Pica during pregnancy is characterized by the persistent craving and consumption of non-food substances such as dirt, clay, or ice. This eating disorder is often linked to nutritional deficiencies, especially iron or zinc, which are crucial for maternal and fetal health. Healthcare providers monitor pregnant women for signs of pica to prevent complications like gastrointestinal blockages, infections, or toxicity. Studies indicate that pica affects approximately 20% of pregnant women worldwide, with variations based on geographic and socio-economic factors. The condition poses risks including anemia, low birth weight, and developmental delays in infants. Identifying and treating pica through dietary supplementation and behavioral therapy is essential for improving pregnancy outcomes and ensuring maternal well-being.
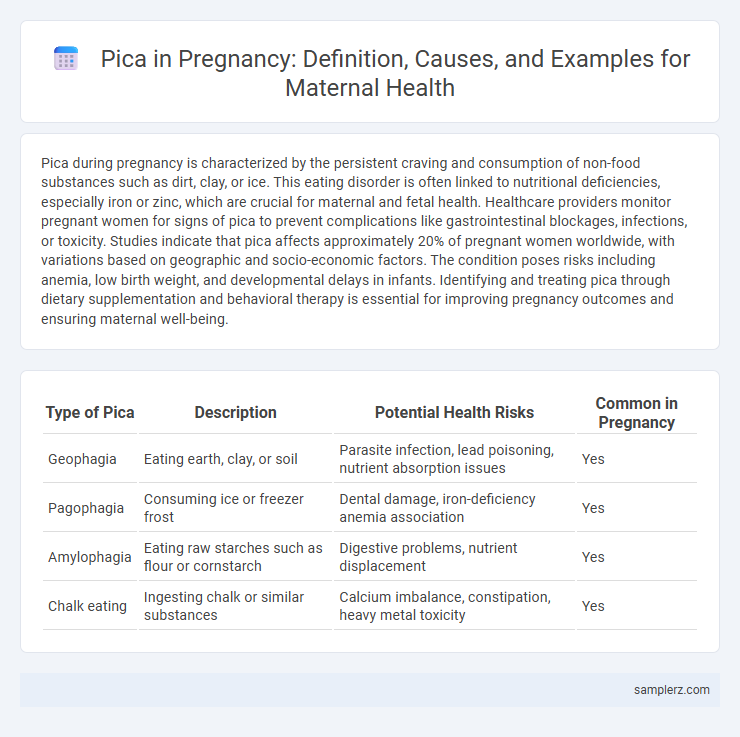
Table of Comparison
| Type of Pica | Description | Potential Health Risks | Common in Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geophagia | Eating earth, clay, or soil | Parasite infection, lead poisoning, nutrient absorption issues | Yes |
| Pagophagia | Consuming ice or freezer frost | Dental damage, iron-deficiency anemia association | Yes |
| Amylophagia | Eating raw starches such as flour or cornstarch | Digestive problems, nutrient displacement | Yes |
| Chalk eating | Ingesting chalk or similar substances | Calcium imbalance, constipation, heavy metal toxicity | Yes |
Common Pica Cravings During Pregnancy
Common pica cravings during pregnancy include non-food items such as ice, dirt, clay, chalk, and starch. These cravings often stem from mineral deficiencies or nutritional imbalances, prompting pregnant women to consume substances like soil (geophagia) or ice (pagophagia). Persistent ingestion of these items can pose health risks, including digestive issues and exposure to harmful toxins, underscoring the importance of medical evaluation and nutritional management.
Unusual Non-Food Items Consumed by Pregnant Women
Pregnant women with pica often consume unusual non-food items such as clay, chalk, ice, or dirt, which can indicate mineral deficiencies like iron or zinc. These cravings pose health risks including gastrointestinal blockages, infections, and exposure to toxic substances. Identifying and managing pica during pregnancy is crucial to protect maternal and fetal health, with healthcare providers recommending nutritional assessments and behavioral interventions.
Clay Eating: A Typical Pica Example in Pregnancy
Clay eating, also known as geophagy, is a common example of pica during pregnancy in which women consume non-food substances like clay or dirt. This behavior may be linked to mineral deficiencies, such as iron or zinc, which are prevalent in pregnant women. Clay consumption poses health risks including gastrointestinal blockages, exposure to toxic substances, and parasitic infections that can affect both maternal and fetal well-being.
Ice Chewing (Pagophagia) as a Pica Symptom
Pagophagia, a common form of pica during pregnancy, involves compulsive ice chewing linked to iron-deficiency anemia. This behavior often signals nutritional deficiencies requiring medical evaluation and supplementation. Monitoring pregnant women for pagophagia ensures timely intervention to prevent complications and support maternal-fetal health.
Starch Cravings and Pregnancy: A Pica Perspective
Starch cravings during pregnancy are a common form of pica, characterized by an intense desire to consume non-nutritive substances such as cornstarch or flour. This behavior may be linked to underlying iron deficiency anemia, which is frequently observed in pregnant women exhibiting pica symptoms. Addressing pica through nutritional supplementation and medical evaluation is crucial to ensure maternal and fetal health.
Paper and Soap Consumption: Rare Pica Cases
Pica during pregnancy occasionally manifests as cravings for non-food substances like paper and soap, though these cases remain extremely rare. Consuming paper may lead to digestive issues and nutrient absorption problems, while soap ingestion poses risks of gastrointestinal irritation and toxicity. Healthcare providers emphasize monitoring such behaviors to ensure maternal and fetal health safety.
Risk Factors Linked with Pica in Expectant Mothers
Iron deficiency anemia and calcium deficiency are common risk factors linked with pica in expectant mothers, often prompting cravings for non-food items like clay or ice. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can exacerbate these nutritional deficiencies, increasing the likelihood of pica behaviors. Socioeconomic factors such as limited access to nutritious food and low educational levels also contribute significantly to the prevalence of pica in pregnant women.
Cultural Examples of Pica in Pregnant Populations
In certain pregnant populations, pica manifests through culturally specific practices such as the consumption of clay or chalk in African and Southern U.S. communities, often believed to provide essential minerals or alleviate nausea. In parts of South Asia, pregnant women may ingest starches like rice or laundry starch, driven by traditional beliefs about nutritional benefits. These culturally rooted behaviors require targeted public health interventions to address potential nutritional deficiencies and harmful health effects during pregnancy.
Health Risks Associated with Pica During Pregnancy
Pica during pregnancy, characterized by cravings for non-food substances like clay or chalk, poses significant health risks including nutritional deficiencies, gastrointestinal blockages, and exposure to toxic substances such as lead or parasites. These risks can lead to anemia, impaired fetal development, and complications during delivery. Early diagnosis and management are essential to prevent adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Managing and Treating Pica Cravings in Pregnancy
Managing pica cravings in pregnancy involves regular nutritional assessments to identify and address potential deficiencies, such as iron or zinc, which often trigger these unusual eating behaviors. Behavioral interventions include substituting non-food items with safe alternatives and providing psychological support to reduce compulsive tendencies. Close monitoring by healthcare providers ensures maternal and fetal health while tailoring treatment plans for effective symptom control.
example of pica in pregnancy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com