A caucus in an election refers to a meeting of members of a specific political party or faction to select candidates or decide policy. For example, the Iowa Democratic Caucus is a prominent early event in the U.S. presidential primary process. During this caucus, party members gather in precincts to discuss and vote on their preferred candidates, influencing the allocation of delegates. The caucus system emphasizes grassroots participation and community deliberation over traditional primaries. It allows parties to assess candidate support through active member engagement rather than simple ballot casting. This method plays a crucial role in shaping the momentum and media coverage of election campaigns by highlighting candidate viability among dedicated party activists.
Table of Comparison
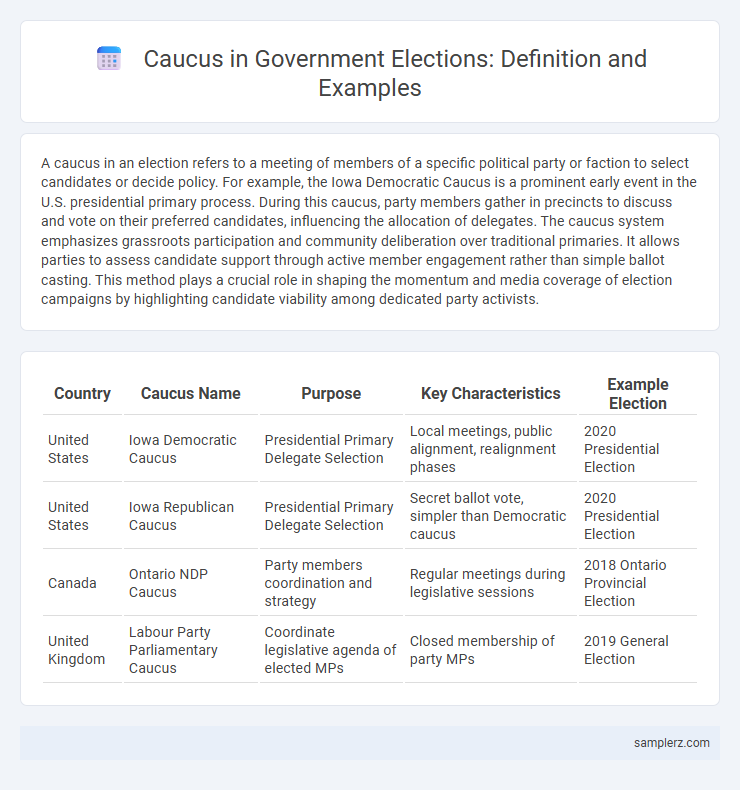
| Country | Caucus Name | Purpose | Key Characteristics | Example Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Iowa Democratic Caucus | Presidential Primary Delegate Selection | Local meetings, public alignment, realignment phases | 2020 Presidential Election |
| United States | Iowa Republican Caucus | Presidential Primary Delegate Selection | Secret ballot vote, simpler than Democratic caucus | 2020 Presidential Election |
| Canada | Ontario NDP Caucus | Party members coordination and strategy | Regular meetings during legislative sessions | 2018 Ontario Provincial Election |
| United Kingdom | Labour Party Parliamentary Caucus | Coordinate legislative agenda of elected MPs | Closed membership of party MPs | 2019 General Election |
Understanding the Caucus System in Elections
The Iowa Democratic Caucus is a prime example of the caucus system in elections, where voters gather in local meetings to discuss and select delegates for party conventions. Unlike primary elections, caucuses emphasize active participation, debate, and consensus-building among party members, reflecting grassroots political engagement. This process influences candidate momentum and media coverage early in the presidential election cycle, highlighting its strategic importance in American politics.
Historical Overview of Caucuses in Government
Caucuses in government have historically played a crucial role in shaping party platforms and candidate selection, with the earliest known example being the Iowa caucus established in 1972, which gained prominence as the first major electoral event in the presidential nomination process. This system encourages direct voter participation and grassroots engagement, differing from primary elections by emphasizing local discussion and consensus-building. Over time, caucuses have evolved into influential forums for party members to strategize and mobilize support, impacting election outcomes and legislative priorities nationwide.
Key Examples of Caucus Processes in U.S. Elections
Key examples of caucus processes in U.S. elections include the Iowa caucuses, which are the first major electoral event of the presidential primary season and set the tone for subsequent contests. During these caucuses, registered party members gather at local precincts to discuss and vote publicly for their preferred candidates, emphasizing grassroots participation. Other notable caucus states, such as Nevada and Wyoming, utilize this method to engage party activists and allocate delegates based on real-time consensus-building discussions.
Notable State Caucuses: Iowa and Nevada
The Iowa caucus is a critical early contest in the U.S. presidential election process, known for its influence in shaping candidate momentum due to its first-in-the-nation status. Nevada's caucus, with a more diverse electorate, provides a strategic test for candidates appealing to Latino and labor constituencies. Both state caucuses utilize in-person gatherings to select delegates, differing from primary elections' ballot-based voting system.
Differences Between Caucuses and Primaries
Caucuses, such as the Iowa Democratic Caucus, involve local gatherings where party members openly discuss and vote for their preferred candidates, emphasizing public debate and consensus-building. Primaries, in contrast, function like standard elections where voters cast secret ballots independently, prioritizing privacy and broader participation. The key difference lies in the caucus's interactive, community-driven process versus the primary's straightforward, private voting mechanism.
Caucus Rules and Procedures Explained
Caucus rules and procedures vary by state but typically involve registered party members gathering in local meetings to discuss and select candidates. Participants express preferences through public voting or physical alignment, with delegates chosen to represent the winning candidate at higher-level conventions. These processes emphasize transparency and grassroots participation, requiring strict adherence to party-specific guidelines to ensure fairness and legitimacy in the electoral system.
Voter Participation in Election Caucuses
Election caucuses, such as the Iowa Democratic Caucus, serve as pivotal forums for voter participation by allowing registered party members to discuss and select their preferred candidates publicly. These gatherings emphasize grassroots involvement, often requiring voters to attend in person and engage in real-time decision-making processes that differ from traditional secret ballots. Voter turnout in caucuses tends to be lower than primaries, but those who participate often demonstrate a high level of political engagement and commitment.
Impact of Caucus Results on Political Parties
Caucus results significantly influence political parties by determining delegate allocation, shaping candidate viability, and signaling voter preferences early in the election cycle. This process can strengthen party unity by highlighting emerging leaders and policy priorities, while also revealing internal divisions that may require strategic adjustments. The outcomes often direct resource distribution and campaign strategies, ultimately affecting the party's success in general elections.
Influential Caucus Outcomes in Past Elections
The Iowa Democratic Caucus has historically set the stage for presidential primaries by providing early momentum to candidates like Barack Obama in 2008 and Pete Buttigieg in 2020, influencing national perceptions and fundraising. Similarly, the Congressional Black Caucus has played a pivotal role in shaping legislative priorities and endorsing candidates who advance civil rights and social justice agendas in key elections. These influential caucuses demonstrate how strategic group endorsements and coordinated voter mobilization can sway election results and policy directions.
The Role of Caucuses in Shaping Government Leadership
Caucuses, such as the U.S. Congressional caucuses, play a critical role in shaping government leadership by organizing members around shared interests or policy goals, thereby influencing legislative agendas and leadership elections. These groups facilitate coordination among legislators to consolidate support for party leaders or policy initiatives, directly impacting the selection of committee chairs and party leadership. The strength and influence of caucuses can determine the balance of power within government institutions and shape the direction of political leadership.
example of caucus in election Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com