A sockpuppet in advocacy refers to a fake online identity created to manipulate public opinion or support a political cause. For instance, during political campaigns, individuals or groups may use sockpuppet accounts on social media to amplify messages, create the illusion of widespread consensus, or discredit opponents. Data analysis of social media patterns often reveals clusters of accounts exhibiting coordinated behavior typical of sockpuppet networks. A notable example occurred during an election cycle when multiple sockpuppet accounts promoted a candidate by posting identical slogans and sharing manipulated news articles. These accounts frequently interacted with each other to inflate visibility, skewing public perception through artificial engagement metrics. Political researchers use entity recognition tools to identify such campaigns by tracking repeated phrases, posting times, and IP addresses linked to sockpuppet activities.
Table of Comparison
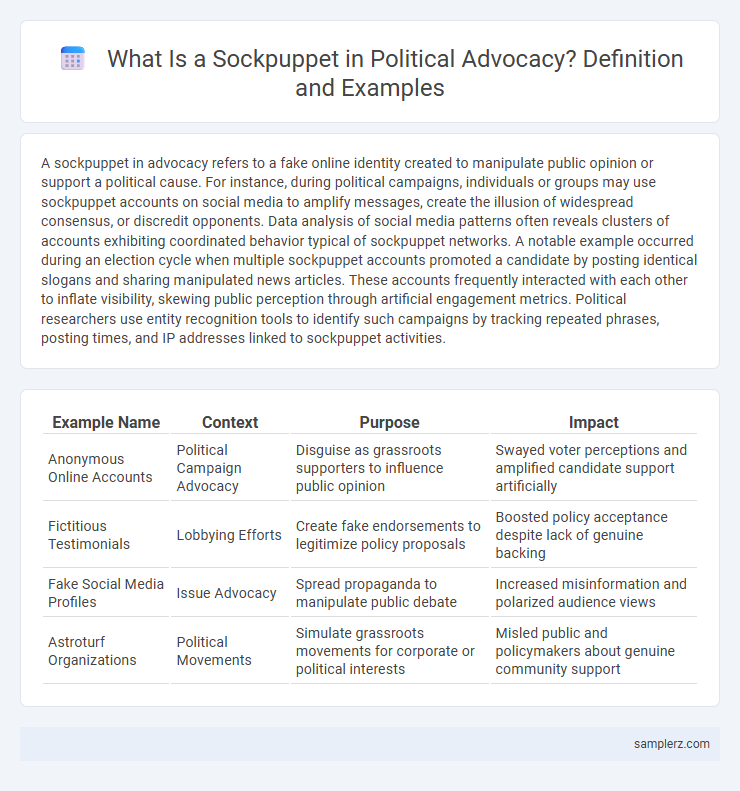
| Example Name | Context | Purpose | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anonymous Online Accounts | Political Campaign Advocacy | Disguise as grassroots supporters to influence public opinion | Swayed voter perceptions and amplified candidate support artificially |
| Fictitious Testimonials | Lobbying Efforts | Create fake endorsements to legitimize policy proposals | Boosted policy acceptance despite lack of genuine backing |
| Fake Social Media Profiles | Issue Advocacy | Spread propaganda to manipulate public debate | Increased misinformation and polarized audience views |
| Astroturf Organizations | Political Movements | Simulate grassroots movements for corporate or political interests | Misled public and policymakers about genuine community support |
Recognizing Sockpuppetry in Political Advocacy
Sockpuppetry in political advocacy involves using fake online personas to manipulate public opinion or amplify specific political agendas. Recognizing sockpuppets includes identifying suspiciously coordinated messaging patterns, repetitive language styles, and synchronized posting times across multiple accounts. Tools like network analysis software and digital forensics help detect these deceptive tactics by revealing hidden connections among purportedly independent advocates.
High-Profile Sockpuppet Scandals in Politics
High-profile sockpuppet scandals in politics often involve false online personas created to manipulate public opinion, such as the case of Russia's Internet Research Agency interfering in the 2016 US presidential election by spreading disinformation through fake social media accounts. Another notable example includes the use of fabricated identities by political operatives to post positive messages or attack opponents during the Brexit campaign. These deceptive tactics undermine democratic processes and erode public trust in political advocacy.
Tactics Used by Advocacy Groups for Sockpuppeting
Advocacy groups use sockpuppeting tactics such as creating fake online personas to spread misleading information and artificially amplify support for their causes. They often operate multiple accounts to infiltrate discussion forums and social media platforms, influencing public opinion and policy debates under the guise of grassroots endorsement. These tactics manipulate perception by obscuring the true origin of messages, thereby undermining transparency in political advocacy.
Case Studies: Sockpuppets Swaying Political Debates
The case of the 2010 Arizona immigration law debate highlights how sockpuppet accounts manipulated social media conversations by posing as grassroots activists advocating for stricter enforcement. Investigations revealed coordinated efforts to flood online forums with fabricated endorsements, skewing public perception and pressuring legislators through manufactured consensus. These sockpuppet-driven campaigns demonstrate the potent influence of inauthentic advocacy in shaping political discourse and policy outcomes.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Advocacy Sockpuppets
Sockpuppets in advocacy, such as fake online personas created to manipulate public opinion, raise significant legal concerns including violations of campaign finance laws and fraudulent misrepresentation. Ethically, these deceptive practices undermine transparency, erode trust in democratic processes, and distort genuine public discourse. Regulatory frameworks increasingly target sockpuppet use to ensure accountability and maintain the integrity of political advocacy.
Detecting Sockpuppet Accounts in Political Movements
Sockpuppet accounts in political movements often mimic genuine activists to manipulate public opinion and inflate support for specific agendas. Detecting these accounts requires analyzing patterns such as synchronized posting times, repetitive messaging, and disproportionate interaction rates compared to authentic users. Advanced machine learning algorithms and network analysis tools are instrumental in uncovering coordinated sockpuppet networks within online advocacy platforms.
Real-World Examples of Sockpuppeting in Election Campaigns
Election campaigns have witnessed sockpuppeting tactics where fake social media accounts amplify candidates' messages or disparage opponents, as seen in the 2016 US presidential election with coordinated disinformation efforts linked to foreign entities. In Brazil's 2018 presidential race, automated bots and fake profiles spread propaganda to manipulate public opinion and undermine rival candidates. These instances highlight the use of deceptive online personas to influence voter perceptions and election outcomes.
The Impact of Sockpuppets on Policy Discussions
Sockpuppets in advocacy manipulate policy discussions by creating false consensus and amplifying predetermined agendas, undermining genuine stakeholder engagement. This deceptive practice distorts public opinion metrics and misleads policymakers, causing decisions to reflect fabricated support rather than authentic community interests. The proliferation of sockpuppet accounts erodes trust in democratic processes and impedes transparent, evidence-based policy formulation.
Notorious Sockpuppet Exposures and Their Outcomes
Notorious sockpuppet exposures in advocacy include the case of "Cecil the Lion," where fake accounts manipulated public sentiment to undermine genuine wildlife conservation campaigns. Another prominent example is the 2018 Facebook scandal, where coordinated sockpuppet networks spread misinformation to influence political debates during the U.S. midterm elections. These exposures often result in account suspensions, increased platform scrutiny, and a loss of public trust in affected advocacy movements.
Combating Sockpuppetry in Online Political Advocacy
Combating sockpuppetry in online political advocacy requires advanced algorithmic detection and user authentication protocols to ensure genuine engagement. Platforms must analyze IP tracking, metadata patterns, and behavioral inconsistencies to identify coordinated fake accounts manipulating political discourse. Transparent policies and real-time monitoring can significantly reduce the influence of deceptive sockpuppet campaigns in digital activism.
example of sockpuppet in advocacy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com