Borborygmus refers to the rumbling or gurgling noises produced by the movement of gas and fluids in the intestines. In cases of diarrhea, borborygmus often becomes more pronounced due to increased intestinal motility and excess fluid in the bowel. Patients with diarrhea may report loud, frequent borborygmi as their digestive system rapidly processes and expels stool. These sounds result from the intestines contracting to move liquid stool quickly through the colon. Diarrheal diseases caused by infections, food intolerances, or inflammatory conditions can all trigger increased borborygmus. Monitoring the presence and intensity of borborygmi can help healthcare providers assess bowel activity and diagnose underlying gastrointestinal disorders.
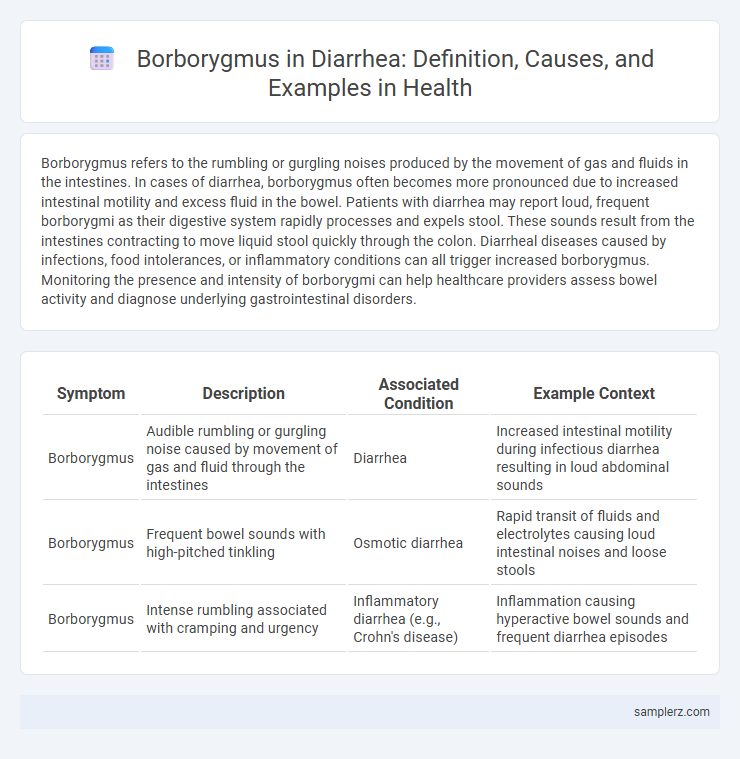
Table of Comparison
| Symptom | Description | Associated Condition | Example Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borborygmus | Audible rumbling or gurgling noise caused by movement of gas and fluid through the intestines | Diarrhea | Increased intestinal motility during infectious diarrhea resulting in loud abdominal sounds |
| Borborygmus | Frequent bowel sounds with high-pitched tinkling | Osmotic diarrhea | Rapid transit of fluids and electrolytes causing loud intestinal noises and loose stools |
| Borborygmus | Intense rumbling associated with cramping and urgency | Inflammatory diarrhea (e.g., Crohn's disease) | Inflammation causing hyperactive bowel sounds and frequent diarrhea episodes |
Understanding Borborygmus: What It Means in Diarrhea
Borborygmus refers to the loud, rumbling sounds produced by gas and fluid moving through the intestines, often intensified during episodes of diarrhea. These amplified bowel noises indicate increased intestinal activity and hypermotility as the digestive system rapidly processes and expels fluids. Understanding borborygmus in diarrhea helps identify how gastrointestinal disturbances affect normal motility patterns and can assist healthcare providers in diagnosing underlying conditions.
Common Causes of Borborygmus during Diarrhea
Borborygmus during diarrhea commonly results from gastrointestinal infections such as viral gastroenteritis or bacterial enteritis, causing increased intestinal motility and fluid secretion. Dietary triggers like lactose intolerance and food allergies frequently lead to enhanced gas production and intestinal rumbling. Inflammatory conditions including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Crohn's disease also contribute to borborygmus by disrupting normal gut function and promoting diarrhea symptoms.
Audible Signs: How Borborygmus Manifests in Diarrheal Episodes
Borborygmus during diarrheal episodes produces loud, rumbling sounds as intestinal muscles contract rapidly to move liquid stool. These audible signs often indicate increased gastrointestinal motility and can signal an underlying infection or irritation. Monitoring the frequency and intensity of borborygmus helps healthcare professionals assess the severity and progression of diarrhea.
Differentiating Borborygmus Sounds in Diarrhea vs. Normal Digestion
Borborygmus in diarrhea presents as loud, frequent, and irregular intestinal rumbling, contrasting with the softer, periodic sounds of normal digestion. During diarrhea, increased motility and fluid content amplify these sounds, aiding in clinical differentiation from typical bowel activity. Accurate identification of borborygmus characteristics helps healthcare providers assess underlying gastrointestinal disturbances.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Borborygmus with Diarrhea
Case studies reveal borborygmus often accompanies episodes of acute infectious diarrhea, with patients reporting loud, rumbling bowel sounds linked to increased intestinal motility and fluid secretion. In one documented case, a 32-year-old female experiencing bacterial gastroenteritis exhibited pronounced borborygmus alongside frequent watery stools, confirming heightened peristalsis as a symptom marker. These real-life examples underscore the diagnostic relevance of borborygmus in assessing diarrhea severity and guiding targeted treatment strategies.
Clinical Significance of Borborygmus in Patients with Diarrhea
Borborygmus, the audible rumbling or gurgling caused by the movement of gas and fluids in the intestines, often intensifies in patients experiencing diarrhea due to increased intestinal motility and fluid content. Clinically, this symptom can indicate hyperactive bowel activity associated with conditions like infectious gastroenteritis, irritable bowel syndrome, or malabsorption syndromes. Monitoring borborygmus frequency and characteristics aids healthcare professionals in diagnosing underlying gastrointestinal disorders and evaluating treatment efficacy in diarrheal illnesses.
Associated Symptoms: When Borborygmus and Diarrhea Co-occur
Borborygmus, characterized by loud, rumbling bowel sounds, often accompanies diarrhea due to increased intestinal motility and fluid content. Associated symptoms typically include abdominal cramping, urgency to defecate, and bloating, which result from hyperactive peristalsis and excessive gas production. This combination signals gastrointestinal disturbances such as infections, irritable bowel syndrome, or inflammatory bowel conditions requiring clinical evaluation.
Evaluating Borborygmus as a Diagnostic Clue in Diarrheal Illness
Borborygmus, characterized by loud, rumbling bowel sounds, often intensifies during diarrheal illness due to increased intestinal motility and fluid movement. Evaluating borborygmus provides valuable diagnostic insight, as its frequency and intensity correlate with underlying conditions such as infectious gastroenteritis or inflammatory bowel disease. Quantifying borborygmus alongside stool analysis and clinical presentation enhances the accuracy of diagnosing the etiology of diarrhea.
Medical Response: What to Do When Borborygmus Accompanies Diarrhea
Borborygmus, characterized by loud, rumbling intestinal sounds, often signals increased gastrointestinal motility during diarrhea. Medical response involves maintaining hydration with oral rehydration solutions and avoiding irritants like caffeine and high-fat foods to reduce bowel spasms. Monitoring symptoms and seeking medical attention is crucial if diarrhea persists beyond 48 hours or is accompanied by severe pain, fever, or blood in stool.
Preventing and Managing Excessive Borborygmus in Diarrheal Conditions
Excessive borborygmus during diarrhea often results from increased intestinal motility and gas accumulation, which can be managed by maintaining adequate hydration and consuming a balanced diet rich in soluble fiber to normalize bowel movements. Probiotics such as Lactobacillus acidophilus have demonstrated effectiveness in restoring gut microbiota balance, reducing both diarrhea frequency and associated borborygmus sounds. Avoiding lactose, caffeine, and high-fat foods can further prevent exacerbation of intestinal cramping and excessive bowel noises.
example of borborygmus in diarrhea Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com