Appropriations in a government budget refer to the legally authorized funds allocated by the legislature for specific government departments, agencies, or programs. For example, a government might appropriate $200 million annually to the Department of Education to support public schools, teacher salaries, and educational materials. These appropriations ensure that money is designated for priority areas and provide legal spending limits within a fiscal year. Another common appropriation example includes funds allocated to national defense, where Congress may approve $700 billion for military operations, equipment procurement, and personnel salaries. This allocation supports the government's infrastructure for national security and disaster response. Appropriations also cover social welfare programs, with specific amounts dedicated to healthcare, unemployment benefits, and housing assistance initiatives.
Table of Comparison
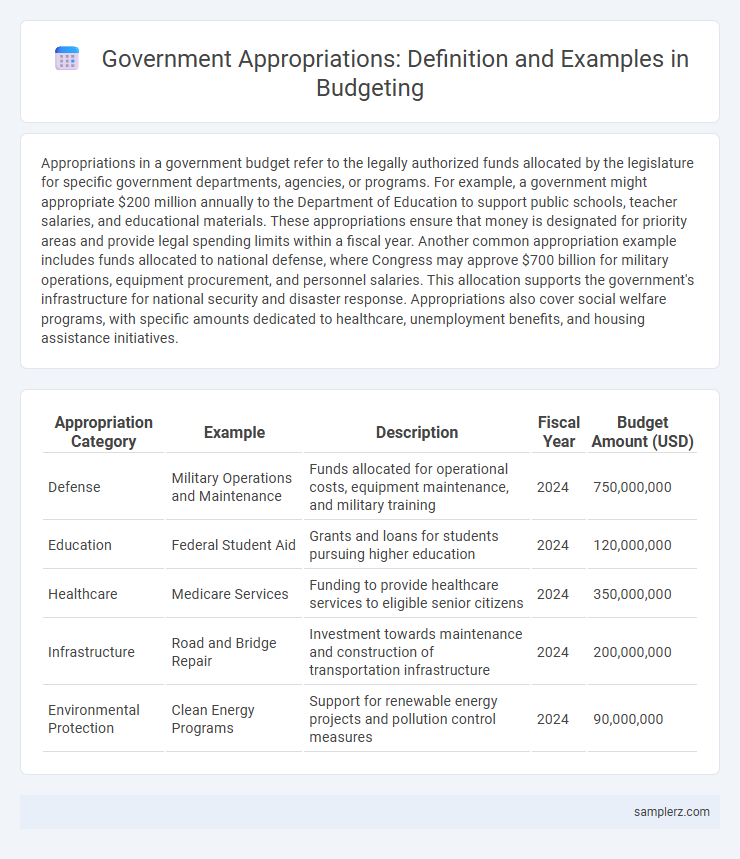
| Appropriation Category | Example | Description | Fiscal Year | Budget Amount (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defense | Military Operations and Maintenance | Funds allocated for operational costs, equipment maintenance, and military training | 2024 | 750,000,000 |
| Education | Federal Student Aid | Grants and loans for students pursuing higher education | 2024 | 120,000,000 |
| Healthcare | Medicare Services | Funding to provide healthcare services to eligible senior citizens | 2024 | 350,000,000 |
| Infrastructure | Road and Bridge Repair | Investment towards maintenance and construction of transportation infrastructure | 2024 | 200,000,000 |
| Environmental Protection | Clean Energy Programs | Support for renewable energy projects and pollution control measures | 2024 | 90,000,000 |
Definition and Importance of Appropriations in Government Budgets
Appropriations in government budgets refer to the legal authorization granted by a legislative body to allocate specific amounts of public funds for designated purposes. This financial control mechanism ensures transparency and accountability in the expenditure of taxpayer money, enabling governments to prioritize spending on essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. Proper appropriations are crucial for maintaining fiscal discipline, preventing overspending, and aligning budget execution with policy objectives.
Key Types of Appropriations in Public Finance
Key types of appropriations in public finance include annual appropriations, which fund government operations for a fiscal year; supplemental appropriations, allocated for unforeseen expenses beyond the initial budget; and continuing appropriations, allowing agencies to maintain operations when new budgets are delayed. Capital appropriations focus on funding long-term investments like infrastructure projects, while mandatory appropriations cover legally required expenditures such as Social Security and Medicare. These appropriations ensure structured financial management and prioritize spending to meet public policy objectives.
Examples of Mandatory Appropriations in National Budgets
Mandatory appropriations in national budgets include entitlement programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid, which receive funding automatically based on eligibility criteria rather than annual approval. These appropriations also cover interest payments on national debt and certain federal employee retirement benefits, ensuring continuous financial obligations are met. The predictable nature of these expenditures limits discretionary spending and shapes long-term fiscal policy decisions.
Discretionary Appropriations: Real-World Instances
Discretionary appropriations in government budgets include funding for defense programs, such as the U.S. Department of Defense allocation for military operations, equipment, and personnel salaries. Another example is education funding through the Department of Education, supporting federal grants and school improvement initiatives. Infrastructure projects financed by the Department of Transportation, like highway construction and public transit development, represent additional instances of discretionary budget appropriations.
Appropriations for Defense and Security: Case Studies
Appropriations for defense and security often constitute a significant portion of national budgets, such as the U.S. Department of Defense receiving over $700 billion in fiscal year 2023 to fund military operations, personnel, and technology development. Case studies from countries like South Korea highlight strategic allocation of defense funds towards advanced missile defense systems and cybersecurity infrastructure to counter regional threats. In contrast, Europe's NATO members prioritize appropriations for joint defense initiatives and modernization of armed forces to enhance collective security capabilities.
Healthcare and Social Welfare Appropriation Examples
Healthcare appropriations in government budgets often include funding for public hospitals, vaccination programs, and mental health services, ensuring accessible and quality care for all citizens. Social welfare appropriations allocate resources to programs such as unemployment benefits, food assistance, and child protective services to support vulnerable populations. These targeted allocations reflect governments' priorities in promoting health equity and social safety nets within national and local budget frameworks.
Education Sector Appropriations in Government Spending
Government spending on education sector appropriations typically includes funding for public schools, higher education institutions, and vocational training programs. These appropriations cover teacher salaries, infrastructure development, educational materials, and student support services to enhance learning outcomes. Prioritizing education in the budget reflects a commitment to human capital development and long-term economic growth.
Infrastructure and Public Works: Notable Appropriation Cases
Infrastructure and public works appropriations in government budgets often prioritize large-scale projects such as highway expansions, bridge repairs, and public transit system upgrades. Notable cases include the allocation of billions for the Interstate Highway System maintenance and the funding of urban mass transit improvements through the Federal Transit Administration. These appropriations ensure critical infrastructure development and maintenance, supporting economic growth and public safety nationwide.
Emergency and Supplemental Appropriations Explained
Emergency and supplemental appropriations address unforeseen government needs outside regular budgeting cycles, funding urgent responses like disaster relief, military operations, or public health crises. These appropriations are designated as emergency spending to bypass standard caps and ensure rapid allocation of resources. Examples include Hurricane Katrina relief funds and supplemental COVID-19 emergency aid bills, highlighting their critical role in flexible government financing.
Oversight and Accountability in Appropriation Processes
The government allocates appropriations for oversight agencies such as the Government Accountability Office (GAO) to ensure transparency and prevent misuse of public funds. Specific budget items include funding for audit operations, compliance monitoring, and performance evaluations of federal programs. These appropriations strengthen accountability by enabling continuous review of spending against legislative intent.
example of appropriations in budget Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com