A caucus in government refers to a meeting of members from a specific political party or group to discuss policies, strategies, and legislative priorities. For example, the House Democratic Caucus in the United States Congress is composed of all Democratic members in the House of Representatives. This caucus plays a crucial role in shaping the party's agenda, coordinating legislative efforts, and electing party leaders. State-level examples include the Republican Caucus in the Oregon Legislature, where members come together to align on state policy goals and electoral strategies. These caucuses often analyze data on voter preferences, upcoming legislation, and committee assignments to optimize political influence. By organizing members around shared goals, caucuses serve as vital entities for strategic planning and collective decision-making within parties.
Table of Comparison
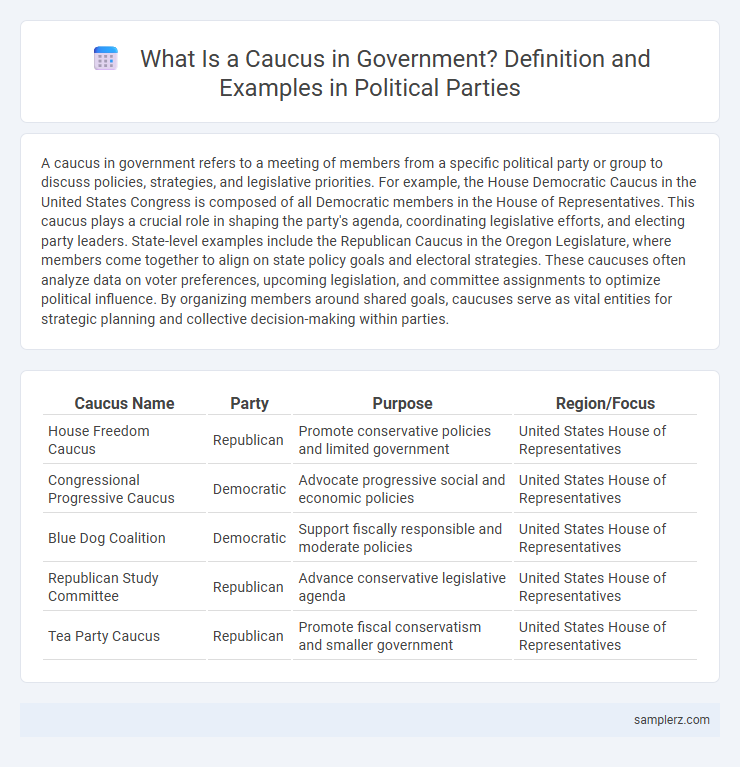
| Caucus Name | Party | Purpose | Region/Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| House Freedom Caucus | Republican | Promote conservative policies and limited government | United States House of Representatives |
| Congressional Progressive Caucus | Democratic | Advocate progressive social and economic policies | United States House of Representatives |
| Blue Dog Coalition | Democratic | Support fiscally responsible and moderate policies | United States House of Representatives |
| Republican Study Committee | Republican | Advance conservative legislative agenda | United States House of Representatives |
| Tea Party Caucus | Republican | Promote fiscal conservatism and smaller government | United States House of Representatives |
Definition and Purpose of a Party Caucus
A party caucus is a meeting of members within a specific political party in a legislative body, such as the House of Representatives or Senate, designed to discuss policies, strategize legislative agendas, and select leadership. Its primary purpose is to unify party members, ensure coordinated voting, and develop consensus on key issues to strengthen the party's influence and effectiveness in government. Examples include the House Democratic Caucus and the Senate Republican Conference, both playing critical roles in shaping legislative priorities and party discipline.
Historical Development of Caucuses in Government
The historical development of caucuses in government traces back to the early 19th century when American political parties used caucuses as key mechanisms for nominating candidates and shaping legislative agendas. Originating in the U.S. Congress, caucuses evolved from informal meetings of party leaders to structured groups representing shared interests or ideologies, such as the House Freedom Caucus and the Congressional Progressive Caucus. These caucuses have influenced policy formation, party discipline, and legislative strategy, reflecting the changing dynamics of political organization and governance over time.
Notable Caucus Examples in Major Political Parties
The Democratic Party features the Congressional Progressive Caucus, advocating for left-leaning policies on economic inequality and social justice. The Republican Party includes the House Freedom Caucus, known for its conservative stance on limited government and fiscal responsibility. These caucuses influence legislative priorities and party agendas within the U.S. Congress.
The Democratic Party Caucus: Structure and Process
The Democratic Party Caucus operates as a critical organizing body within the U.S. Congress, consisting of all Democratic members in both the House of Representatives and the Senate. It establishes leadership roles, coordinates legislative strategies, and facilitates communication among Democratic lawmakers to advance party priorities. The caucus employs structured meetings and committees to deliberate policy issues, ensuring unified decision-making and effective advocacy for the party's platform.
The Republican Party Caucus: Key Features
The Republican Party Caucus serves as a critical assembly of party members who coordinate legislative strategies and unify policy positions within the government. Key features include strict adherence to conservative principles, a structured leadership hierarchy, and regular caucus meetings that shape party agendas on issues such as fiscal responsibility and national security. This caucus influences legislative outcomes by consolidating votes and fostering collaboration among Republican lawmakers at both state and federal levels.
State-Level Caucuses: Unique Practices and Variations
State-level caucuses exhibit unique practices shaped by regional political cultures, such as Iowa's Democratic caucus, which employs a public alignment process influencing delegate allocation. Minnesota's Republican caucus integrates township meetings, reflecting localized decision-making traditions that affect candidate endorsement and grassroots mobilization. Variations in caucus rules and participation eligibility across states demonstrate the diversity in party engagement and influence the broader electoral dynamics.
The Iowa Caucus: A Case Study
The Iowa Caucus serves as a pivotal example of a state-level party caucus, shaping presidential nomination outcomes through its early voting process. Participants gather in local precincts to discuss and publicly realign their candidate preferences, providing a grassroots measure of party support. This event is strategically significant, offering momentum and media attention that can influence subsequent primaries and caucuses nationwide.
Caucus vs. Primary: Core Differences and Impacts
A caucus functions as a local gathering where party members openly discuss and select candidates, emphasizing direct participation and debate unlike the confidential, ballot-based primary elections. Caucuses often foster grassroots enthusiasm and stronger party cohesion by requiring active engagement, while primaries provide a broader, more inclusive voting process that can increase overall turnout. The contrasting structures impact candidate momentum and party dynamics, influencing campaign strategies and voter mobilization efforts differently.
Caucus Outcomes and Their Influence on Party Policies
Caucus outcomes significantly shape party policies by consolidating member positions on key legislative priorities, influencing the party's platform and strategic direction. For example, the Congressional Progressive Caucus often pushes the Democratic Party towards more progressive policies on healthcare and climate change, affecting legislative proposals and party messaging. This internal consensus-building process enables parties to present unified stances, enhancing coherence in policy advocacy and election strategies.
The Role of Caucuses in Leadership Selection
Caucuses in political parties serve as critical forums where party members convene to deliberate and decide on leadership candidates, shaping the party's strategic direction. By facilitating consensus-building and promoting internal democracy, caucuses influence key leadership appointments and policy priorities. Their role in leadership selection ensures that chosen leaders have strong support within the party, enhancing cohesion and effectiveness in governance.
example of caucus in party Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com