Heterodoxy in opinion refers to views that deviate from established or orthodox beliefs within a particular context. For example, in the realm of religion, heterodox opinions challenge mainstream doctrines, such as questioning the infallibility of sacred texts or proposing alternative interpretations of spiritual teachings. These opinions can provoke debate and inspire new perspectives, fostering intellectual diversity. In politics, heterodox opinions often arise when individuals or groups advocate for policies that contradict dominant party platforms or widely accepted ideologies. An example includes advocating for economic models combining elements of capitalism and socialism, which is unconventional compared to pure market-driven or centralized economies. These opinions contribute to the richness of political discourse by introducing innovative solutions and encouraging critical examination of prevailing systems.
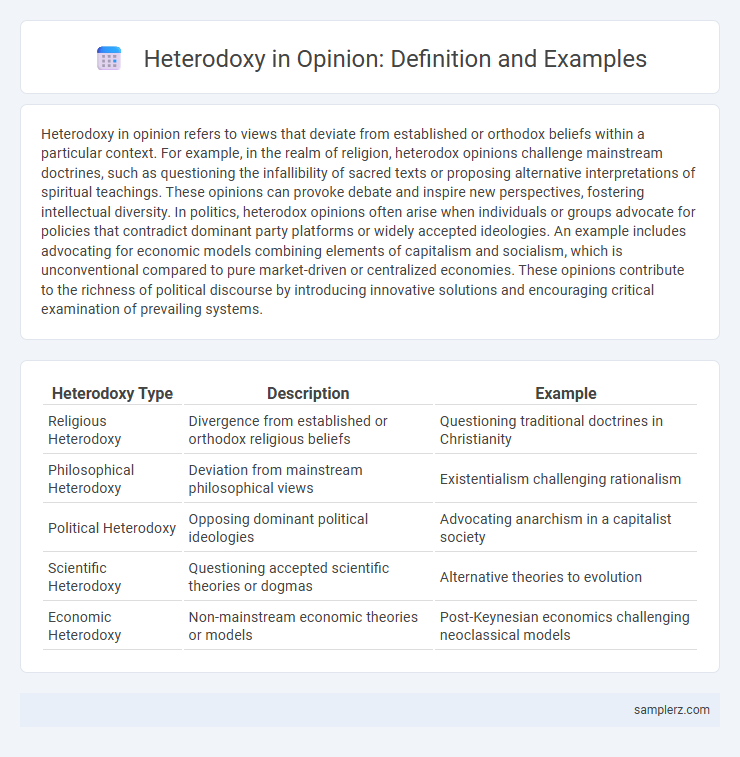
Table of Comparison
| Heterodoxy Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Religious Heterodoxy | Divergence from established or orthodox religious beliefs | Questioning traditional doctrines in Christianity |
| Philosophical Heterodoxy | Deviation from mainstream philosophical views | Existentialism challenging rationalism |
| Political Heterodoxy | Opposing dominant political ideologies | Advocating anarchism in a capitalist society |
| Scientific Heterodoxy | Questioning accepted scientific theories or dogmas | Alternative theories to evolution |
| Economic Heterodoxy | Non-mainstream economic theories or models | Post-Keynesian economics challenging neoclassical models |
Defining Heterodoxy in Modern Opinion
Heterodoxy in modern opinion refers to views that challenge or deviate from established beliefs, norms, or orthodox doctrines within social, political, or religious contexts. It often manifests as critical dissent or alternative perspectives that question mainstream narratives, such as non-conformist political ideologies or unorthodox religious interpretations. This dynamic fosters intellectual diversity and drives societal progress by encouraging debate and reevaluation of accepted truths.
Historical Examples of Heterodox Opinions
Galileo Galilei's support for heliocentrism in the 17th century challenged the prevailing geocentric worldview endorsed by the Catholic Church, exemplifying heterodox opinion that spurred significant scientific revolution. Similarly, Voltaire's critique of established religious and political dogmas during the Enlightenment period promoted secularism and individual rights, defying orthodox authority. These historical examples highlight how heterodox opinions have driven intellectual progress and reshaped societal paradigms.
Heterodoxy vs. Orthodoxy: Key Distinctions
Heterodoxy challenges prevailing orthodox opinions by introducing alternative viewpoints that question established beliefs, often fostering innovation and critical thinking. Key distinctions between heterodoxy and orthodoxy lie in their adherence to accepted doctrines, where orthodoxy upholds conventional wisdom, while heterodoxy embraces dissent and diversity of thought. This dynamic tension drives intellectual progress, highlighting the value of heterodoxy in expanding the boundaries of acceptable discourse.
Famous Figures Who Challenged Majority Opinion
Galileo Galilei defied the dominant 17th-century belief that the Earth was the center of the universe by advocating heliocentrism, which sparked intense controversy and persecution. Similarly, Rosa Parks challenged the widespread acceptance of racial segregation by refusing to give up her bus seat, igniting the civil rights movement. These figures exemplify how heterodoxy in opinion can provoke societal transformation by confronting and reshaping majority perspectives.
The Role of Heterodox Ideas in Social Change
Heterodox ideas challenge prevailing social norms by introducing alternative perspectives that question established beliefs, thereby driving societal evolution. Historical examples, such as civil rights movements and feminist theories, highlight how unconventional opinions catalyze policy reforms and cultural shifts. The persistence of dissenting voices in public discourse fosters innovation and resilience within societies, essential for adaptive social progress.
Heterodoxy in Political Discourse
Heterodoxy in political discourse challenges mainstream ideologies by introducing unconventional viewpoints that question established power structures and policy norms. These dissenting opinions often stimulate critical debate, fostering a more pluralistic and dynamic political environment. Embracing heterodox perspectives can lead to innovative solutions and limit the risks of ideological rigidity within democratic societies.
The Risks and Rewards of Holding Heterodox Opinions
Holding heterodox opinions challenges mainstream thinking and can lead to innovative breakthroughs in philosophy, science, and culture. Risks include social ostracism, professional setbacks, and cognitive isolation, as seen in cases like Galileo's heliocentrism or Nash's game theory insights. Rewards encompass intellectual growth, paradigm shifts, and lasting influence on knowledge and societal progress, demonstrating the critical role of dissent in advancing collective understanding.
Media Representation of Heterodox Perspectives
Media representation of heterodox perspectives often challenges mainstream narratives by highlighting unconventional viewpoints that question dominant ideologies. Independent and alternative media outlets amplify marginalized voices, fostering critical discourse around topics like political dissent and cultural diversity. This heterodoxy in media promotes pluralism and encourages audiences to engage with complex, often underrepresented opinions.
Contemporary Instances of Heterodoxy in Public Debate
Contemporary instances of heterodoxy in public debate often emerge through voices challenging mainstream narratives on climate change policies, questioning established economic models, or advocating unorthodox approaches to social justice. These heterodox opinions disrupt conventional consensus by introducing alternative perspectives grounded in unconventional evidence or interpretations. Such dissenting views play a critical role in expanding public discourse and prompting policy innovation, despite facing resistance from dominant ideological frameworks.
Encouraging Constructive Heterodoxy in Society
Encouraging constructive heterodoxy in society fosters innovation by challenging mainstream opinions and promoting diverse perspectives that drive critical thinking. Societies embracing heterodox viewpoints experience enriched public discourse, enabling more robust problem-solving and resilience against groupthink. Cultivating environments where dissenting opinions are respected enhances social cohesion and advances democratic processes by ensuring that minority voices contribute meaningfully to collective decision-making.
example of heterodoxy in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com