Cyclecars integrate seamlessly into urban infrastructure through narrow parking lanes and adapted traffic signals optimized for smaller vehicle dimensions. Dedicated cyclecar lanes reduce congestion and enhance safety by separating them from larger vehicles in city traffic. Smart city technologies support cyclecar navigation with real-time traffic data and energy-efficient routing tailored to compact urban mobility.
Resident Perspectives: Cyclecar Experience in Daily Commutes
Residents appreciate cyclecars for their compact size, which simplifies parking and navigation through congested urban streets. Their fuel efficiency and lower emissions contribute to a greener city environment, aligning with sustainability goals. Many users report enhanced convenience for short-distance commuting, reducing reliance on larger vehicles and public transit.
Future Trends: Cyclecars Shaping Sustainable City Mobility
Cyclecars are emerging as a pivotal solution in sustainable urban mobility, offering compact, energy-efficient transportation tailored for congested city environments. Innovations in electric powertrains and lightweight materials enable cyclecars to reduce carbon emissions and minimize parking space requirements. Integration with smart city infrastructure and shared mobility platforms highlights their potential to revolutionize future urban transport systems.
example of cyclecar in city Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com