An example of an affective response in opinion can be seen in reactions to a new movie release. When individuals describe their feelings of joy, disappointment, or excitement after watching the film, they express an emotional connection that shapes their overall opinion. These feelings influence their likelihood to recommend the movie or avoid it in the future. Another instance of affective response appears in product reviews. Customers often highlight emotions such as satisfaction or frustration based on their experience with a product's performance. These emotional reactions provide valuable insight into consumer preferences and impact brand loyalty and purchasing decisions.
Table of Comparison
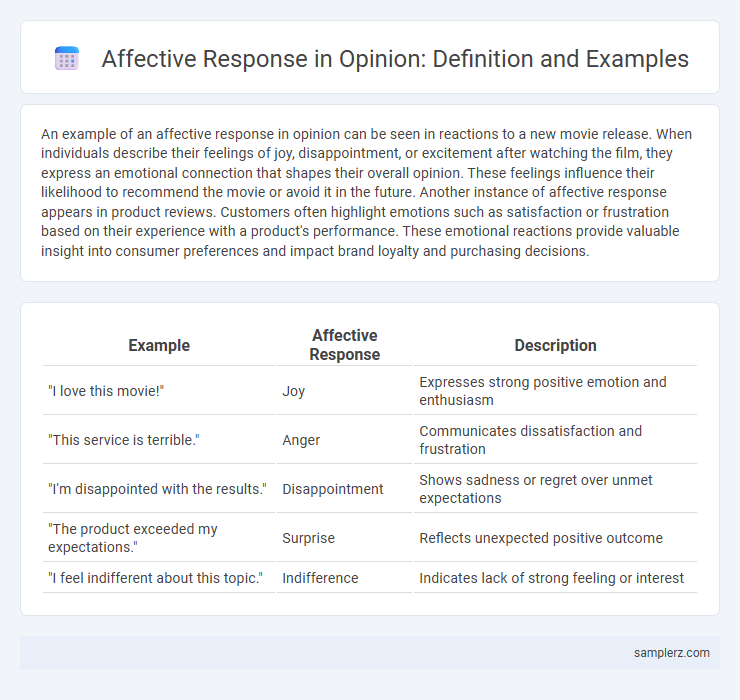
| Example | Affective Response | Description |
|---|---|---|
| "I love this movie!" | Joy | Expresses strong positive emotion and enthusiasm |
| "This service is terrible." | Anger | Communicates dissatisfaction and frustration |
| "I'm disappointed with the results." | Disappointment | Shows sadness or regret over unmet expectations |
| "The product exceeded my expectations." | Surprise | Reflects unexpected positive outcome |
| "I feel indifferent about this topic." | Indifference | Indicates lack of strong feeling or interest |
Understanding Affective Responses in Opinion Formation
Affective responses play a crucial role in opinion formation by shaping individual attitudes through emotions and feelings associated with a topic. These emotional reactions often influence cognitive evaluations and decision-making processes, leading to stronger and more enduring opinions. Recognizing the impact of affective responses helps explain why people may hold polarized views despite similar factual information.
Common Examples of Affective Responses in Opinions
Common examples of affective responses in opinions include feelings of joy, anger, fear, or disgust triggered by a specific event or situation. Emotional reactions such as empathy toward a character in a story or frustration with a political decision often shape how opinions are formed and expressed. These affective responses influence not only personal viewpoints but also social and cultural attitudes.
Emotional Language Shaping Public Opinion
Emotional language powerfully shapes public opinion by tapping into individuals' feelings, often triggering empathy, anger, or fear. Politicians and media outlets strategically use emotionally charged words to influence attitudes and strengthen support for policies or candidates. Studies show that narratives infused with emotional appeals increase message retention and motivate social action more effectively than purely factual content.
Role of Personal Experience in Affective Opinion Responses
Personal experience significantly shapes affective opinion responses by anchoring emotions to specific memories or events. Emotional reactions often intensify when individuals recall personal encounters related to the topic, reinforcing their attitudes and beliefs. This deep connection between experience and sentiment highlights how subjective history influences the strength and nature of opinions.
How Positive Emotions Influence Opinions
Positive emotions significantly shape opinions by enhancing receptivity and fostering favorable attitudes toward ideas or products. Experiencing joy or enthusiasm can increase persuasion effectiveness, making individuals more likely to endorse a viewpoint or make a purchase. Emotional engagement strengthens memory retention of information, reinforcing positive associations and influencing future decision-making processes.
Negative Affective Responses and Biased Judgments
Negative affective responses often manifest as feelings of anger, disgust, or fear, leading to biased judgments that skew objective evaluation. These emotional reactions can cause individuals to dismiss valid evidence or reinforce stereotypes, thereby undermining rational discourse. Understanding the impact of such affective biases is crucial for improving critical thinking and reducing polarized opinions.
The Impact of Empathy on Expressing Opinions
Empathy enhances affective responses in opinion expression by enabling individuals to connect emotionally with others' experiences, fostering deeper understanding and compassion. This emotional engagement often leads to more nuanced and respectful opinions, as empathy allows people to consider diverse perspectives genuinely. Studies show that empathetic communication reduces conflict and promotes constructive dialogue by bridging emotional gaps in discussions.
Fear and Anxiety in Shaping Social Attitudes
Fear and anxiety significantly influence social attitudes by heightening perceived threats and reinforcing in-group biases, leading to increased prejudice or social exclusion. These affective responses trigger defensive behaviors that shape public opinion on issues like immigration, public safety, and health crises. Understanding the emotional underpinnings of fear and anxiety provides insight into the formation of polarized viewpoints and resistance to social change.
The Power of Surprise and Curiosity in Opinion Change
Surprise triggers strong emotional reactions that challenge existing beliefs, making individuals more open to reconsidering their opinions. Curiosity motivates people to seek out new information and explore different perspectives, fostering a natural environment for opinion change. Research shows that unexpected information combined with inquisitive engagement significantly accelerates shifts in attitude and belief systems.
Strategies to Recognize Affective Responses in Opinion Writing
Identifying affective responses in opinion writing involves analyzing emotional cues such as word choice, tone, and intensity to understand the writer's feelings and attitude toward the subject. Strategies include examining sensory language, figurative expressions, and personal anecdotes that evoke empathy or convey passion. Employing sentiment analysis tools can also enhance recognition of positive, negative, or mixed emotions embedded in the opinion text.
example of affective response in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com