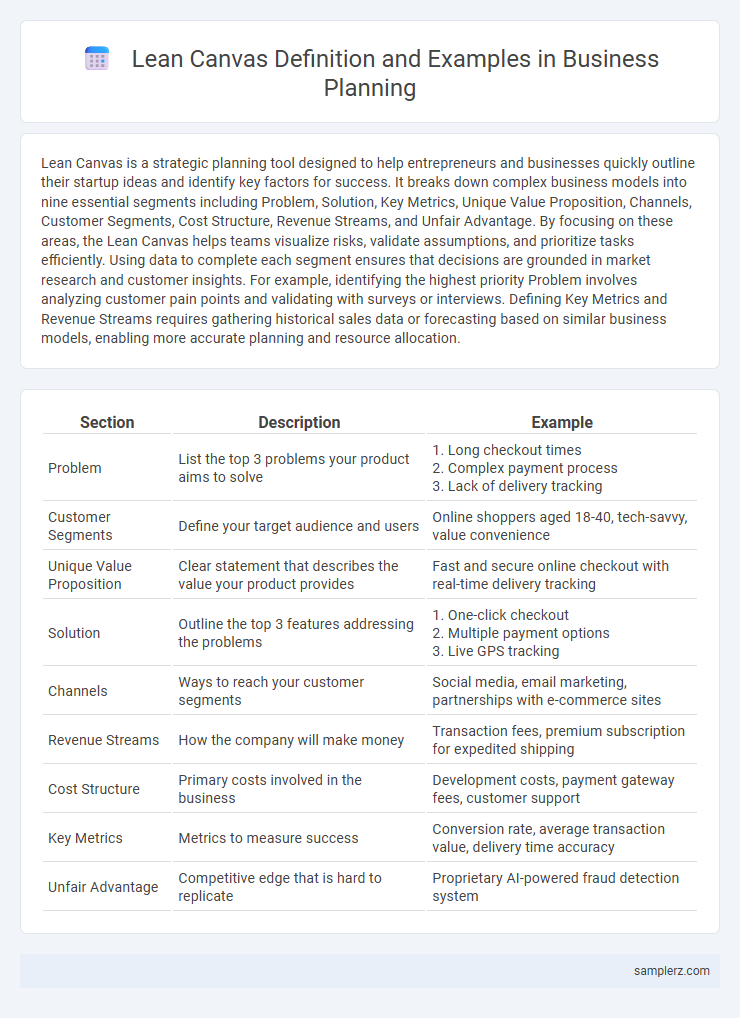
Lean Canvas is a strategic planning tool designed to help entrepreneurs and businesses quickly outline their startup ideas and identify key factors for success. It breaks down complex business models into nine essential segments including Problem, Solution, Key Metrics, Unique Value Proposition, Channels, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams, and Unfair Advantage. By focusing on these areas, the Lean Canvas helps teams visualize risks, validate assumptions, and prioritize tasks efficiently. Using data to complete each segment ensures that decisions are grounded in market research and customer insights. For example, identifying the highest priority Problem involves analyzing customer pain points and validating with surveys or interviews. Defining Key Metrics and Revenue Streams requires gathering historical sales data or forecasting based on similar business models, enabling more accurate planning and resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Problem | List the top 3 problems your product aims to solve | 1. Long checkout times 2. Complex payment process 3. Lack of delivery tracking |
| Customer Segments | Define your target audience and users | Online shoppers aged 18-40, tech-savvy, value convenience |
| Unique Value Proposition | Clear statement that describes the value your product provides | Fast and secure online checkout with real-time delivery tracking |
| Solution | Outline the top 3 features addressing the problems | 1. One-click checkout 2. Multiple payment options 3. Live GPS tracking |
| Channels | Ways to reach your customer segments | Social media, email marketing, partnerships with e-commerce sites |
| Revenue Streams | How the company will make money | Transaction fees, premium subscription for expedited shipping |
| Cost Structure | Primary costs involved in the business | Development costs, payment gateway fees, customer support |
| Key Metrics | Metrics to measure success | Conversion rate, average transaction value, delivery time accuracy |
| Unfair Advantage | Competitive edge that is hard to replicate | Proprietary AI-powered fraud detection system |
Introduction to Lean Canvas in Business Planning
Lean Canvas is a strategic tool designed to streamline business planning by focusing on key elements such as problem identification, customer segments, unique value propositions, and revenue streams. Its concise, one-page format allows entrepreneurs to quickly visualize and iterate on their business models while minimizing risks. By emphasizing actionable metrics and customer-centric insights, Lean Canvas enhances decision-making and accelerates the path from concept to market validation.
Key Components of the Lean Canvas Model
The Lean Canvas model includes key components such as Problem, Solution, Key Metrics, Unique Value Proposition, Channels, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams, and Unfair Advantage. Each element focuses on identifying critical business assumptions to optimize startup success and reduce risks. This strategic planning tool helps entrepreneurs quickly validate ideas through iterative testing and customer feedback.
Identifying Customer Segments with Lean Canvas
Identifying customer segments using Lean Canvas involves pinpointing specific groups of potential customers based on demographics, behaviors, and pain points to tailor value propositions effectively. This process enables entrepreneurs to concentrate on high-priority market niches and validate assumptions through targeted problem-solution fit testing. Lean Canvas facilitates clear visualization of customer profiles, enhancing strategic planning and resource allocation for product-market fit success.
Defining the Unique Value Proposition
A Lean Canvas defines the Unique Value Proposition (UVP) by pinpointing the key benefits that differentiate a business from competitors, addressing specific customer pain points. This UVP emphasizes clear, concise messaging to quickly convey why customers should choose the product or service. Effective UVPs improve market fit and guide strategic planning by aligning product features with customer needs.
Problem and Solution Mapping through Lean Canvas
Problem and Solution Mapping in Lean Canvas is a critical step in business planning that identifies key customer pain points and aligns actionable solutions to address them effectively. By clearly defining the problem segments, entrepreneurs can tailor value propositions and prioritize features that directly meet market needs, increasing the likelihood of product-market fit. This targeted approach reduces waste and accelerates validation cycles, enhancing overall business model clarity and adaptability.
Channels: How Your Product Reaches Customers
Lean Canvas channels include direct sales, online platforms, and strategic partnerships to effectively deliver products to customers. Utilizing multiple channels like social media marketing, email campaigns, and retail distribution maximizes product accessibility. Clear identification of the most cost-effective channels ensures optimized customer acquisition and growth.
Revenue Streams and Cost Structure Analysis
Lean Canvas emphasizes identifying diverse Revenue Streams such as subscription fees, one-time payments, and affiliate commissions to maximize profitability. Analyzing Cost Structure involves categorizing fixed and variable expenses, including production costs, marketing budgets, and operational overheads, to optimize resource allocation. Clear mapping of these financial elements enables agile pivoting and sustainable business growth.
Validating Hypotheses Using Lean Canvas
Validating hypotheses using Lean Canvas involves systematically testing assumptions about customer problems, solutions, and market fit. Entrepreneurs identify key risks by mapping out problem statements, unique value propositions, and early adopters on the canvas. This structured approach accelerates learning through rapid experimentation and iterative feedback loops, minimizing wasted resources and increasing the likelihood of product-market fit.
Lean Canvas for Startups: Real-World Examples
Lean Canvas for startups offers a practical framework to streamline business planning by focusing on problem identification, unique value propositions, customer segments, and key metrics. Real-world examples include Airbnb, which used Lean Canvas to validate demand for short-term rentals and refine its customer acquisition strategy, and Dropbox, leveraging the canvas to rapidly test hypotheses around file sharing needs and viral growth mechanisms. These cases highlight how Lean Canvas accelerates iteration, minimizes waste, and supports scalable growth for emerging ventures.
Steps to Create Your Own Lean Canvas for Business Planning
Identify your business problem, customer segments, and unique value proposition to form the foundation of your Lean Canvas. Outline your key metrics, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams to visualize how your business will operate and generate profit. Validate assumptions through continuous customer feedback and iterate your Lean Canvas to enhance strategic decision-making and reduce risks.
example of lean canvas in planning Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com