SKU rationalization in a boutique involves analyzing sales data and customer preferences to identify underperforming products. By focusing on high-margin and fast-selling items, boutiques can reduce inventory costs and enhance the shopping experience. Eliminating slow-moving SKUs allows for better stock management and improved turnover rates. Retailers use SKU rationalization to optimize shelf space and improve profitability in boutique settings. Data analysis reveals patterns in customer demand, enabling boutiques to tailor their assortments more effectively. This process helps boutiques maintain a curated selection that aligns with brand identity and market trends.
Table of Comparison
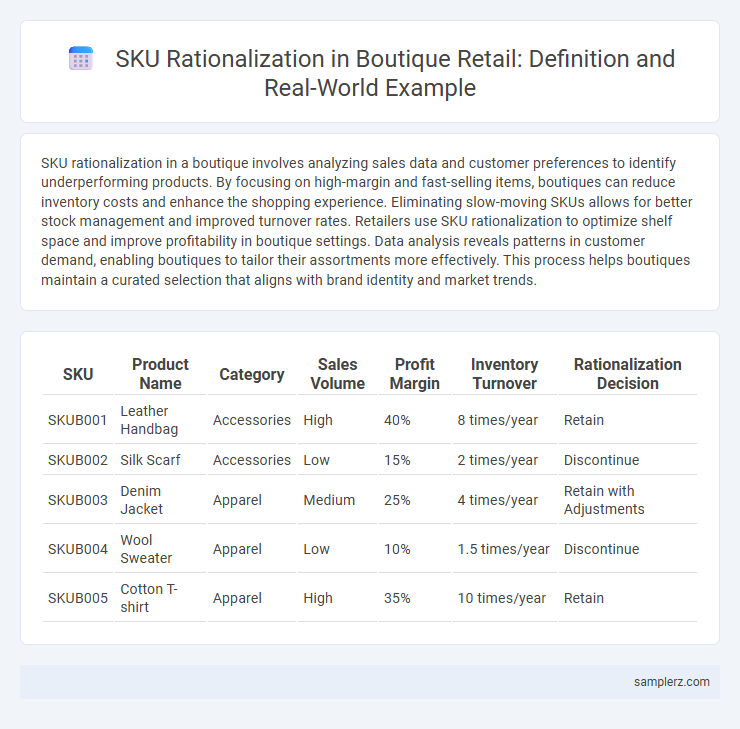
| SKU | Product Name | Category | Sales Volume | Profit Margin | Inventory Turnover | Rationalization Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SKUB001 | Leather Handbag | Accessories | High | 40% | 8 times/year | Retain |
| SKUB002 | Silk Scarf | Accessories | Low | 15% | 2 times/year | Discontinue |
| SKUB003 | Denim Jacket | Apparel | Medium | 25% | 4 times/year | Retain with Adjustments |
| SKUB004 | Wool Sweater | Apparel | Low | 10% | 1.5 times/year | Discontinue |
| SKUB005 | Cotton T-shirt | Apparel | High | 35% | 10 times/year | Retain |
Understanding SKU Rationalization in Boutique Retail
SKU rationalization in boutique retail involves analyzing sales data, customer preferences, and inventory turnover to identify underperforming products for removal. By focusing on high-demand items and eliminating redundant or low-margin SKUs, boutiques improve stock efficiency and enhance the customer shopping experience. This targeted approach reduces carrying costs and optimizes product assortment to drive profitability.
Identifying Low-Performing SKUs in a Boutique Setting
Analyzing sales data and inventory turnover rates helps identify low-performing SKUs in a boutique setting, enabling targeted removal of underperforming products. For example, tracking SKUs with less than 10 units sold per month and high holding costs can reveal items that drain resources without generating revenue. Removing these SKUs optimizes shelf space, reduces carrying costs, and increases overall boutique profitability.
Criteria for Boutique SKU Rationalization
SKU rationalization in boutiques focuses on criteria such as sales velocity, profit margins, and inventory turnover rates to optimize product assortment. Customer preferences and seasonal trends are analyzed to ensure alignment with brand identity and maximize shelf space efficiency. Incorporating data-driven insights from point-of-sale systems enhances decision-making and reduces underperforming SKUs, improving overall profitability.
The Impact of SKU Rationalization on Inventory Efficiency
SKU rationalization in boutique retail streamlines product assortments by eliminating slow-moving or redundant SKUs, significantly improving inventory turnover rates. This process reduces carrying costs and minimizes stock obsolescence, enhancing overall inventory efficiency. Optimized SKU portfolios enable boutiques to allocate shelf space more effectively, boosting sales per square foot and customer satisfaction.
Boutique Case Study: Streamlining Accessories Selection
A boutique reduced its SKU count by 30% through a targeted SKU rationalization process focused on accessories, eliminating underperforming items that contributed less than 5% to sales. By analyzing sales data and customer preferences, the boutique optimized inventory turnover and improved shelf space efficiency. This strategic reduction enhanced profitability while maintaining a curated selection aligned with brand identity and customer demand.
Data-Driven Decisions for SKU Reduction in Boutiques
Boutique retailers use POS data and inventory turnover rates to identify slow-moving SKUs, enabling precise stock optimization. Analyzing customer purchase patterns and seasonal trends helps prioritize high-demand items, reducing overstock and markdowns. Implementing data-driven SKU rationalization increases profitability by streamlining product assortment and enhancing inventory efficiency.
Benefits of Eliminating Redundant SKUs for Small Retailers
Eliminating redundant SKUs in boutique retail enhances inventory management by reducing storage costs and minimizing stockouts. Small retailers can streamline purchasing processes, improving cash flow and allowing investment in high-demand products. This targeted SKU rationalization increases operational efficiency and boosts profit margins through better product assortment alignment with customer preferences.
Customer Experience Improvements After SKU Rationalization
Reducing the number of SKUs in a boutique can streamline inventory management and enhance product availability, leading to faster restocking and fewer out-of-stock scenarios. This optimization allows staff to better assist customers with expert knowledge on a curated selection, improving personalized shopping experiences. Enhanced assortments based on customer preferences increase satisfaction and drive repeat visits, ultimately boosting boutique sales and brand loyalty.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Boutique SKU Optimization
Tracking sell-through rates and gross margin return on investment (GMROI) are critical KPIs for measuring the success of SKU rationalization in boutiques, revealing how well each product drives profitability and turnover. Monitoring inventory turnover ratio helps identify slow-moving SKUs that tie up capital, while customer purchase frequency and average transaction value indicate the impact on consumer behavior post-optimization. Analyzing these metrics enables boutiques to streamline assortments, reduce carrying costs, and enhance overall retail performance.
Next Steps: Maintaining a Curated Boutique SKU Portfolio
To maintain a curated boutique SKU portfolio, regularly analyze sales performance metrics and customer preferences to identify underperforming products for removal. Implement a dynamic replenishment strategy that prioritizes high-margin and fast-selling SKUs while limiting new product introductions based on market trends. Leverage inventory management software to monitor stock levels, ensuring optimal variety without overstocking, thereby enhancing profitability and customer satisfaction.
example of SKU rationalization in boutique Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com