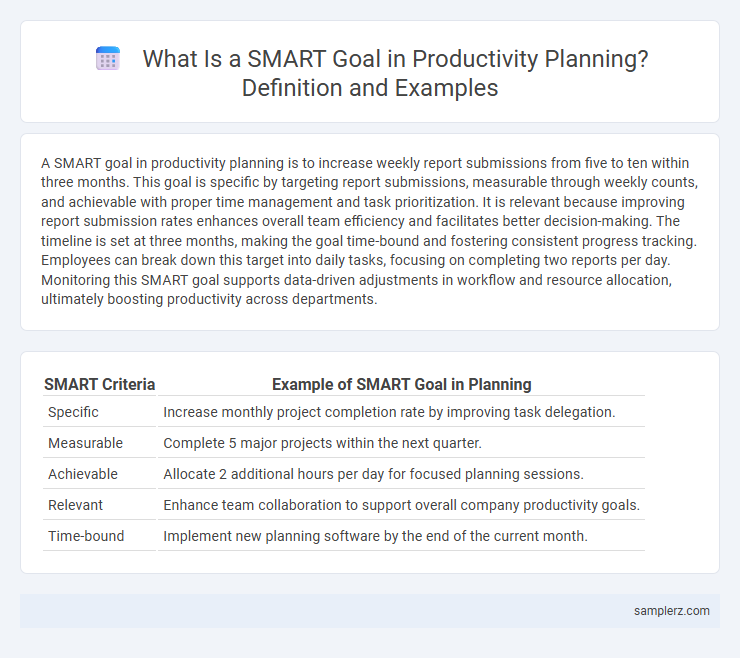
A SMART goal in productivity planning is to increase weekly report submissions from five to ten within three months. This goal is specific by targeting report submissions, measurable through weekly counts, and achievable with proper time management and task prioritization. It is relevant because improving report submission rates enhances overall team efficiency and facilitates better decision-making. The timeline is set at three months, making the goal time-bound and fostering consistent progress tracking. Employees can break down this target into daily tasks, focusing on completing two reports per day. Monitoring this SMART goal supports data-driven adjustments in workflow and resource allocation, ultimately boosting productivity across departments.
Table of Comparison
| SMART Criteria | Example of SMART Goal in Planning |
|---|---|
| Specific | Increase monthly project completion rate by improving task delegation. |
| Measurable | Complete 5 major projects within the next quarter. |
| Achievable | Allocate 2 additional hours per day for focused planning sessions. |
| Relevant | Enhance team collaboration to support overall company productivity goals. |
| Time-bound | Implement new planning software by the end of the current month. |
Introduction to SMART Goals in Planning
Setting a SMART goal in planning involves creating objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For example, increasing weekly team output by 20% within three months by implementing task automation tools ensures clarity and trackable progress. This structured approach enhances productivity by aligning efforts with precise targets and deadlines.
Importance of SMART Goals for Productivity
Setting a SMART goal such as "Increase daily output by 20% within three months by prioritizing tasks and minimizing distractions" provides clear, measurable targets that drive focused effort. SMART goals enhance productivity by ensuring objectives are specific, attainable, and time-bound, which improves motivation and accountability. This structured approach helps individuals and teams allocate resources efficiently and track progress effectively.
Defining Specific Goals for Effective Planning
Defining specific goals involves setting clear, measurable objectives such as increasing weekly project completion rates by 15% within three months. This approach aligns with the SMART criteria by ensuring goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Precise goal definition enhances focus and resource allocation, driving effective productivity planning.
Setting Measurable Objectives in Planning
Setting measurable objectives in planning enhances productivity by defining clear, quantifiable targets such as increasing project completion rates by 20% within six months. Establishing specific metrics enables tracking progress and facilitates timely adjustments to strategies. This approach ensures alignment with overall business goals and promotes accountability across teams.
Achievable Targets: Balancing Ambition and Reality
Setting achievable SMART goals in productivity involves defining clear, realistic targets that challenge without overwhelming, such as completing five high-priority tasks daily to improve workflow efficiency. Balancing ambition and reality ensures steady progress by aligning goals with available resources and current skills. This approach minimizes burnout and fosters consistent performance improvement over time.
Ensuring Relevance in Your Planning Goals
Set a SMART goal such as increasing weekly project completion rates by 15% within three months by prioritizing tasks directly aligned with departmental objectives. Ensuring relevance involves regularly reviewing goals against changing business priorities to avoid misallocation of resources. This approach maintains focus on impactful activities that drive overall productivity and organizational success.
Time-Bound Criteria for Successful Goal Setting
Setting a SMART goal with a clear Time-Bound criterion involves specifying a deadline to enhance accountability and progress tracking, such as "Complete the quarterly sales report by March 31st." This deadline-driven approach ensures tasks align with overall project timelines and prevents procrastination. Strict adherence to time frames directly contributes to measurable productivity improvements.
Real-World SMART Goal Examples in Project Planning
A Real-World SMART goal in project planning might be: "Increase client project delivery rate by 20% within six months by implementing a new project management software and conducting bi-weekly team training sessions." This goal is Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Tracking progress through predefined milestones ensures focused execution and timely adjustments.
SMART Goal Example: Improving Team Efficiency
Improving team efficiency can be achieved by setting a SMART goal such as increasing project completion rates by 20% within three months through implementing weekly progress meetings and task prioritization tools. This goal is Specific, Measurable with clear metrics, Achievable given available resources, Relevant to overall productivity, and Time-bound with a defined deadline. Tracking performance data weekly ensures accountability and facilitates timely adjustments to maintain progress toward enhanced efficiency.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting SMART Goals
Tracking progress in SMART goal planning involves regularly measuring specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives using tools like progress charts or digital apps. Adjusting SMART goals requires analyzing performance data and making necessary refinements to objectives, timelines, or resources to ensure continuous alignment with overall productivity targets. This dynamic approach enhances accountability and drives sustained improvement in goal attainment.
example of SMART goal in planning Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com