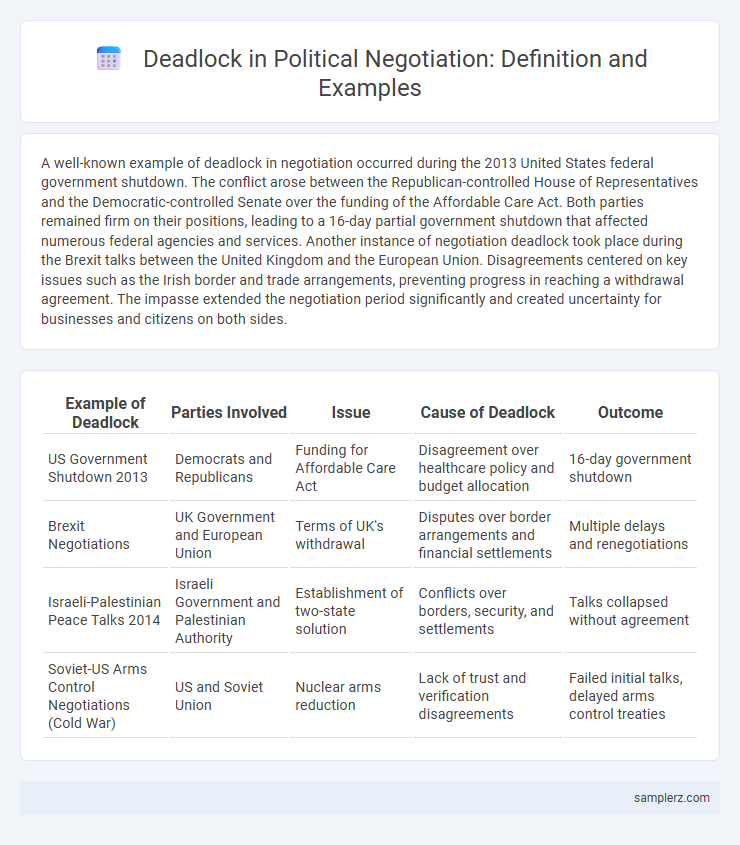
A well-known example of deadlock in negotiation occurred during the 2013 United States federal government shutdown. The conflict arose between the Republican-controlled House of Representatives and the Democratic-controlled Senate over the funding of the Affordable Care Act. Both parties remained firm on their positions, leading to a 16-day partial government shutdown that affected numerous federal agencies and services. Another instance of negotiation deadlock took place during the Brexit talks between the United Kingdom and the European Union. Disagreements centered on key issues such as the Irish border and trade arrangements, preventing progress in reaching a withdrawal agreement. The impasse extended the negotiation period significantly and created uncertainty for businesses and citizens on both sides.
Table of Comparison
| Example of Deadlock | Parties Involved | Issue | Cause of Deadlock | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US Government Shutdown 2013 | Democrats and Republicans | Funding for Affordable Care Act | Disagreement over healthcare policy and budget allocation | 16-day government shutdown |
| Brexit Negotiations | UK Government and European Union | Terms of UK's withdrawal | Disputes over border arrangements and financial settlements | Multiple delays and renegotiations |
| Israeli-Palestinian Peace Talks 2014 | Israeli Government and Palestinian Authority | Establishment of two-state solution | Conflicts over borders, security, and settlements | Talks collapsed without agreement |
| Soviet-US Arms Control Negotiations (Cold War) | US and Soviet Union | Nuclear arms reduction | Lack of trust and verification disagreements | Failed initial talks, delayed arms control treaties |
Government Shutdowns: Classic Deadlock Scenarios
Government shutdowns exemplify classic deadlock scenarios where political parties fail to reach consensus on budget agreements, causing federal operations to halt temporarily. These impasses often arise from deep ideological conflicts over spending priorities, leading to prolonged negotiations without compromise. The 2013 and 2018-2019 U.S. government shutdowns highlight the severe impact of such deadlocks on public services and economic stability.
Parliamentary Gridlock over Budget Approvals
Parliamentary gridlock over budget approvals occurs when legislative bodies fail to reach consensus on funding allocations, resulting in government shutdowns and stalled public services. This deadlock often arises from partisan divisions where opposing parties block each other's budget proposals to leverage political gains. The prolonged impasse undermines economic stability by delaying essential government operations and eroding public trust in political institutions.
Coalition Talks Stalled by Irreconcilable Differences
Coalition talks in parliamentary systems often reach deadlock due to irreconcilable differences over policy priorities, leadership roles, and ministerial appointments. For example, the 2019 Israel Knesset elections saw prolonged negotiations collapse as major parties failed to agree on basic governance frameworks, triggering repeat elections. Such stalemates underscore the challenges of forming stable governments in fragmented political landscapes.
Bipartisan Stalemates on Healthcare Reform
Bipartisan stalemates on healthcare reform frequently occur when opposing parties fail to reconcile differences on policy priorities such as coverage mandates and funding mechanisms. The 2017 attempts to repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act exemplify deadlock, with Republicans divided over the extent of market regulations and Democrats unified in opposition. This impasse results in legislative gridlock, delaying critical reforms and perpetuating systemic inefficiencies in the U.S. healthcare system.
Diplomatic Deadlock in International Peace Talks
Diplomatic deadlock in international peace talks often arises when conflicting parties rigidly adhere to incompatible demands, such as territorial disputes or sovereignty issues, leading to prolonged stalemates. The Israeli-Palestinian peace negotiations exemplify this, where core issues like borders, security, and the status of Jerusalem remain unresolved despite multiple rounds of dialogue. Such deadlocks hinder conflict resolution by fostering mistrust and reducing opportunities for compromise in global diplomacy.
Legislative Impasse on Immigration Policy
The legislative impasse on immigration policy exemplifies a deadlock in negotiation where partisan divisions prevent the passage of comprehensive reform. Key stakeholders remain entrenched in conflicting priorities regarding border security and pathways to citizenship, stalling progress. This stalemate underscores the challenges lawmakers face in reconciling deeply polarized agendas within the legislative process.
Treaty Negotiations Failing Over Security Concerns
Treaty negotiations frequently encounter deadlocks when participating nations raise irreconcilable security concerns, such as mutual distrust over disarmament verification measures. The 2019 arms control talks between the United States and Russia exemplified this deadlock, as disagreements on missile testing and inspection protocols halted progress. Such stalemates often persist due to conflicting national interests and the high stakes involved in maintaining strategic stability.
Constitutional Amendments Blocked by Minority Opposition
Constitutional amendments frequently face deadlock when minority opposition wields veto power in legislative bodies, effectively stalling crucial reforms. An illustrative case is the United States, where the requirement of a two-thirds majority in Congress allows a determined minority to block amendments, as seen in failed efforts to abolish the Electoral College or implement comprehensive campaign finance reform. Such stalemates highlight how minority blocks can prevent constitutional progress despite majority support, emphasizing the complexities of amending foundational legal frameworks.
Electoral Reform Efforts Stuck in Political Deadlock
Electoral reform efforts in various democracies often face political deadlock due to conflicting interests among major parties reluctant to alter the status quo that benefits their electoral advantages. In countries like Canada, repeated attempts to introduce proportional representation or alternative voting systems have stalled in parliamentary committees or failed to pass critical thresholds amid partisan disputes. Such deadlocks highlight the entrenched challenges in achieving consensus on electoral changes that could reshape political power dynamics.
Deadlock in Climate Policy Negotiations
Deadlock in climate policy negotiations often occurs when developed and developing nations clash over emission reduction commitments and financial aid responsibilities, stalling global progress. The 2009 Copenhagen Summit exemplified this deadlock, with disagreements on binding targets and funding mechanisms leading to minimal consensus. Such impasses hinder timely implementation of critical measures to mitigate climate change impacts worldwide.
example of deadlock in negotiation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com