A government mandate in administration refers to an official order or directive issued by an authoritative body that requires specific actions or policies to be implemented. For example, a public health department may issue a mandate requiring all healthcare facilities to report infection rates within 24 hours to monitor disease outbreaks effectively. These mandates ensure that government agencies and public institutions adhere to standardized procedures and uphold regulatory compliance. Another example of a government mandate involves environmental regulations where agencies must enforce limits on industrial emissions. Such mandates are essential for reducing pollution and protecting public health by imposing strict controls on factories and power plants. Government mandates establish clear responsibilities for administrative bodies to achieve policy goals efficiently and transparently.
Table of Comparison
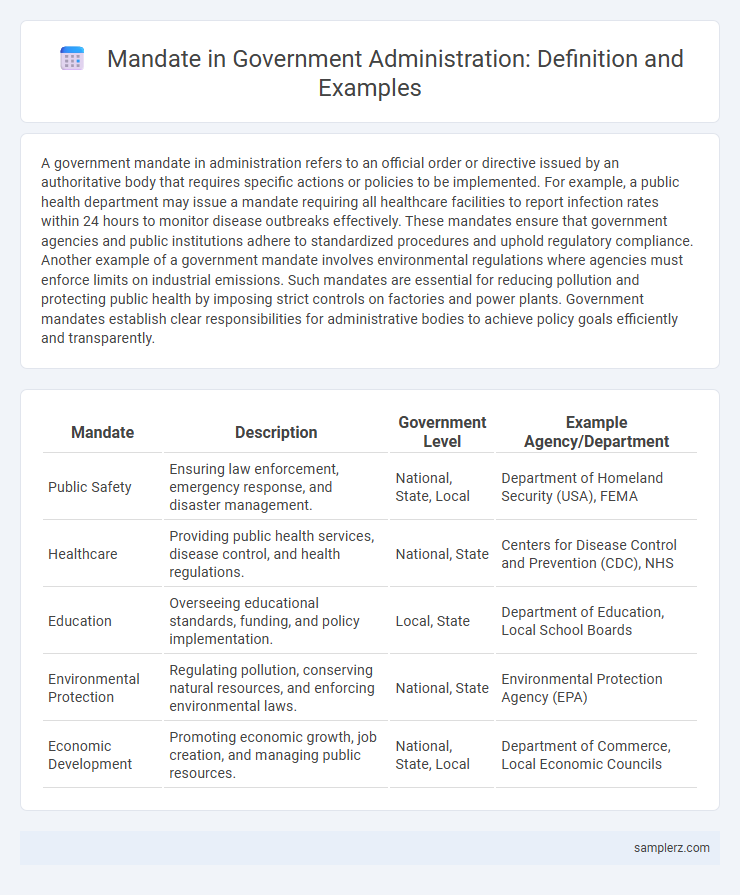
| Mandate | Description | Government Level | Example Agency/Department |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Safety | Ensuring law enforcement, emergency response, and disaster management. | National, State, Local | Department of Homeland Security (USA), FEMA |
| Healthcare | Providing public health services, disease control, and health regulations. | National, State | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), NHS |
| Education | Overseeing educational standards, funding, and policy implementation. | Local, State | Department of Education, Local School Boards |
| Environmental Protection | Regulating pollution, conserving natural resources, and enforcing environmental laws. | National, State | Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) |
| Economic Development | Promoting economic growth, job creation, and managing public resources. | National, State, Local | Department of Commerce, Local Economic Councils |
Definition and Importance of Mandates in Government Administration
Mandates in government administration refer to authoritative orders or directives issued by higher government bodies or officials that require specific actions to be implemented by subordinate agencies or departments. These mandates are crucial for ensuring uniform policy execution, maintaining accountability, and achieving legislative or executive goals within public administration. The clear definition and adherence to mandates foster efficient governance, legal compliance, and the consistent delivery of public services.
Historical Examples of Administrative Mandates
The New Deal programs in the 1930s serve as a significant historical example of administrative mandates, where the U.S. federal government, under President Franklin D. Roosevelt, enforced wide-ranging regulations and economic reforms to combat the Great Depression. Another notable case includes the implementation of the Social Security Act of 1935, mandating social welfare provisions and reshaping governmental responsibility towards citizens' economic security. Post-World War II mandates, such as the Marshall Plan, directed administrative efforts internationally, emphasizing government-driven economic recovery and strategic aid distribution.
How Mandates Shape Public Policy Implementation
Mandates in government administration create legally binding requirements that direct agencies to achieve specific policy goals, ensuring uniformity and accountability in public service delivery. These mandates facilitate the allocation of resources, set performance standards, and drive compliance mechanisms, significantly influencing how public policies are executed across different jurisdictions. The effectiveness of public policy implementation depends on the clarity of mandates, the capacity of administrative bodies, and the monitoring systems established by government authorities.
Federal vs State Mandates: Key Differences
Federal mandates require state and local governments to comply with certain rules or regulations often tied to the receipt of federal funding, while state mandates impose obligations directly from state governments to local entities without federal involvement. Key differences include the scope of authority, with federal mandates addressing nationwide issues such as environmental protection or civil rights, and state mandates focusing on localized concerns like education standards or public health. Compliance with federal mandates typically influences state policies through conditional funding, whereas state mandates often carry legal requirements enforceable within the state jurisdiction.
Notable Mandates in Regulatory Reform
Notable mandates in regulatory reform include the Administrative Procedure Act (APA) of 1946, which standardizes rulemaking processes to ensure transparency and public participation. The Regulatory Flexibility Act mandates agencies to assess the impact of regulations on small businesses, promoting economic fairness. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act introduced comprehensive financial regulations to enhance accountability and reduce systemic risk.
Mandates for Public Health Administration
Mandates in Public Health Administration include regulations requiring vaccinations, quarantine enforcement during infectious disease outbreaks, and implementation of sanitation standards in public facilities. These mandates empower government agencies to protect population health by preventing disease spread and ensuring safe environments. Compliance with such mandates is essential for managing public health crises and promoting community well-being.
Education Sector Mandates and Their Impact
Education sector mandates typically require schools to implement standardized curricula to ensure consistent learning outcomes nationwide. These mandates often include policies on teacher certification, student assessment, and resource allocation aimed at improving educational quality and equity. The impact of such mandates is evident in increased accountability, enhanced student performance metrics, and reduced disparities in access to education.
Environmental Protection Mandates in Practice
Environmental protection mandates in government administration often require agencies to enforce regulations such as the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act, ensuring pollution control and natural resource conservation. These mandates compel local and federal bodies to implement sustainability initiatives, monitor emission levels, and promote renewable energy projects. Compliance with such mandates directly influences policy development and resource allocation aimed at reducing environmental impact nationwide.
Challenges in Enforcing Administrative Mandates
Enforcing administrative mandates often encounters challenges such as bureaucratic resistance, limited resources, and legal ambiguities that hinder effective implementation. Conflicting interests within government agencies can delay decision-making processes, while insufficient funding restricts the capacity to monitor compliance and enforce regulations. These obstacles necessitate streamlined procedures and clear statutory guidelines to ensure mandates are executed efficiently and transparently.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Government Mandates
Evaluating the effectiveness of government mandates involves analyzing compliance rates, socio-economic impact, and policy outcomes to ensure alignment with public goals. Metrics such as reduced emissions from environmental regulations or increased vaccination rates for public health mandates provide measurable indicators of success. Continuous assessment using data-driven methods helps refine mandates and enhances accountability within administrative frameworks.
example of mandate in administration Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com