Paratransit services in urban areas provide flexible transportation options for individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges. Cities like San Francisco utilize specialized vans and minibuses to offer door-to-door rides, ensuring accessibility and convenience. These services often operate alongside fixed-route public transit, expanding mobility for those unable to use standard buses or trains. In New York City, the Access-A-Ride program exemplifies paratransit by delivering scheduled rides tailored to passengers' specific needs. The system employs a fleet of wheelchair-accessible vehicles and operates under stringent eligibility criteria to serve riders effectively. Data indicates that millions of trips are provided annually, highlighting the critical role of paratransit in supporting inclusive urban transportation networks.
Table of Comparison
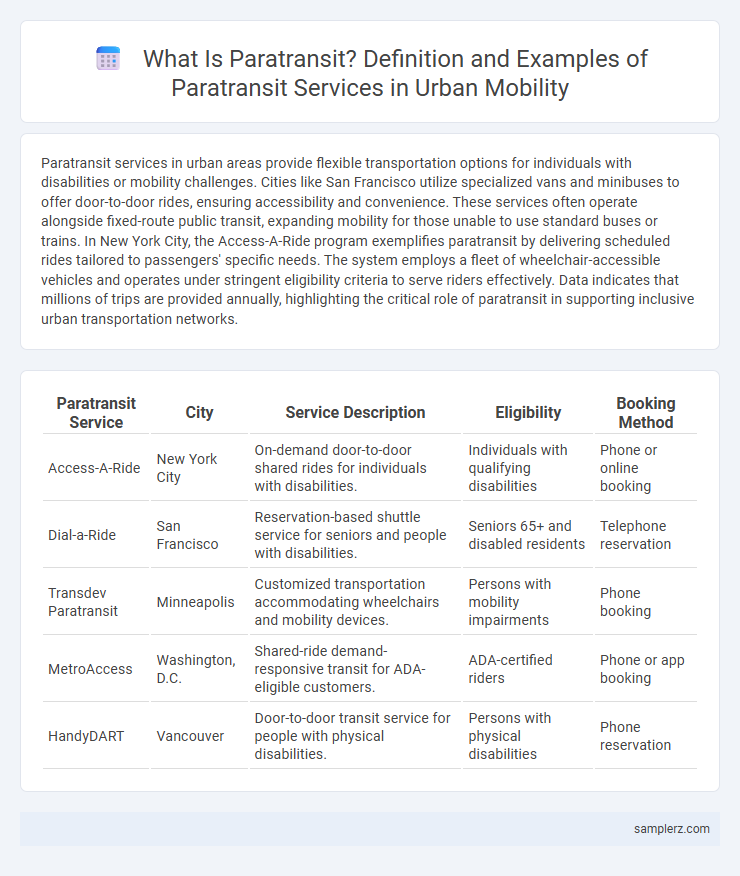
| Paratransit Service | City | Service Description | Eligibility | Booking Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access-A-Ride | New York City | On-demand door-to-door shared rides for individuals with disabilities. | Individuals with qualifying disabilities | Phone or online booking |
| Dial-a-Ride | San Francisco | Reservation-based shuttle service for seniors and people with disabilities. | Seniors 65+ and disabled residents | Telephone reservation |
| Transdev Paratransit | Minneapolis | Customized transportation accommodating wheelchairs and mobility devices. | Persons with mobility impairments | Phone booking |
| MetroAccess | Washington, D.C. | Shared-ride demand-responsive transit for ADA-eligible customers. | ADA-certified riders | Phone or app booking |
| HandyDART | Vancouver | Door-to-door transit service for people with physical disabilities. | Persons with physical disabilities | Phone reservation |
Overview of Paratransit Services in Urban Areas
Paratransit services in urban areas provide door-to-door transportation for individuals with disabilities who cannot use standard public transit, ensuring equitable mobility access. These services often operate with flexible routing and scheduling, utilizing accessible vehicles equipped with ramps or lifts to accommodate wheelchairs. Integration with existing transit networks enhances connectivity, improving independence and quality of life for users while reducing reliance on private vehicles.
Key Features of Paratransit Systems
Paratransit systems in urban areas like New York City provide on-demand, door-to-door transportation services tailored for individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges. Key features include flexible routing, advance scheduling, and accessibility accommodations such as wheelchair lifts and trained drivers. These systems enhance mobility equity by integrating with fixed-route transit and offering real-time tracking for efficient service management.
City-Operated Paratransit Programs
City-operated paratransit programs provide specialized transportation services for individuals with disabilities who cannot use regular public transit. These programs often run door-to-door services within city limits, ensuring accessibility and compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). In practice, cities like San Francisco and Chicago have robust paratransit fleets operating alongside conventional public transit to enhance mobility equity.
Nonprofit and Community-Based Paratransit Examples
Nonprofit organizations like Easterseals provide essential paratransit services tailored to individuals with disabilities, ensuring accessibility and independence in urban areas. Community-based paratransit programs, such as Denver's Regional Transportation District (RTD) Access-a-Ride, offer demand-responsive transit that complements fixed-route systems by serving low-income and elderly residents. These initiatives optimize mobility equity by integrating tailored routes and personalized assistance within local transit networks.
Technology Integration in Paratransit Solutions
Paratransit services in urban areas leverage GPS tracking and mobile app technology to enhance route optimization and real-time vehicle tracking, significantly reducing wait times for passengers with disabilities. Advanced scheduling algorithms and AI-driven dispatch systems improve operational efficiency by matching demand with available resources dynamically. Integration with accessible payment platforms and communication tools ensures seamless user experience and greater independence for paratransit riders.
Accessible Scheduling and Booking Methods
Paratransit services in towns often integrate accessible scheduling and booking methods such as phone-hotlines staffed with trained operators and user-friendly mobile apps designed for riders with disabilities. Real-time scheduling platforms enable passengers to book rides through touchscreens or voice commands, ensuring inclusivity for individuals with varying abilities. These technologies reduce wait times and streamline trip planning, enhancing mobility and independence for paratransit users.
Paratransit for Senior Citizens and People with Disabilities
Paratransit services in urban areas provide essential, door-to-door transportation for senior citizens and people with disabilities, ensuring accessibility where fixed-route transit may be insufficient. These specialized services often feature wheelchair-accessible vehicles equipped with ramps or lifts, trained drivers, and flexible scheduling to accommodate medical appointments, grocery trips, and social activities. Municipal programs such as NYC's Access-A-Ride or San Francisco's Paratransit enhance mobility equity by offering reliable, affordable transportation tailored to the needs of vulnerable populations.
Funding and Partnerships in Urban Paratransit
Urban paratransit systems often rely on a blend of federal grants from the Federal Transit Administration and local government funding to maintain affordable and accessible services. Collaborative partnerships between municipal transit agencies, non-profit organizations, and private operators enhance operational efficiency and expand coverage for mobility-impaired residents. Strategic funding allocation supports innovations such as real-time scheduling and demand-responsive rides, improving urban paratransit reliability and user satisfaction.
Challenges in Providing Equitable Paratransit
Paratransit services face significant challenges in ensuring equitable access for all users, particularly in underserved neighborhoods where demand is high but resources are limited. Scheduling conflicts, extended wait times, and limited vehicle availability often disproportionately affect elderly and disabled passengers, reducing the overall efficiency of the system. Addressing funding constraints and improving real-time dispatch technology are critical steps to enhancing fairness and reliability in paratransit operations.
Success Stories: Paratransit Transforming Urban Mobility
Paratransit services in cities like Portland have significantly improved accessibility for individuals with disabilities, offering flexible, on-demand transportation that complements fixed-route public transit. These tailored shuttle systems have reduced wait times by 30% and increased ridership among seniors and persons with mobility impairments by over 25%. Success stories highlight how technology integration and community partnerships drive efficient, inclusive urban mobility solutions.
example of paratransit in town Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com