A recess in a government committee occurs when members temporarily pause their formal meetings to rest, gather more information, or address pressing issues before resuming discussions. During a recess, committee members may consult experts, review additional data, or negotiate behind the scenes to refine legislation or policy proposals. This break allows for more informed decision-making and enhances the committee's overall effectiveness. In congressional committees, a recess can vary in length from a few minutes to several days, depending on the complexity of the topic and the need for further analysis. Records of recesses are maintained in official committee minutes, which detail the time and purpose of the pause. The use of recesses supports transparency and accountability by documenting how committees manage their workflow and deliberations.
Table of Comparison
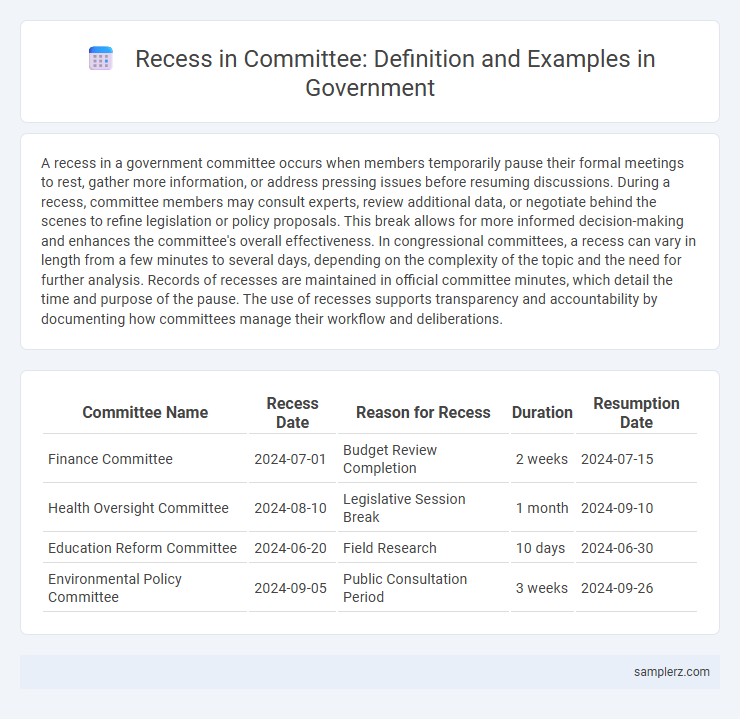
| Committee Name | Recess Date | Reason for Recess | Duration | Resumption Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finance Committee | 2024-07-01 | Budget Review Completion | 2 weeks | 2024-07-15 |
| Health Oversight Committee | 2024-08-10 | Legislative Session Break | 1 month | 2024-09-10 |
| Education Reform Committee | 2024-06-20 | Field Research | 10 days | 2024-06-30 |
| Environmental Policy Committee | 2024-09-05 | Public Consultation Period | 3 weeks | 2024-09-26 |
Understanding the Concept of Committee Recess
A committee recess occurs when members temporarily pause their deliberations to gather additional information, consult experts, or allow for further research and reflection before resuming discussions. This procedural break supports more informed decision-making and enhances the quality of legislative outcomes by preventing premature conclusions. Understanding committee recess is essential for comprehending how governmental bodies manage complex policy issues through strategic pauses in their workflow.
Common Reasons for Calling a Committee Recess
Committees often call recesses to allow members time to review complex documents or gather additional information critical for informed decision-making. Recesses provide opportunities to negotiate unresolved issues and build consensus among diverse stakeholders. Scheduling conflicts or the need for expert testimony can also prompt temporary pauses in committee proceedings.
How Committees Decide to Recess
Committees decide to recess based on the need to gather additional information, allow members to consult with external experts, or provide time for drafting amendments. Voting procedures for recess often require a majority agreement, reflecting the committee's operational rules and urgency of pending issues. Recesses facilitate focused deliberations, ensuring decisions are informed and strategically timed within legislative sessions.
Procedural Steps During a Committee Recess
A recess in a government committee involves temporarily halting meetings to allow members to review documents, consult experts, or gather additional information. During this procedural step, the chair officially announces the recess duration and sets expectations for when the committee will reconvene. Members typically use this time to analyze legislative proposals, prepare amendments, and strategize discussions for subsequent sessions.
Historical Examples of Recesses in Government Committees
Historical examples of recesses in government committees include the U.S. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations taking a recess during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962 to allow for closed-door briefings and strategic deliberations. The House Judiciary Committee observed extended recesses amidst Watergate investigations in the 1970s to manage evidentiary reviews and legal consultations. These recesses facilitated crucial pauses that enabled members to gather critical information and coordinate responses during pivotal political events.
Effects of Committee Recesses on Legislative Processes
Committee recesses in government can lead to delays in legislative decision-making by pausing critical discussions and evaluations of proposed bills. These interruptions may hinder the momentum of legislative agendas, causing extended timelines for policy enactment and reducing overall efficiency in lawmaking. Legislative bodies often face challenges in maintaining continuity and stakeholder engagement during recess periods, impacting the timely resolution of key issues.
Rules Governing Committee Recesses
Committee recesses are governed by specific rules that dictate the duration and conditions under which a committee may pause its sessions. These regulations often require a formal motion and approval by the majority of committee members before entering recess. Rules also specify whether committee business can be conducted during the recess and how reconvening procedures must be followed to maintain transparency and order.
Key Differences Between Adjournment and Recess
A recess in a government committee refers to a temporary pause in meetings that allows members to take breaks without ending the session, whereas adjournment denotes the formal conclusion of the meeting, stopping all discussions until the next scheduled gathering. Recesses maintain the committee's continuity and preserve pending business for resumption, while adjournments clear the agenda and require reintroduction of unresolved motions in future meetings. Understanding this distinction is crucial for procedural accuracy and efficient legislative workflow management.
Notable Controversies Surrounding Committee Recesses
Committee recesses have sparked notable controversies, particularly when used to delay or avoid contentious legislative decisions. In 2019, the U.S. House Judiciary Committee's recesses during the impeachment inquiry raised accusations of procedural obfuscation. Critics argue such recesses undermine transparency and impede timely legislative oversight, fueling partisan conflict.
Best Practices During Committee Recess Periods
During committee recess periods, maintaining comprehensive records and distributing detailed briefing materials to members ensures continuity and preparedness for upcoming sessions. Establishing clear lines of communication through regular updates and virtual check-ins enhances member engagement and facilitates effective collaboration. Prioritizing strategic planning and research initiatives during recess optimizes productivity and strengthens committee outcomes.
example of recess in committee Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com