In real estate and construction, a plinth refers to the base or platform upon which a building stands. It is typically constructed using concrete, stone, or brick materials to provide a stable foundation and protect the structure from moisture and ground movement. The plinth height plays a crucial role in preventing water seepage and ensuring the durability of the building. An example of a plinth in a building can be seen in residential houses, where the plinth is raised above ground level to safeguard the walls from dampness. Commercial buildings often use a concrete plinth to support heavy structural loads and maintain alignment. In architectural design, the plinth also contributes to the aesthetic appeal by giving the building a defined base.
Table of Comparison
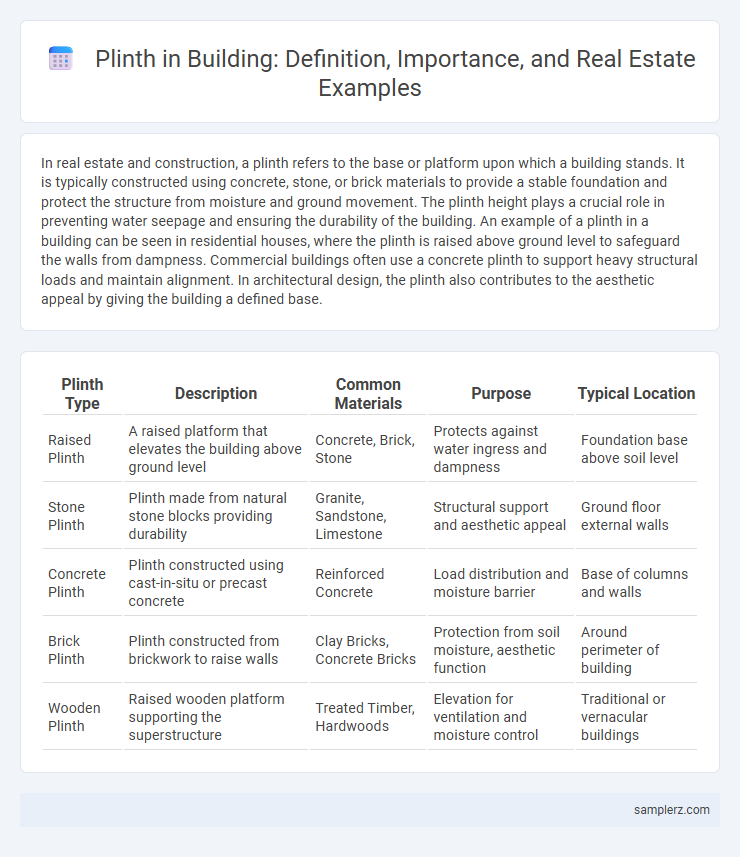
| Plinth Type | Description | Common Materials | Purpose | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raised Plinth | A raised platform that elevates the building above ground level | Concrete, Brick, Stone | Protects against water ingress and dampness | Foundation base above soil level |
| Stone Plinth | Plinth made from natural stone blocks providing durability | Granite, Sandstone, Limestone | Structural support and aesthetic appeal | Ground floor external walls |
| Concrete Plinth | Plinth constructed using cast-in-situ or precast concrete | Reinforced Concrete | Load distribution and moisture barrier | Base of columns and walls |
| Brick Plinth | Plinth constructed from brickwork to raise walls | Clay Bricks, Concrete Bricks | Protection from soil moisture, aesthetic function | Around perimeter of building |
| Wooden Plinth | Raised wooden platform supporting the superstructure | Treated Timber, Hardwoods | Elevation for ventilation and moisture control | Traditional or vernacular buildings |
Definition and Importance of Plinth in Building Construction
The plinth in building construction refers to the base or platform on which a structure is erected, typically made of concrete or masonry, providing a stable foundation above ground level. It serves the crucial function of distributing the load of the building evenly to the ground, preventing settlement and moisture penetration. Properly designed plinths enhance the durability and safety of structures by maintaining stability and protecting the walls from dampness and soil pressure.
Key Features of a Standard Plinth
A standard plinth in real estate construction typically features reinforced concrete with dimensions tailored to support the building's load and prevent settlement. Key features include moisture protection through damp-proof courses, proper alignment to ensure level floors, and adequate thickness ranging from 150mm to 300mm to withstand structural stresses. These elements contribute to the stability and longevity of the foundation while improving resistance to environmental factors like water seepage and soil movement.
Common Materials Used for Plinth Construction
Common materials used for plinth construction include cement concrete, stone masonry, and brick masonry, each providing a sturdy and moisture-resistant base for buildings. Cement concrete plinths consist of a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregates, ensuring durability and strength. Stone masonry plinths often use granite or basalt, offering excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to weathering.
Functional Role of Plinths in Real Estate Structures
Plinths in real estate structures function primarily as the foundational base that distributes the weight of the building evenly to prevent settlement and structural damage. Serving as a barrier against moisture and soil erosion, plinths enhance the durability and longevity of the construction. Their role in elevating the superstructure above ground level also safeguards interior spaces from flooding and pest infiltration.
Popular Plinth Designs Used in Modern Buildings
Popular plinth designs in modern buildings incorporate reinforced concrete for durability and moisture resistance, often featuring stone cladding to enhance aesthetic appeal and protect the structure at the base. Raised plinths with stepped or cantilevered profiles improve drainage and prevent water ingress, crucial for building longevity. Incorporating thermal insulation materials within the plinth design also contributes to energy efficiency and comfort in contemporary real estate developments.
How Plinth Height Impacts Building Safety
Plinth height, the elevated base of a building above ground level, plays a crucial role in preventing water seepage and foundation damage, especially in flood-prone areas. A properly designed plinth height enhances structural integrity by reducing moisture-related issues like dampness and erosion, which can compromise the foundation's durability. Real estate investors and builders must prioritize optimal plinth height to ensure long-term safety and minimize costly repairs.
Cost Considerations for Constructing a Plinth
The cost considerations for constructing a plinth in real estate primarily involve materials such as concrete, bricks, and steel reinforcement, which directly affect budget allocation. Labor charges and site-specific factors, including soil condition and foundation depth, significantly influence overall expenditure. Efficient planning and quality material selection are essential to minimize unexpected costs while ensuring structural stability.
Examples of Plinth Usage in Residential Projects
Plinths serve as the foundational base in residential buildings, elevating structures above ground level to prevent moisture penetration and enhance durability. Common examples include raised plinths in traditional bungalows in India, which protect against flooding, and concrete plinth beams in urban apartments that provide structural stability. Residential projects often incorporate decorative brick or stone cladding on plinths to improve aesthetic appeal while maintaining functional support.
Plinth in Commercial and Industrial Real Estate
Plinth in commercial and industrial real estate serves as the crucial base structure that supports walls and columns, ensuring stability and load distribution in warehouses and office buildings. This elevated platform protects against water ingress and ground moisture, enhancing durability for industrial facilities subjected to heavy machinery and high traffic. Optimizing plinth design can significantly improve foundation strength and prevent structural damage in commercial properties.
Maintenance Tips for Ensuring Plinth Durability
Regular inspection of the plinth for cracks or water seepage is essential to prevent structural damage in buildings. Applying a waterproofing layer and ensuring proper drainage around the foundation helps maintain the plinth's durability against weather-related erosion. Periodic cleaning and timely repairs of damaged parts significantly extend the lifespan of the building's plinth.
example of plinth in building Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com