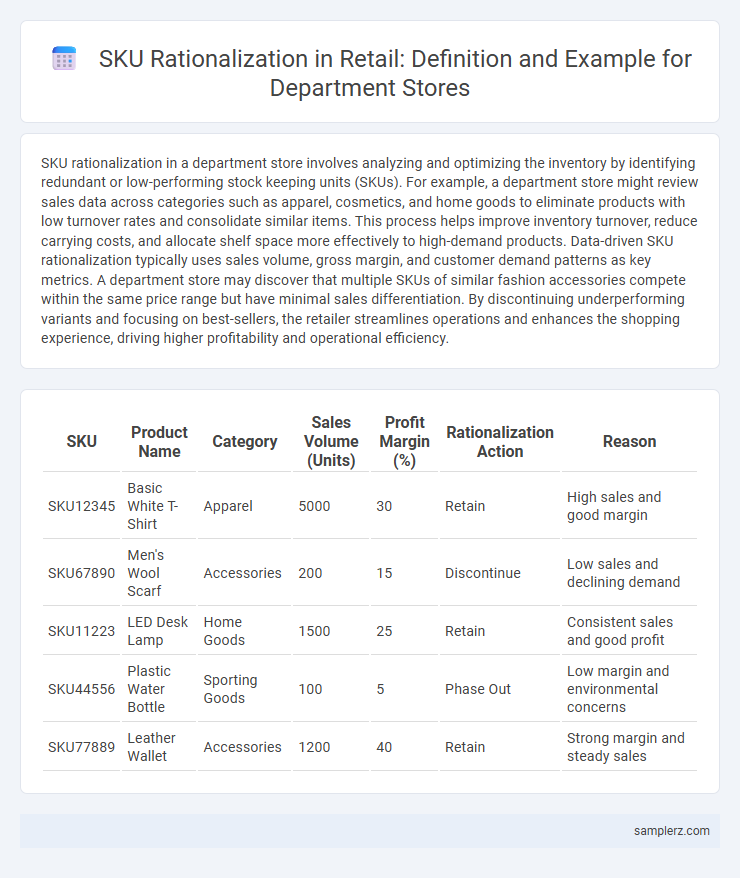
SKU rationalization in a department store involves analyzing and optimizing the inventory by identifying redundant or low-performing stock keeping units (SKUs). For example, a department store might review sales data across categories such as apparel, cosmetics, and home goods to eliminate products with low turnover rates and consolidate similar items. This process helps improve inventory turnover, reduce carrying costs, and allocate shelf space more effectively to high-demand products. Data-driven SKU rationalization typically uses sales volume, gross margin, and customer demand patterns as key metrics. A department store may discover that multiple SKUs of similar fashion accessories compete within the same price range but have minimal sales differentiation. By discontinuing underperforming variants and focusing on best-sellers, the retailer streamlines operations and enhances the shopping experience, driving higher profitability and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| SKU | Product Name | Category | Sales Volume (Units) | Profit Margin (%) | Rationalization Action | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SKU12345 | Basic White T-Shirt | Apparel | 5000 | 30 | Retain | High sales and good margin |
| SKU67890 | Men's Wool Scarf | Accessories | 200 | 15 | Discontinue | Low sales and declining demand |
| SKU11223 | LED Desk Lamp | Home Goods | 1500 | 25 | Retain | Consistent sales and good profit |
| SKU44556 | Plastic Water Bottle | Sporting Goods | 100 | 5 | Phase Out | Low margin and environmental concerns |
| SKU77889 | Leather Wallet | Accessories | 1200 | 40 | Retain | Strong margin and steady sales |
Introduction to SKU Rationalization in Department Stores
SKU rationalization in department stores involves systematically analyzing inventory data to identify underperforming or redundant stock keeping units, enabling retailers to optimize shelf space and improve inventory turnover. By evaluating sales velocity, gross margins, and customer demand patterns, retailers can eliminate slow-moving SKUs and focus on high-impact products, leading to increased profitability and enhanced customer satisfaction. Effective SKU rationalization also supports streamlined supply chain management and reduces operational costs in large department store environments.
Identifying Overlapping SKUs in Product Categories
SKU rationalization in department stores involves identifying overlapping SKUs within product categories to streamline inventory and improve profitability. By analyzing sales data, inventory levels, and product attributes, retailers can pinpoint redundant items that serve similar customer needs but dilute overall sales performance. Eliminating these overlapping SKUs reduces operational costs and enhances shelf space efficiency while allowing better focus on high-demand, differentiated products.
Data-Driven Analysis: Sales Performance and Shelf Space
Analyzing sales performance data of over 10,000 SKUs revealed that 30% accounted for 85% of total revenue, prompting a strategic reduction in low-performing items. Optimizing shelf space by reallocating areas from underperforming SKUs to bestsellers increased overall sales by 15%. Data-driven SKU rationalization enhanced inventory turnover rates and improved customer satisfaction through a more curated product selection.
Streamlining Apparel Collections through SKU Rationalization
SKU rationalization in department stores streamlines apparel collections by identifying and eliminating underperforming SKUs, thereby optimizing shelf space and inventory turnover. Data analytics focus on sales velocity, profit margins, and customer preferences to retain high-demand styles and sizes. This targeted reduction in SKUs enhances operational efficiency, reduces carrying costs, and improves overall merchandise mix appeal.
Case Study: Reducing Redundant Home Goods SKUs
A leading department store implemented SKU rationalization by analyzing sales data and customer preferences to eliminate underperforming home goods products. The initiative reduced redundant SKUs by 30%, streamlining inventory and improving shelf space efficiency. This resulted in a 15% increase in turnover rate and reduced carrying costs in the home goods category.
Impact of SKU Rationalization on Inventory Turnover
SKU rationalization in department stores streamlines product assortments, resulting in higher inventory turnover by reducing slow-moving or obsolete items. By focusing on high-performing SKUs, stores can optimize stock levels, minimize holding costs, and accelerate cash flow. This strategic inventory management enhances operational efficiency and boosts overall profitability.
Enhancing Customer Experience with Curated Assortments
SKU rationalization in department stores involves analyzing sales data and customer preferences to eliminate underperforming products, thereby streamlining the inventory to feature high-demand and trending items. Curated assortments enhance customer experience by reducing choice overload, making it easier for shoppers to find relevant, quality products aligned with their tastes and needs. Optimizing SKUs not only increases shelf efficiency but also drives higher customer satisfaction and repeat visits through targeted, engaging selections.
Tools and Technologies for Effective SKU Rationalization
Implementing advanced inventory management systems and AI-powered analytics enables department stores to perform precise SKU rationalization by identifying underperforming products within the Tools and Technologies category. Utilizing data-driven tools like predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms helps optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and improve product assortment decisions. Integration of real-time sales data and customer behavior insights maximizes operational efficiency and boosts profitability in SKU management.
Collaboration Strategies Between Merchandising and Supply Chain
Merchandising and supply chain teams in department stores streamline SKU rationalization by sharing real-time sales analytics and inventory turnover data to identify underperforming products. Collaborative forecasting and demand planning reduce excess stock and optimize shelf space, enhancing product assortment aligned with customer preferences. Joint supplier negotiations prioritize high-velocity SKUs, improving inventory turnover rates and reducing carrying costs.
Measuring Success: KPIs Post-SKU Rationalization
Post-SKU rationalization in department stores, key performance indicators such as inventory turnover rate, sales per square foot, and gross margin return on investment (GMROI) serve as critical measures of success. Monitoring a reduction in stockouts and carrying costs alongside an increase in customer satisfaction scores indicates effective SKU optimization. Tracking these KPIs allows retailers to evaluate the impact of SKU rationalization on operational efficiency and profitability.
example of SKU rationalization in department store Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com