Inventory shrinkage in retail occurs when the actual stock count is less than the recorded inventory levels in the system. This discrepancy can result from theft, damage, administrative errors, or supplier fraud. For example, a clothing store may record 1,000 units of a particular shirt, but physical counts reveal only 950 units, indicating a shrinkage of 50 items. Shrinkage impacts a retailer's revenue and profitability by causing lost sales opportunities and increased operational costs. Data analytics tools help identify patterns and hot spots where shrinkage is prevalent, often highlighting specific stores or product categories like electronics or cosmetics. Effective loss prevention strategies focus on enhancing inventory tracking accuracy and implementing security measures to reduce shrinkage rates.
Table of Comparison
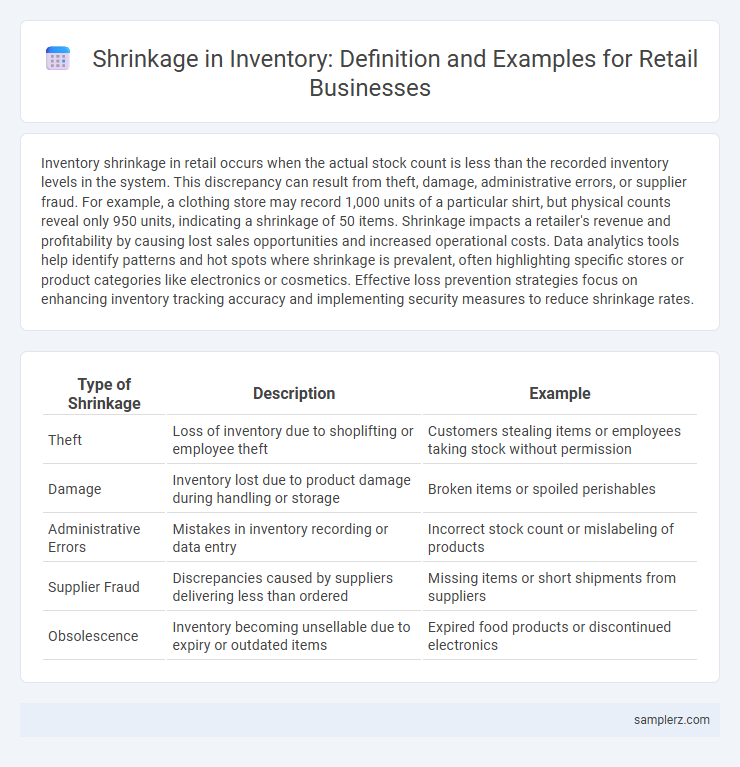
| Type of Shrinkage | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Theft | Loss of inventory due to shoplifting or employee theft | Customers stealing items or employees taking stock without permission |
| Damage | Inventory lost due to product damage during handling or storage | Broken items or spoiled perishables |
| Administrative Errors | Mistakes in inventory recording or data entry | Incorrect stock count or mislabeling of products |
| Supplier Fraud | Discrepancies caused by suppliers delivering less than ordered | Missing items or short shipments from suppliers |
| Obsolescence | Inventory becoming unsellable due to expiry or outdated items | Expired food products or discontinued electronics |
Common Causes of Inventory Shrinkage in Retail
Inventory shrinkage in retail frequently results from shoplifting, employee theft, and administrative errors such as inaccurate record-keeping or mislabeling. Supply chain issues, including damaged goods and supplier fraud, also significantly contribute to inventory losses. Effective inventory management systems and loss prevention strategies can mitigate these common causes of shrinkage.
Theft as a Major Contributor to Inventory Shrinkage
Theft accounts for approximately 40% to 60% of total inventory shrinkage in retail environments, significantly impacting profit margins and operational efficiency. Shoplifting by customers and employee theft are primary contributors, with organized retail crime causing multi-million dollar losses annually. Implementing advanced security measures like RFID tags and surveillance systems helps mitigate theft-related shrinkage and improve inventory accuracy.
Employee Fraud and Its Impact on Retail Stock Loss
Employee fraud significantly contributes to retail inventory shrinkage through tactics like unauthorized discounts, employee theft, and manipulation of sales records. This type of shrinkage directly affects stock levels, reducing available products and leading to financial losses that harm overall profitability. Implementing strict inventory controls and employee monitoring systems can mitigate these risks and preserve retail stock integrity.
Administrative Errors Leading to Inventory Discrepancies
Administrative errors, such as incorrect data entry or mislabeling products, frequently cause inventory shrinkage in retail environments. These discrepancies often result from inaccurate stock counts, improper documentation, or failure to update inventory management systems promptly. Retailers experiencing administrative errors can see significant financial losses and disruptions in supply chain efficiency.
Supplier Fraud: How Vendor Practices Cause Shrinkage
Supplier fraud significantly contributes to inventory shrinkage in retail through practices like short shipments, where vendors knowingly deliver fewer products than invoiced, and invoice padding, which involves charging retailers for goods not delivered. Fake returns occur when suppliers process returns for nonexistent or previously sold items, artificially inflating stock records and causing losses. Such fraudulent vendor activities undermine inventory accuracy and directly impact retail profit margins.
Damage and Spoilage: Unseen Sources of Inventory Loss
Damage and spoilage account for a significant portion of retail inventory shrinkage, often caused by improper handling, poor storage conditions, and expired products. Perishable goods such as fresh produce, dairy, and meat are particularly susceptible to spoilage, resulting in both financial loss and waste. Implementing rigorous inventory management systems and regular quality inspections helps minimize these unseen losses in retail operations.
Misplacement and Miscounts in Retail Inventory
Shrinkage in retail inventory often results from misplacement, where products are incorrectly shelved or stored, causing lost sales and distorted stock levels. Miscounts during manual inventory audits lead to inaccurate stock records, affecting replenishment decisions and profitability. Effective inventory management systems and regular cycle counts help mitigate errors related to misplacement and miscounts, reducing overall shrinkage.
Return Fraud: How Returns Drive Inventory Shrinkage
Return fraud significantly contributes to inventory shrinkage by allowing dishonest customers to exploit store return policies. Common tactics include returning stolen merchandise, used items, or counterfeit products, resulting in inaccurate stock levels and financial losses. Retailers face increased costs due to these fraudulent returns, which disrupt inventory management and reduce overall profitability.
Inaccurate Stock Records and Inventory Management Issues
In retail, shrinkage often results from inaccurate stock records due to errors in data entry or failure to update transactions promptly, leading to discrepancies between actual inventory and system records. Inventory management issues such as improper stock rotation, inefficient tracking systems, and lack of regular audits further exacerbate the problem, causing lost sales and increased operational costs. Effective use of automated inventory software and real-time stock monitoring can significantly reduce shrinkage caused by these inaccuracies.
Preventing Shrinkage: Best Practices for Retailers
Retail inventory shrinkage often results from theft, administrative errors, and supplier fraud, directly impacting profit margins. Implementing comprehensive loss prevention strategies, such as regular inventory audits, employee training programs, and advanced surveillance systems, significantly reduces shrinkage. Leveraging data analytics to identify patterns in shrinkage enables retailers to proactively address vulnerabilities and optimize stock management.
example of shrinkage in inventory Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com