A quango, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organization, plays a significant role in political oversight by acting as an intermediary between the government and the public. One prominent example is the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, which regulates financial markets and ensures consumer protection. The FCA operates independently but is funded by the government, blending public accountability with regulatory autonomy. Another key example of a quango in political oversight is the Environment Agency, responsible for regulating and monitoring environmental policy compliance. This body collects and analyzes environmental data, enforcing regulations to protect natural resources and public health. Quangos like the Environment Agency provide specialized expertise that supports government policy implementation and ensures regulatory standards are met efficiently.
Table of Comparison
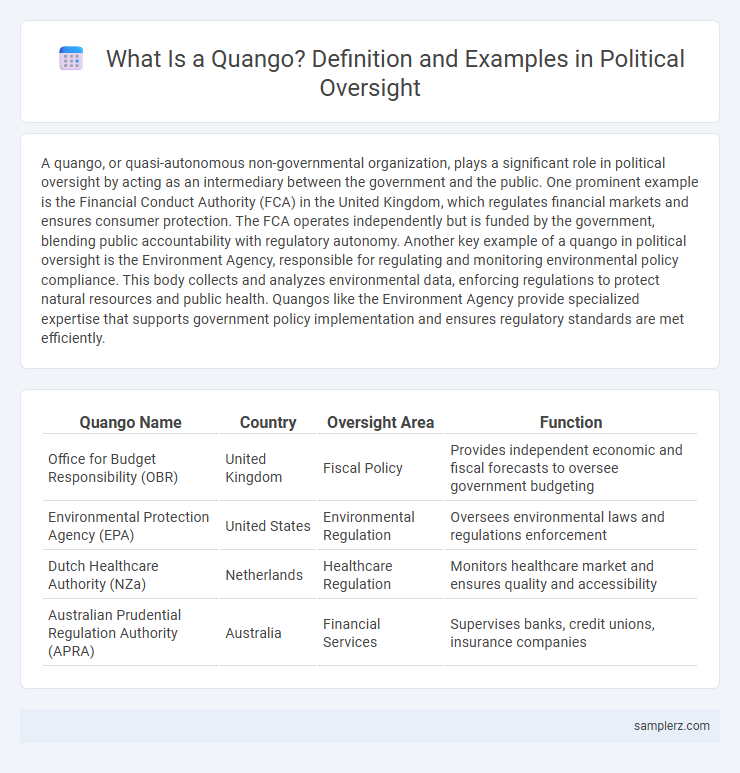
| Quango Name | Country | Oversight Area | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) | United Kingdom | Fiscal Policy | Provides independent economic and fiscal forecasts to oversee government budgeting |
| Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) | United States | Environmental Regulation | Oversees environmental laws and regulations enforcement |
| Dutch Healthcare Authority (NZa) | Netherlands | Healthcare Regulation | Monitors healthcare market and ensures quality and accessibility |
| Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) | Australia | Financial Services | Supervises banks, credit unions, insurance companies |
Overview of QUANGOs in Political Oversight
Quasi-Autonomous Non-Governmental Organizations (QUANGOs) play a critical role in political oversight by ensuring government accountability and policy implementation. Examples include the UK's Arts Council England and the Environment Agency, which operate independently yet are funded by the government to provide specialized regulatory and advisory functions. These entities enhance transparency and efficiency in public administration by combining governmental authority with operational autonomy.
Defining the Oversight Role of QUANGOs
Quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations (QUANGOs) serve as pivotal oversight bodies by monitoring government policies and ensuring accountability in public administration. These entities operate independently from direct ministerial control, enabling objective evaluation and regulation of service delivery within sectors such as healthcare, education, and environmental protection. The oversight role of QUANGOs includes scrutinizing government performance, advising policymakers, and safeguarding public interests through transparent and impartial governance.
Historic Examples of QUANGOs Overseeing Public Policy
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the UK serves as a historic example of a quango overseeing public health policy by providing evidence-based guidance on healthcare treatments and standards. The UK Audit Commission, established in 1983, functioned as a quango monitoring local government expenditures and ensuring financial accountability until its abolition in 2015. Another notable quango, the Equal Opportunities Commission, played a critical role in shaping gender equality policies and enforcing anti-discrimination laws before merging into the Equality and Human Rights Commission in 2007.
Key Oversight QUANGOs in the UK Government
The UK Government relies on key oversight Quangos such as the National Audit Office (NAO), which scrutinizes public spending and ensures value for money across departments. The Public Standards Committee monitors adherence to ethical standards among public officials, maintaining accountability and transparency. Additionally, the Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) provides independent economic forecasts and fiscal analysis to support government decision-making.
QUANGOs and Regulatory Oversight: Case Studies
Quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations (QUANGOs) such as the UK's Environment Agency exemplify regulatory oversight by operating independently while enforcing government policies on environmental protection. These bodies balance regulatory functions and public accountability, ensuring compliance with statutory environmental standards through monitoring and enforcement. Case studies reveal that QUANGOs like the Office for Standards in Education, Children's Services and Skills (Ofsted) provide crucial oversight by evaluating educational institutions, enhancing policy implementation efficacy without direct political interference.
Success Stories: QUANGOs Improving Accountability
The National Audit Office (NAO), a prominent quango in the UK, exemplifies success in enhancing governmental accountability by rigorously evaluating public expenditure and providing actionable recommendations. Its independent oversight has led to significant improvements in transparency and efficiency across various government departments. This model demonstrates how quangos can play a pivotal role in strengthening public trust and ensuring responsible use of taxpayer funds.
Challenges Faced by Oversight QUANGOs
Oversight quangos such as the UK's National Audit Office face challenges including limited enforcement powers, political interference, and resource constraints that hamper effective accountability. These bodies often struggle with balancing independence and government collaboration, which can undermine public trust in their impartiality. Fragmented oversight frameworks further complicate coordination and comprehensive evaluation of public sector performance.
Comparing QUANGO Oversight Across Countries
Quangos such as the UK's Arts Council, Germany's Federal Employment Agency, and Canada's Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission illustrate diverse models of government oversight with varying degrees of autonomy and accountability. The UK's Arts Council operates with significant independence, relying on government funding but setting its own strategic priorities, while Germany's Federal Employment Agency is more directly integrated into the federal government's labor policies. In contrast, Canada's CRTC combines regulatory authority with public consultation processes, balancing oversight with stakeholder engagement to ensure transparent governance.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of QUANGO Oversight
The National Audit Office (NAO) serves as a key example of quango oversight, rigorously evaluating the performance and financial accountability of quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations (quangos). Effective NAO oversight enhances transparency by conducting comprehensive audits that identify discrepancies and recommend improvements in governance structures. Evaluating quango oversight mechanisms involves measuring the impact of these audits on policy implementation, organizational efficiency, and public trust in government institutions.
Future Trends in QUANGO-led Oversight
Quangos such as the UK's National Audit Office are expected to increasingly utilize advanced data analytics and AI to enhance transparency and accountability in public sector oversight. Emerging trends indicate a growing emphasis on collaborative governance models, integrating quangos with digital platforms to improve stakeholder engagement and public trust. Future developments may also prioritize sustainable policy monitoring, leveraging real-time data to address environmental and social challenges effectively.
example of quango in oversight Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com