Subjectivism in opinion highlights the idea that personal feelings and perspectives shape individual judgments. For instance, two people may watch the same movie but have opposite opinions because their emotional responses and experiences differ. This approach emphasizes that opinions are not absolute truths but reflections of personal viewpoints. In the realm of art criticism, subjectivism often appears when evaluating paintings or music, where taste varies widely among individuals. A painting praised by one person for its vibrant colors might be disliked by another who finds it chaotic or unstructured. Such examples showcase the role of subjective interpretation in forming opinions across various domains.
Table of Comparison
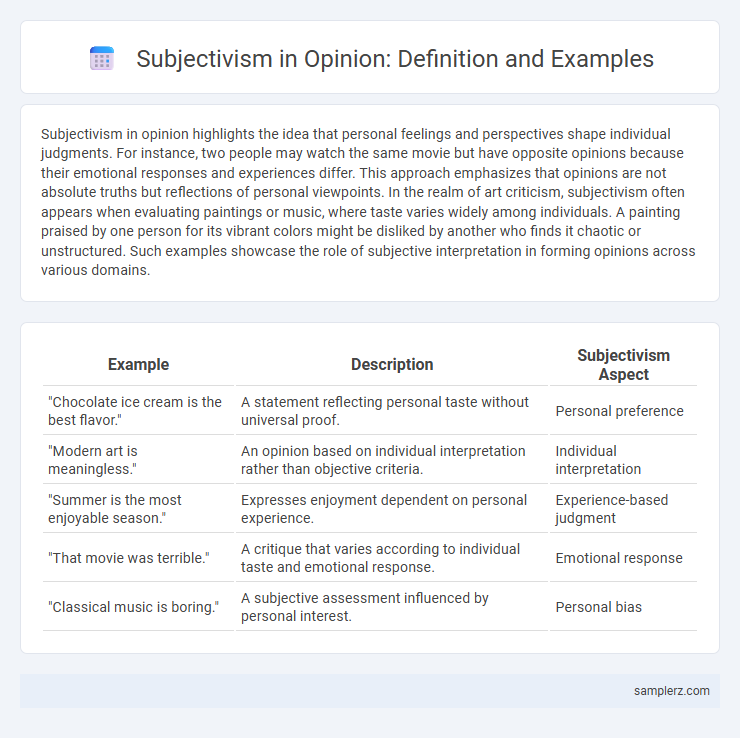
| Example | Description | Subjectivism Aspect |
|---|---|---|
| "Chocolate ice cream is the best flavor." | A statement reflecting personal taste without universal proof. | Personal preference |
| "Modern art is meaningless." | An opinion based on individual interpretation rather than objective criteria. | Individual interpretation |
| "Summer is the most enjoyable season." | Expresses enjoyment dependent on personal experience. | Experience-based judgment |
| "That movie was terrible." | A critique that varies according to individual taste and emotional response. | Emotional response |
| "Classical music is boring." | A subjective assessment influenced by personal interest. | Personal bias |
Defining Subjectivism in Opinion Pieces
Subjectivism in opinion pieces centers on the personal beliefs, feelings, and experiences of the author, rather than objective facts or universal truths. This approach highlights how individual perspectives shape interpretations and arguments, emphasizing that opinions are influenced by unique contexts. By defining subjectivism, opinion writers acknowledge the inherent bias and variability in human viewpoints.
Personal Beliefs as the Basis of Judgment
Personal beliefs serve as the foundation for subjective opinions, deeply influencing how individuals interpret events and form judgments. These beliefs are shaped by unique experiences, emotions, and cultural backgrounds, leading to varied perspectives even on the same issue. As a result, personal bias inherently colors subjective assessments, highlighting the central role of individual conviction in forming opinions.
The Role of Feelings in Shaping Opinions
Feelings play a crucial role in shaping opinions, as they often serve as the primary basis for subjective judgments. Emotional responses influence individual perspectives more than objective facts, leading to diverse interpretations of the same issue. This subjectivism highlights how personal experiences and emotions create unique viewpoints, underscoring the role of affect in opinion formation.
Cultural Influences on Subjective Perspectives
Cultural influences shape subjective perspectives by embedding values, beliefs, and traditions within individual viewpoints, leading to diverse interpretations of the same issue across societies. For instance, concepts of beauty, morality, or success vary significantly between cultures, illustrating how opinions are often deeply rooted in culturally specific norms. This cultural subjectivism highlights that personal opinions are not merely individual but are framed by broader social and historical contexts.
How Experience Drives Individual Interpretation
Experience shapes individual interpretation by filtering perceptions through personal memories and emotions, leading to diverse subjective opinions. This subjectivism illustrates that no two individuals perceive the same event identically, as lived experiences color their understanding uniquely. Consequently, opinions become personalized narratives rather than objective truths.
Value Judgments in Subjective Opinions
Value judgments in subjective opinions reflect individual preferences and cultural backgrounds rather than objective facts. For instance, assertions like "art is beautiful" or "honesty is the highest virtue" stem from personal beliefs shaped by experiences and societal norms. These judgments highlight how subjectivism varies perceptions of worth and importance across different individuals.
Bias and Subjectivism in Public Discourse
Bias and subjectivism in public discourse often manifest through selective framing of facts and emotional language that reinforces personal or group identities. This distortion shapes opinions by filtering information through individual experiences and cultural backgrounds, undermining objective analysis. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for fostering critical thinking and promoting more balanced dialogue in social and political conversations.
Ethical Debates Framed by Subjective Views
Ethical debates often highlight subjectivism by showcasing how individual moral judgments vary based on personal experiences and cultural backgrounds. For example, discussions on euthanasia reveal contrasting opinions rooted in subjective interpretations of dignity and suffering. These differing ethical perspectives emphasize how subjective views shape and frame moral controversies.
Subjectivism in Social Media Opinions
Subjectivism in social media opinions manifests through personalized interpretations and emotional biases that shape individual perspectives. Users often express viewpoints influenced by their unique experiences, cultural backgrounds, and personal values, resulting in diverse and subjective content across platforms. This phenomenon highlights the importance of recognizing the variability and relativity inherent in online discourse.
Navigating Subjective vs. Objective Opinions
Navigating the divide between subjective and objective opinions requires recognizing that subjective opinions are influenced by personal experiences, emotions, and individual perspectives, whereas objective opinions rely on factual evidence and measurable data. Subjectivism often manifests in differing interpretations of the same event, highlighting the importance of critical thinking in evaluating biases and personal preferences. Understanding this distinction enables clearer communication and more nuanced discussions in both academic and everyday contexts.
example of subjectivism in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com