The rickshaw is a widely recognized mode of passenger conveyance, especially in densely populated urban areas across Asia. This vehicle operates either manually by a driver on foot or cycle, or as an auto-rickshaw powered by a small engine. Rickshaws are highly efficient for short-distance travel due to their compact size and ability to navigate through narrow streets. In terms of data, millions of rickshaws transport passengers daily, reducing congestion and providing affordable mobility options. The passenger capacity typically ranges from two to three individuals, making rickshaws suitable for personal or small group travel. This entity's presence significantly impacts local transportation ecosystems by offering an eco-friendly alternative to larger motor vehicles.
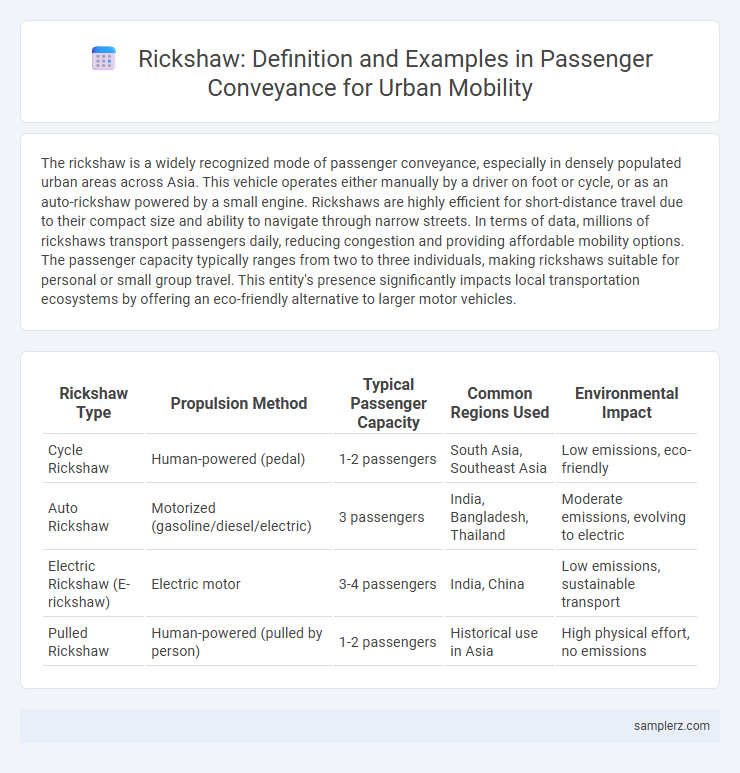
Table of Comparison
| Rickshaw Type | Propulsion Method | Typical Passenger Capacity | Common Regions Used | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle Rickshaw | Human-powered (pedal) | 1-2 passengers | South Asia, Southeast Asia | Low emissions, eco-friendly |
| Auto Rickshaw | Motorized (gasoline/diesel/electric) | 3 passengers | India, Bangladesh, Thailand | Moderate emissions, evolving to electric |
| Electric Rickshaw (E-rickshaw) | Electric motor | 3-4 passengers | India, China | Low emissions, sustainable transport |
| Pulled Rickshaw | Human-powered (pulled by person) | 1-2 passengers | Historical use in Asia | High physical effort, no emissions |
Introduction to Rickshaws in Urban Mobility
Rickshaws serve as a vital component of urban mobility, offering eco-friendly and affordable passenger conveyance in densely populated cities. This mode of transport, often human-powered or electric-assisted, enhances last-mile connectivity and reduces traffic congestion. Their adaptability to narrow streets and short-distance travel positions rickshaws as a sustainable solution in modern urban transportation systems.
Historical Evolution of Rickshaw Passenger Services
Rickshaws originated in Japan during the late 19th century, revolutionizing urban passenger conveyance by providing an affordable and efficient transport option. Their widespread adoption across Asia marked a shift from traditional transport methods to human-powered vehicles that accommodated increasing urban populations. Over time, innovations such as cycle rickshaws and auto-rickshaws emerged, reflecting technological advancements and changing mobility needs.
Types of Rickshaws Used for Passenger Conveyance
Cycle rickshaws, auto rickshaws, and electric rickshaws represent the primary types used for passenger conveyance, each varying in propulsion method and capacity. Cycle rickshaws are human-powered and ideal for short distances, while auto rickshaws rely on small internal combustion engines, offering faster travel and greater range. Electric rickshaws, gaining popularity for their eco-friendly nature, combine battery-powered motors with moderate speed and passenger capacity, making them a sustainable urban transport option.
Rickshaws in Different Countries: Regional Variations
Rickshaws serve as a vital mode of passenger conveyance across South and Southeast Asia, with notable regional variations in design and usage. In India and Bangladesh, cycle rickshaws are predominantly used for short urban commutes, while in Japan, rickshaws are more tourist-oriented and pulled manually for scenic tours. The Philippines features motorized tricycles, offering higher speed and capacity, adapting the traditional rickshaw concept to local urban mobility needs.
Environmental Impact of Passenger Rickshaws
Passenger rickshaws significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to conventional motorized vehicles, as they typically rely on human power or electric assistance. Their compact size and low energy consumption contribute to decreased air pollution and lower noise levels in urban environments. Incorporating rickshaws into public transport systems promotes sustainable mobility by minimizing the environmental footprint of short-distance passenger conveyance.
Modern Innovations in Rickshaw Design
Innovations in rickshaw design have introduced electric-powered models that enhance energy efficiency and reduce emissions in urban passenger transport. Advanced battery technologies and lightweight materials improve range and durability, making electric rickshaws a sustainable alternative to traditional fuel-based models. Integration of GPS navigation and digital payment systems further modernizes rickshaw services, increasing convenience and safety for passengers.
Rickshaw Fare Systems and Passenger Experience
Rickshaw fare systems often utilize metered or negotiated pricing models, impacting passenger experience by balancing transparency and flexibility. Digital innovations like mobile payment apps and GPS integration enhance convenience and fare accuracy for passengers. However, inconsistent fare structures across regions can lead to confusion and dissatisfaction among riders.
Integration of Rickshaws with Public Transit Networks
Rickshaws serve as a crucial last-mile connectivity solution, seamlessly linking passengers from public transit hubs to their final destinations. Their integration with bus and metro systems enhances overall mobility by providing flexible, cost-effective transport in congested urban areas. Coordinated schedules and designated pick-up zones further optimize passenger flow and reduce transit times.
Challenges Facing Rickshaw Operators and Passengers
Rickshaw operators face challenges such as limited income due to fluctuating passenger demand and rising fuel or maintenance costs, impacting their livelihood. Passengers experience issues including safety concerns, inadequate regulation, and limited comfort during travel. Urban congestion and competition from modern transport modes further complicate the viability of rickshaw-based passenger conveyance.
The Future of Rickshaws in Sustainable Urban Transport
Electric rickshaws are revolutionizing sustainable urban transport by offering zero-emission passenger conveyance solutions in congested cities. Advances in battery technology and solar charging infrastructure enhance their efficiency, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering urban air pollution. Integrating smart GPS and IoT connectivity further optimizes route management, making electric rickshaws a vital component of future eco-friendly mobility systems.
example of rickshaw in passenger conveyance Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com