In the context of opinion, the subject position often reflects a personal stance or perspective on a given topic. For instance, a writer might state, "I believe renewable energy is essential for future sustainability," where the subject "I" explicitly expresses an individual viewpoint. This position can also manifest in collective opinions, such as "We think government policies should support climate change initiatives," emphasizing shared beliefs within a group. Subject positions in opinion pieces serve to frame the argument and establish credibility by signaling the origin of the perspective. Entities like authors, commentators, or organizations use phrases such as "It seems to me" or "Our data suggests" to anchor the opinion within a subjective or evidence-based context. The strategic use of subject positions influences audience reception by clarifying whether the viewpoint is personal, communal, or endorsed by authoritative data.
Table of Comparison
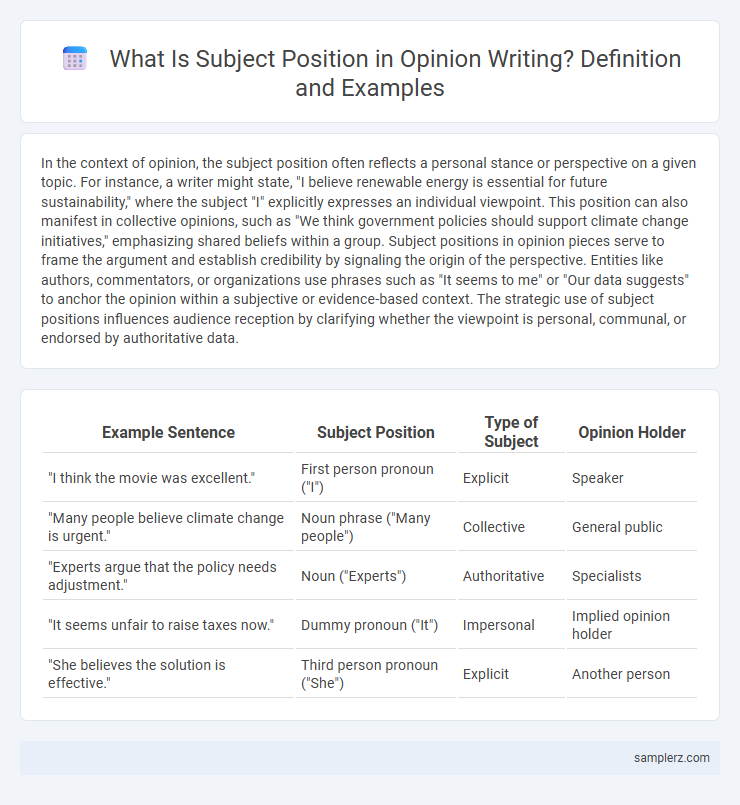
| Example Sentence | Subject Position | Type of Subject | Opinion Holder |
|---|---|---|---|
| "I think the movie was excellent." | First person pronoun ("I") | Explicit | Speaker |
| "Many people believe climate change is urgent." | Noun phrase ("Many people") | Collective | General public |
| "Experts argue that the policy needs adjustment." | Noun ("Experts") | Authoritative | Specialists |
| "It seems unfair to raise taxes now." | Dummy pronoun ("It") | Impersonal | Implied opinion holder |
| "She believes the solution is effective." | Third person pronoun ("She") | Explicit | Another person |
Defining Subject Position in Opinion Writing
Subject position in opinion writing refers to the writer's stance or perspective on a specific issue, shaping the tone and argument throughout the text. It involves clearly articulating the viewpoint, supported by evidence and reasoning to persuade the audience effectively. A well-defined subject position ensures clarity, guiding readers through the opinion and reinforcing the writer's credibility and intent.
Personal Narratives: Expressing Unique Perspectives
Personal narratives allow individuals to convey their unique perspectives by sharing specific experiences that shape their viewpoint. This subject position highlights the authenticity and emotional depth behind opinions, grounding abstract ideas in real-life context. Harnessing personal stories enhances the relatability and impact of the expressed opinion, making it more compelling to the audience.
The Role of Identity in Forming Opinions
Identity plays a crucial role in shaping opinions by influencing the values, beliefs, and experiences individuals use to interpret information. Social identity factors such as ethnicity, religion, and political affiliation often determine how individuals prioritize issues and assess arguments. Recognizing this connection helps explain why opinions vary significantly across different communities and cultural groups.
Cultural Background as a Subject Position
Cultural background as a subject position shapes individual perspectives through deeply ingrained values, traditions, and social norms that influence opinions and interpretations. This position affects communication styles, decision-making processes, and conflict resolution approaches, highlighting the diversity of viewpoints rooted in cultural experiences. Recognizing cultural background as a subject position enables more nuanced understanding and empathy in cross-cultural interactions and discourse.
Expert vs. Layperson: Framing Authority in Opinions
Experts hold authority in opinion pieces by leveraging specialized knowledge and credentials, enhancing the credibility and persuasiveness of their arguments. Laypersons contribute diverse perspectives rooted in personal experience, which can resonate with broader audiences and foster relatability. The framing of authority in opinions shapes how readers interpret the validity and significance of the presented viewpoints.
Political Affiliation and Opinion Perspectives
Political affiliation heavily influences opinion perspectives, shaping how individuals interpret events and policies through partisan lenses. Research shows conservatives often prioritize tradition and security, while liberals emphasize equality and social justice in their viewpoints. Understanding these subject positions reveals the interplay between ideology and public discourse, highlighting biases that affect political communication and decision-making.
Gendered Subject Positions in Opinion Articles
Gendered subject positions in opinion articles often reflect societal biases, positioning men as authoritative experts and women as emotional or personal commentators. This dynamic shapes readers' perception, reinforcing stereotypes through language choices and framing techniques. Recognizing these patterns is essential for promoting balanced representation and challenging gendered assumptions in media discourse.
Socioeconomic Status and Viewpoint Formation
Socioeconomic status significantly influences viewpoint formation by shaping access to education, resources, and social networks, which determine individuals' perspectives on societal issues. People from higher socioeconomic backgrounds often have greater exposure to diverse information and critical thinking opportunities, leading to more nuanced opinions. Conversely, those from lower socioeconomic statuses may develop viewpoints rooted in immediate economic concerns and lived experiences, highlighting the role of class-based context in opinion diversity.
Generational Differences Shaping Subject Position
Generational differences significantly shape subject positions by influencing perspectives on social, political, and cultural issues. Millennials often prioritize digital connectivity and climate action, reflecting their values in social discourse, while Baby Boomers may emphasize tradition and economic stability, shaping contrasting opinions. These evolving generational viewpoints highlight how subject positions are constructed through lived experiences and historical contexts.
Intersectionality and Multi-faceted Subject Positions
Intersectionality reveals how individuals simultaneously occupy multiple subject positions shaped by race, gender, class, and other social categories, creating complex experiences of privilege and oppression. Multi-faceted subject positions emphasize that identity cannot be reduced to a single axis but must be understood through overlapping social and political contexts. These layered identities influence perspectives and underscore the importance of inclusive approaches in policy and social justice.
example of subject position in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com